The modern mobile applications have to be functional even when the internet connection speed is slow or absent. Many business applications require constant communication with the server. In such cases, there might be a problem with delays in low-connectivity situations. In such cases, implementing an offline mode in the application is a must.
This method is based on developing a Flutter application that supports offline functionality while synchronizing the data with the Odoo ERP system. The users can use the application offline to view, add, and edit the data. The offline data will be stored locally on the device and synchronized with the Odoo server when the connection returns.
This method provides a more reliable application that is fast and user-friendly, even in low-connectivity situations.
Why Offline Mode Is Important
Offline functionality is also important in many business cases. Many field workers, sales teams, and event teams work in environments where internet connectivity is either poor or unreliable. Without this feature, users may be unable to use the app, thus providing a poor experience.
Benefits derived from the app’s offline mode:
- Continuous usage without any dependence on internet connectivity
- Faster access to data through local storage
- Less load on the server and network infrastructure
- Improved reliability and user satisfaction
Overview of Flutter–Odoo Integration
Flutter is a cross-platform development tool to create fast and responsive mobile applications.
Odoo is a powerful open-source ERP tool, which is generally utilized for managing business activities such as sales, events, inventory, and customers.
In a normal online scenario:
- The request is sent to the Odoo server by the Flutter application.
- The request is processed by Odoo, and the response is sent back to the application.
- The response is rendered to the user by the application.
This method is not feasible if the device is offline. To overcome this, we will implement a storage solution and a synchronization approach.
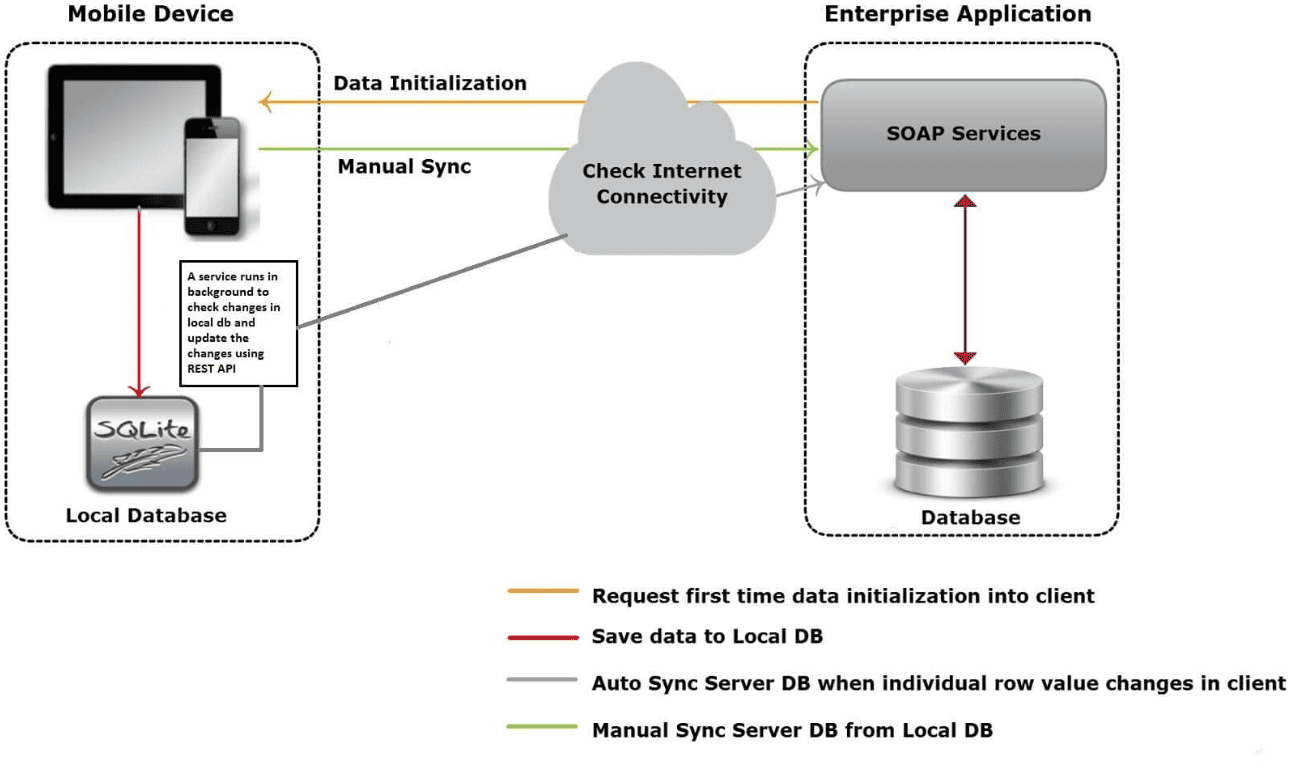
What Is Odoo RPC?
Odoo has a Remote Procedure Call (RPC) interface that enables other applications to interact with its server.
Two main types:
Using RPC, a Flutter app is able to:
- Authenticate users
- Fetch records
- Create new records
- Update existing records
- Execute server-side methods
The offline-enabled system consists of three main components:
- Odoo Server
- Stores final business data
- Flutter App
- Works both online and offline
- Local Database
- Holds offline changes before sync
Flow:
- Online > Fetch data from Odoo > Save locally
- Offline > Read/write from local database
- Reconnected > Sync pending changes to server
How Does the Offline Workflow Operate?
Online Mode
- The app fetches data from Odoo via RPC.
- Data is stored in the local database.
- The UI displays local data.
Offline Mode
- No internet connection.
- The app reads data from the local database.
- The user creates or edits records.
- Changes are saved locally with a pending status.
Reconnected Mode
- Internet becomes available.
- App detects connectivity.
- Pending changes are sent to Odoo.
- Local records are marked as synced.
Choosing a Local Database in Flutter
Common options:
| Database | Best For |
| SQLite | Structured relational data |
| Hive | Fast key-value storage |
| Isar | High-performance NoSQL storage |
| SharedPreferences | Small settings |
Requirements
Software Requirements
- Flutter SDK (3.x or later)
- Dart SDK
- Android Studio or VS Code
- Odoo server (Odoo 15+ recommended)
- Emulator or physical device
Flutter Dependencies
Add these packages to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
connectivity_plus: ^6.0.3
sqflite: ^2.3.3
path: ^1.9.0
odoo_rpc: ^0.4.0
Install packages:
flutter pub get
Setting Up Odoo RPC in Flutter
Create Odoo Client:
import 'package:odoo_rpc/odoo_rpc.dart';
final client = OdooClient('http://localhost:8069');
Explanation
- OdooClient connects your Flutter app to the Odoo server.
- Replace the URL with your actual Odoo server address.
- This client is used for all RPC calls
Authenticate User:
Future<void> login() async {
final session = await client.authenticate(
'odoo_db',
'admin',
'admin',
);
print('User ID: ${session.userId}');
}Explanation
- authenticate() logs into Odoo.
- Parameters:
- If successful, it returns a session with the user ID.
- This session is required before making API calls.
Fetching Data from Odoo:
Example: Fetch events from Odoo:
Future<List<dynamic>> fetchEvents() async {
final result = await client.callKw({
'model': 'event.event',
'method': 'search_read',
'args': [],
'kwargs': {
'fields': ['id', 'name'],
},
});
return result;
}Explanation
- callKw() calls an Odoo model method.
- model: the Odoo model name.
- method: the method to call.
- search_read: searches and reads records.
- fields: specifies which fields to return.
This function fetches events from Odoo.
Local Database Setup (SQLite)
Initialize Database:
Future<Database> initDb() async {
final dbPath = await getDatabasesPath();
final path = join(dbPath, 'app.db');
return openDatabase(
path,
version: 1,
onCreate: (db, version) {
return db.execute('''
CREATE TABLE events(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
syncStatus TEXT,
updatedAt TEXT
)
''');
},
);
}Explanation
- getDatabasesPath()
- Returns the correct directory for storing databases.
- join(dbPath, 'app.db')
- Creates the full path using the path package.
- openDatabase()
- Opens or creates the database.
- onCreate
- Runs only when the database is created for the first time.
- Creates the events table.
Data Model with Sync Status
class EventModel {
final int id;
final String name;
final String syncStatus;
final DateTime updatedAt;
EventModel({
required this.id,
required this.name,
required this.syncStatus,
required this.updatedAt,
});
}Explanation
Each record contains:
- id > unique identifier
- name > event name
- syncStatus > pending, synced, or failed
- updatedAt > timestamp for conflict handling
Creating Records Offline
Code
Future<void> addOfflineEvent(Database db, String name) async {
await db.insert(
'events',
{
'id': DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpoch,
'name': name,
'syncStatus': 'pending',
'updatedAt': DateTime.now().toIso8601String(),
},
);
}Explanation
- Creates a new event locally.
- Uses timestamp as a temporary ID.
- Marks record as pending.
- This record will be synced later.
Syncing Offline Data to Odoo
Future<void> syncPendingData(Database db) async {
final pending = await db.query(
'events',
where: 'syncStatus = ?',
whereArgs: ['pending'],
);
for (var record in pending) {
try {
await client.callKw({
'model': 'event.event',
'method': 'create',
'args': [
{'name': record['name']}
],
'kwargs': {},
});
await db.update(
'events',
{'syncStatus': 'synced'},
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [record['id']],
);
} catch (e) {
await db.update(
'events',
{'syncStatus': 'failed'},
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [record['id']],
);
}
}
}Explanation
- Query all records with syncStatus = pending.
- Loop through each record.
- Send it to Odoo using RPC.
- If successful:
- If failed:
Detecting Connectivity and Auto Sync
import 'package:connectivity_plus/connectivity_plus.dart';
Future<bool> isOnline() async {
final result = await Connectivity().checkConnectivity();
return result != ConnectivityResult.none;
}
Future<void> trySync(Database db) async {
if (await isOnline()) {
await syncPendingData(db);
}
}
Explanation
- checkConnectivity() checks network status.
- If online:
- syncPendingData() is triggered.
- Can be called:
Understanding connectivity_plus
What is connectivity_plus?
connectivity_plus is a Flutter plugin used to detect the network connection status of a device. It helps the app determine whether it is:
- Connected to Wi-Fi
- Using mobile data
- Completely offline
In an offline-first app, this package is essential because it decides:
- When to sync data
- When to switch to offline mode
- When to retry failed operations
Example:
Project Structure:
lib/
+-- main.dart
+-- models/
¦ +-- event_model.dart
+-- database/
¦ +-- db_helper.dart
+-- services/
¦ +-- odoo_service.dart
¦ +-- sync_service.dart
Data Model
models/event_model.dart
class EventModel {
final int id;
final String name;
final String syncStatus;
final DateTime updatedAt;
EventModel({
required this.id,
required this.name,
required this.syncStatus,
required this.updatedAt,
});
Map<String, dynamic> toMap() {
return {
'id': id,
'name': name,
'syncStatus': syncStatus,
'updatedAt': updatedAt.toIso8601String(),
};
}
}Local Database
database/db_helper.dart
import 'package:sqflite/sqflite.dart';
import 'package:path/path.dart';
class DBHelper {
static Database? _db;
static Future<Database> get database async {
if (_db != null) return _db!;
_db = await initDb();
return _db!;
}
static Future<Database> initDb() async {
final dbPath = await getDatabasesPath();
final path = join(dbPath, 'app.db');
return openDatabase(
path,
version: 1,
onCreate: (db, version) async {
await db.execute('''
CREATE TABLE events(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
syncStatus TEXT,
updatedAt TEXT
)
''');
},
);
}
static Future<void> insertEvent(Map<String, dynamic> data) async {
final db = await database;
await db.insert('events', data);
}
static Future<List<Map<String, dynamic>>> getPendingEvents() async {
final db = await database;
return db.query(
'events',
where: 'syncStatus = ?',
whereArgs: ['pending'],
);
}
static Future<void> markAsSynced(int id) async {
final db = await database;
await db.update(
'events',
{'syncStatus': 'synced'},
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [id],
);
}
}
Odoo RPC Service
services/odoo_service.dart
import 'package:odoo_rpc/odoo_rpc.dart';
class OdooService {
late OdooClient client;
OdooService() {
client = OdooClient('http://localhost:8069');
}
Future<void> login() async {
await client.authenticate(
'odoo_db',
'admin',
'admin',
);
}
Future<void> createEvent(String name) async {
await client.callKw({
'model': 'event.event',
'method': 'create',
'args': [
{'name': name}
],
'kwargs': {},
});
}
}
Sync Service
services/sync_service.dart
import 'package:connectivity_plus/connectivity_plus.dart';
import '../database/database_helper.dart';
import 'odoo_services.dart';
class SyncService {
final OdooService odooService = OdooService();
final Connectivity _connectivity = Connectivity();
void startAutoSync() {
_connectivity.onConnectivityChanged.listen((result) async {
if (result != ConnectivityResult.none) {
await trySync();
}
});
}
Future<bool> isOnline() async {
final result = await _connectivity.checkConnectivity();
return result != ConnectivityResult.none;
}
Future<void> syncPendingData() async {
final pending = await DBHelper.getPendingEvents();
for (var record in pending) {
try {
await odooService.createEvent(record['name']);
await DBHelper.markAsSynced(record['id']);
} catch (e) {
// handle failure if needed
}
}
}
Future<void> trySync() async {
if (await isOnline()) {
await odooService.login();
await syncPendingData();
}
}
}
Main App UI
Main.dart
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:sqflite_common_ffi/sqflite_ffi.dart';
import 'database/database_helper.dart';
import 'model/event_model.dart';
import 'services/sync_services.dart';
void main() {
// Required for Windows, Linux, macOS
if (Platform.isWindows || Platform.isLinux || Platform.isMacOS) {
sqfliteFfiInit();
databaseFactory = databaseFactoryFfi;
}
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(
title: 'Offline Odoo App',
home: EventScreen(),
);
}
}
class EventScreen extends StatefulWidget {
const EventScreen({super.key});
@override
State<EventScreen> createState() => _EventScreenState();
}
class _EventScreenState extends State<EventScreen> {
final TextEditingController controller = TextEditingController();
final SyncService syncService = SyncService();
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
// Start automatic sync when connection returns
syncService.startAutoSync();
// Try sync on screen load
syncService.trySync();
}
Future<void> addEvent() async {
try {
final name = controller.text.trim();
if (name.isEmpty) return;
final event = EventModel(
id: DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpoch,
name: name,
syncStatus: 'pending',
updatedAt: DateTime.now(),
);
// Save locally first
await DBHelper.insertEvent(event.toMap());
// Check connectivity
final isOnline = await syncService.isOnline();
if (isOnline) {
await syncService.trySync();
if (mounted) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text("Event saved and synced")),
);
}
} else {
if (mounted) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text("Event saved offline")),
);
}
}
// Clear text field in both cases
controller.clear();
} catch (e) {
if (mounted) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(content: Text("Error: ${e.toString()}")),
);
}
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text("Offline Odoo Events"),
),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
children: [
TextField(
controller: controller,
decoration: const InputDecoration(
labelText: "Event Name",
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: addEvent,
child: const Text("Add Event"),
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
How the Code Works (Flow)
- User enters the event name.
- The event is saved in the local SQLite database with pending status.
- The app checks internet connectivity.
If online:
- Logs into Odoo via RPC
- Sends pending events
- Marks them as synced
Creating Mobo mobile business applications that depend entirely on an uninterrupted internet connection may result in an unstable performance and an overall bad user experience. In a real-world scenario, the internet connectivity might not always be stable for field staff, event managers, or sales teams. The offline-first strategy ensures that the application runs irrespective of internet connectivity.
In this blog post, we have seen how an application can be developed using Flutter with offline support and synchronized with the Odoo ERP system using the RPC protocol. The inclusion of a local database using SQLite, internet connectivity detection, and a structured synchronization process enables the application to save user interactions offline and synchronize them when the internet connectivity is restored.
This architecture has many advantages:
- Uninterrupted productivity without internet dependency
- Faster data access using the local storage
- Auto-synchronization with the server
- Increased reliability for a better user experience
Offline support for applications is no longer an advanced feature; it has become an essential requirement for modern applications. Using Flutter for cross-platform development and Odoo for backend development, along with an efficient synchronization process, allows developers to create powerful applications with a great user experience.
To read more about How to Read Odoo Records with Filters (Domains) in Flutter, refer to our blog How to Read Odoo Records with Filters (Domains) in Flutter.