Odoo 19 utilizes XML-based view definitions to shape the user interface's appearance and functionality across the system. Almost everything a user interacts with—forms, list views, search views, Kanban cards, wizards, and dashboards—is defined using XML. This makes the UI structured, consistent, and easy to understand, both for users and developers.
Whether you are creating a new custom module or adjusting an existing one, XML plays a key role in controlling the interface. By using XML attributes, you can decide how fields appear, how buttons behave, and how different UI elements respond to user actions. You can show or hide components, control layouts, and fine-tune the overall experience to match specific requirements.
This XML-driven approach gives developers clear control over the interface while keeping everything organized and readable. It allows the UI to be customized in a clean and maintainable way, making Odoo 19 flexible enough to adapt to different business needs while still feeling simple and intuitive to use.
This blog explains all useful XML attributes, their purpose, and real examples—including changes introduced in Odoo 19.
Core XML Attributes in Odoo 19
These attributes work inside view elements like <field>, <form>, <list>, <button>, <xpath> etc.
1) String – Used to set the user-visible label.
<field name="price" string="Selling Price"/>
2) Name – Used to reference a field, button, action, or container.
<field name="description"/>
3) Class – Adds CSS classes for styling.
<field name="status" class="text-danger fw-bold"/>
4) Invisible – Hide the field (boolean).
<field name="secret_note" invisible="1"/>
5) Readonly – Make a field uneditable.
<field name="price" readonly="1"/>
6) Required – Marks field as mandatory.
<field name="buyer_id" required="1"/>
7) Position – Used in inherited views to place new XML elements.
<xpath expr="//field[@name='name']" position="after">
<field name="property_type"/>
</xpath>
Values:
- before
- after
- inside
- replace
- attributes
8) Widget – Defines how the field displays.
<field name="image" widget="image"/>
Common widgets:
- image
- many2many_tags
- monetary
- password
- statusbar
- priority
- progressbar
Conditional Attributes
Supported expressions:
- ==
- !=
- in
- not in
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- boolean fields
Example: conditionally readonly
<field name="price" readonly="state != 'draft'"/>
Example: conditionally invisible
<field name="sale_price" invisible="promo == False"/>
Example: required only when sold
<field name="buyer_id" required="state == 'sold'"/>
Special Attributes for Buttons
Buttons support extra attributes that define their behavior.
1) special
Triggers Odoo built-in actions.
- save Save the record
- cancel Discard changes
Examples:
<button special="save" string="Save"/>
<button special="cancel" class="btn-secondary"/>
2) type
Defines the button type.
- object Calls a Python method
- action Executes an Odoo server action/window action
Python method call:
<button name="action_mark_sold" type="object" string="Mark Sold"/>
3) confirm
Shows confirmation popup.
<button type="object" confirm="Are you sure?" name="action_delete"/>
4) icon
Adds an icon (OWL UI supports FontAwesome).
<button string="Approve" icon="fa-check"/>
View-Level XML Attributes
Apply to <form>, <list>, <kanban>, <search>, etc.
1) create, edit, delete
Enable/disable operations.
<list editable="bottom" create="false" delete="false">
2) default_order
Default sort order.
<list default_order="field_name desc">
3) editable
Make a list editable.
Values:
<list editable="top">
4) decoration-*
Applies CSS based on conditions (list/kanban).
<list>
<field name="state" decoration-danger="state == 'cancel'"/>
</list>
Decoration examples:
- danger
- warning
- success
- muted
- info
Example: Simple Estate Form View
<!-- Form View -->
<record id="estate_property_form" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">estate.property.form</field>
<field name="model">estate.property</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<form string="Estate Property">
<header>
<button name="action_mark_sold"
type="object"
string="Mark Sold"
class="btn-primary"
invisible="state != 'offer_accepted'"/>
<button special="save" string="Save" class="btn-success"/>
<button special="cancel" string="Discard"/>
<field name="state" widget="statusbar" options="{'clickable': '1'}"/>
</header>
<sheet>
<group>
<field name="name" required="1"/>
<field name="property_type"/>
<field name="price" readonly="state != 'draft'"/>
<field name="bedrooms"/>
<field name="sold_price" invisible="state != 'sold'"/>
</group>
<group>
<field name="description"/>
</group>
</sheet>
</form>
</field>
</record>
State in ‘draft’:
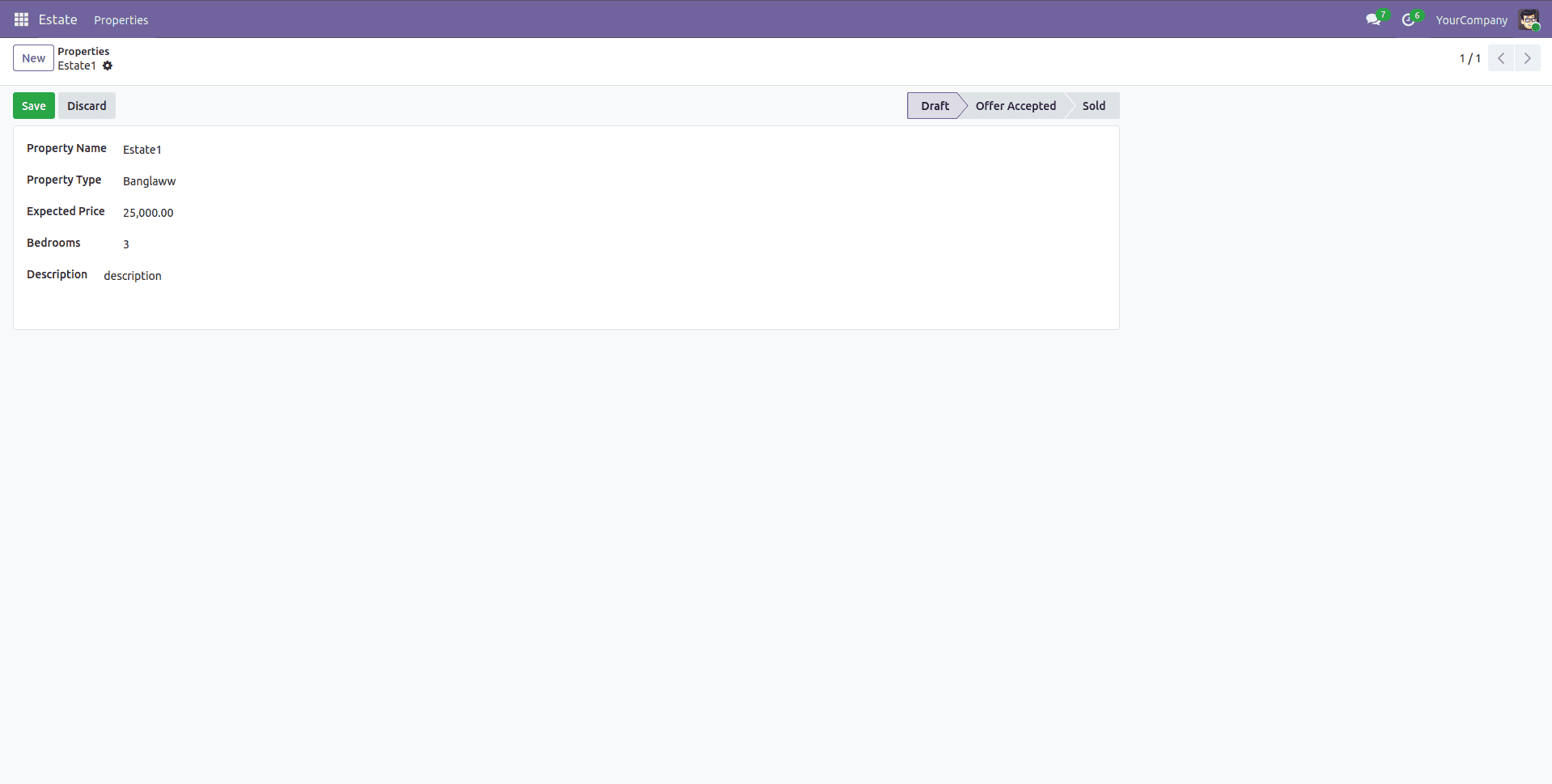
- ‘Mark Sold’ button invisible
- ‘Expected Price’ is not readonly
- ‘Sold Price’ field invisible
State in ‘offer_accepted’:

- ‘Mark Sold’ button visible
- ‘Expected Price’ readonly
- ‘Sold Price’ field invisible
State in ‘sold’:

- ‘Mark Sold’ button invisible
- Expected Price readonly
- ‘Sold Price’ field visible
Conclusion
Odoo 19 introduces a more simplified and consistent XML syntax, making view development much cleaner and easier to manage compared to older versions. The reduced complexity helps developers read, write, and maintain views more efficiently, especially when working on large or long-term projects. With clearer structure and fewer unnecessary elements, XML files are easier to understand and less prone to errors.
By gaining a solid understanding of XML attributes and how UI logic behaves in OWL-based forms, developers can design views that are not only functional but also responsive and intuitive. This knowledge allows you to control how elements are displayed, how users interact with fields and buttons, and how the overall interface flows during everyday operations.
When used effectively, these improvements enable you to build powerful, optimized, and user-friendly views within custom modules. The result is a smoother user experience, better performance, and cleaner code that aligns well with Odoo 19’s modern framework and long-term maintainability goals.
To read more about Overview of Form View Attributes in Odoo 19, refer to our blog Overview of Form View Attributes in Odoo 19.