This guide explains how to authenticate a Flutter app against mobo using the odoo_rpc package and how to:
- Configure the server URL (http:// / https://, including local IPs)
- Fetch database list from the server
- Login (authenticate) with username + password
- Persist session using an app session model
- Reuse/refresh sessions and build an authenticated OdooClient
- Store accounts + passwords safely (SharedPreferences + Secure Storage)
What does "Token" mean in Odoo?
Mobo typically does not use JWT for mobile app authentication by default. Instead, authentication produces a server session, and the client continues requests using a session id.
The "token-like" value you'll most often deal with is:
session_id
That session_id is sent back to the server as a cookie in subsequent calls.
Prerequisites
- A mobo server running and reachable from your device/emulator.
- A database is available on that server.
- A valid mobo user (email/login + password).
1) Install packages
This project uses:
- odoo_rpc: ^0.7.1
- shared_preferences: ^2.3.3
- flutter_secure_storage: ^10.0.0
- provider: ^6.1.5+1 (state management used in this project; you can use any state management approach you prefer)
Add (or confirm) them in pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
odoo_rpc: ^0.7.1
shared_preferences: ^2.3.3
flutter_secure_storage: ^10.0.0
provider: ^6.1.5+1
Then install:
flutter pub get
Step 1: Server URL input (HTTP / HTTPS)
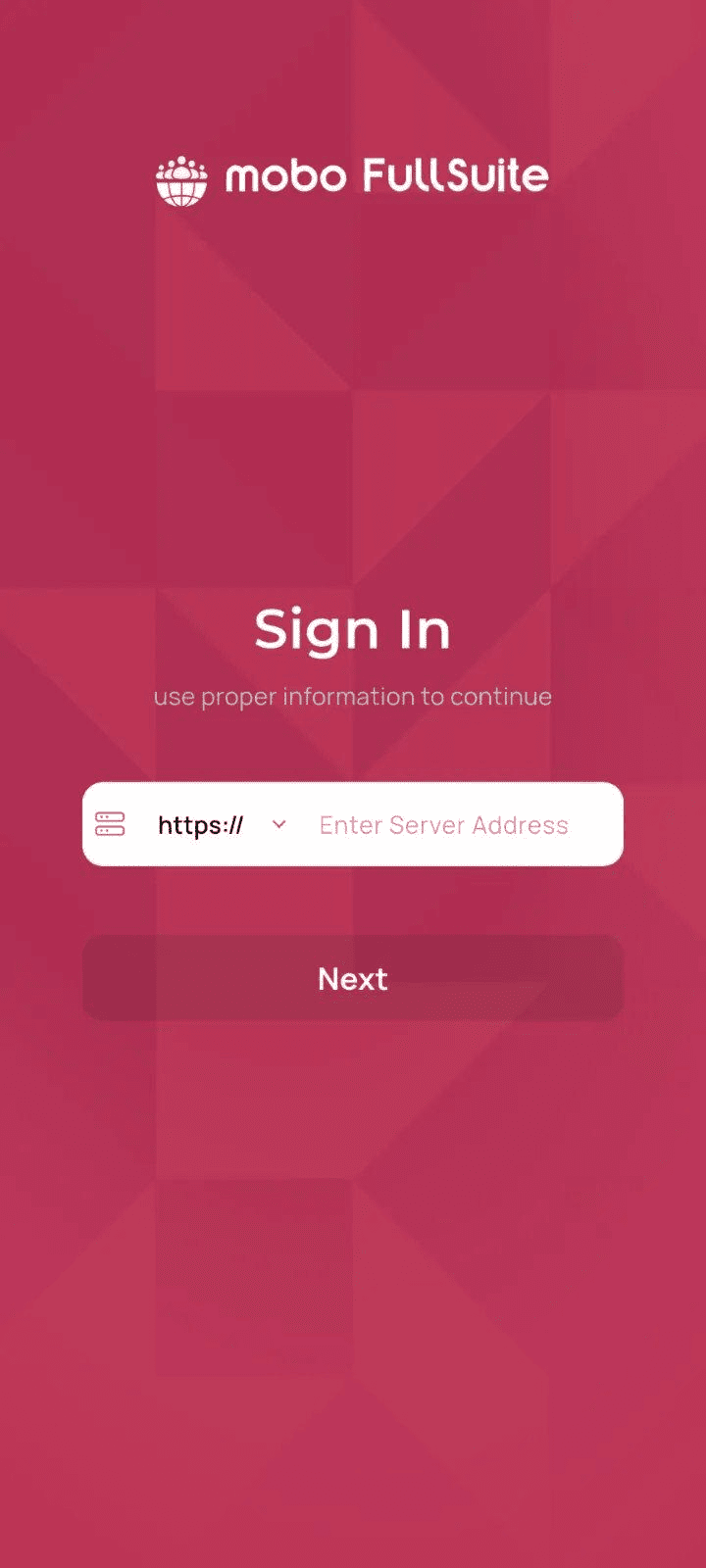
The user can type/paste:
http://192.168.1.50:8069
Or:
https://mycompany.odoo.com
Why HTTP matters for local mobo
In local/testing setups, mobo is often served over HTTP.
- If you use https:// with a server that only supports HTTP, you may see SSL / handshake errors.
- This app explicitly supports switching protocol via the UI and also validates the URL.
URL normalization (how the app builds a full URL)
The app uses a helper to ensure the URL has a scheme:
String getFullUrl() {
final url = urlController.text.trim();
if (url.isEmpty) return '';
if (url.startsWith('http://') || url.startsWith('https://')) {
return url;
}
return '$_selectedProtocol$url';
}Splitting a full URL into protocol + domain (used for suggestions)
When a user taps an autocomplete suggestion (a full URL), the provider splits it and stores only the domain in the input field:
void setUrlFromFullUrl(String fullUrl) {
final protocol = extractProtocol(fullUrl);
final domain = extractDomain(fullUrl);
_selectedProtocol = protocol;
urlController.text = domain;
}And the helpers:
String extractProtocol(String fullUrl) {
if (fullUrl.startsWith('https://')) return 'https://';
if (fullUrl.startsWith('http://')) return 'http://';
return _selectedProtocol;
}
String extractDomain(String fullUrl) {
if (fullUrl.startsWith('https://')) return fullUrl.substring(8);
if (fullUrl.startsWith('http://')) return fullUrl.substring(7);
return fullUrl;
}URL validation (domain, IP, port)
Before fetching databases, the provider validates the URL:
bool isValidUrl(String url) {
try {
String urlToValidate = url.trim();
if (urlToValidate.isEmpty) return false;
final urlRegExp = RegExp(
r'^(https?:\\/\\/)?'
r'(([a-z\\d]([a-z\\d-]*[a-z\\d])*)\\.)+[a-z]{2,}|'
r'((\\d{1,3}\\.){3}\\d{1,3})'
r'(\\:\\d+)?(\\/[-a-z\\d%_.~+]*)*'
r'(\\?[;&a-z\\d%_.~+=-]*)?'
r'(\\#[-a-z\\d_]*)?$',
caseSensitive: false,
);
if (!urlRegExp.hasMatch(urlToValidate)) {
if (urlToValidate.contains(' ') || urlToValidate.contains('!!')) return false;
}
if (!urlToValidate.startsWith('http://') && !urlToValidate.startsWith('https://')) {
urlToValidate = '$_selectedProtocol$urlToValidate';
}
final uri = Uri.parse(urlToValidate);
return uri.hasScheme && uri.host.isNotEmpty && !uri.host.contains(' ');
} catch (_) {
return false;
}
}Step 2: Fetch database list from mobo
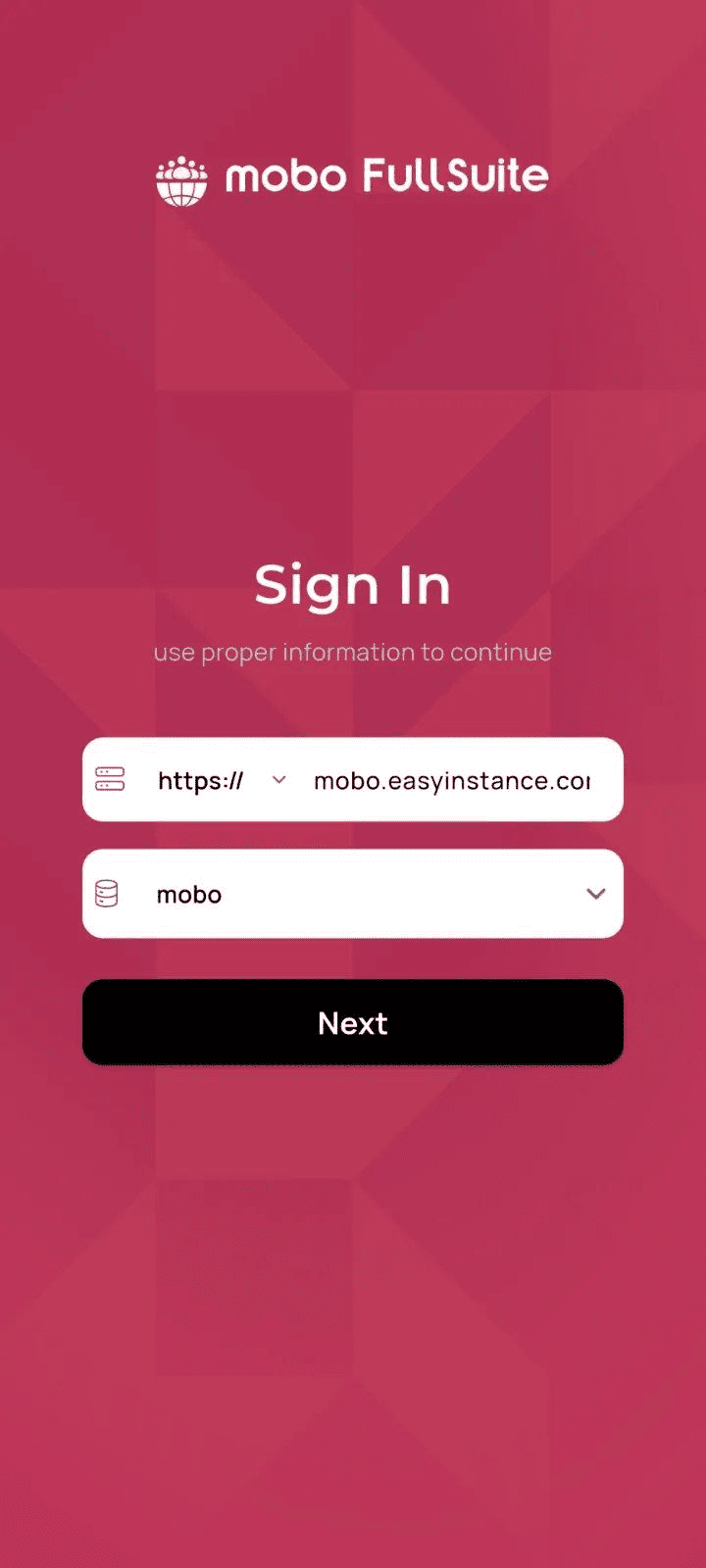
After entering a valid server URL, the app calls mobo’s database listing endpoint:
/web/database/list
The relevant RPC call:
final response = await client!.callRPC('/web/database/list', 'call', {});
final dbList = response as List<dynamic>;Database fetching (full flow with normalization + timeout)
The fetchDatabaseList() method also normalizes the URL and applies platform-specific timeouts:
final baseUrl = _normalizeUrl(urlController.text);
client = clientFactory != null ? clientFactory!(baseUrl) : OdooClient(baseUrl);
final timeoutDuration = Platform.isIOS
? const Duration(seconds: 30)
: const Duration(seconds: 15);
final response = await client!.callRPC('/web/database/list', 'call', {})
.timeout(timeoutDuration, onTimeout: () {
throw TimeoutException(
'Request timed out after ${timeoutDuration.inSeconds} seconds',
timeoutDuration,
);
});
Good UX detail: Persist the validated server URL
Once databases are successfully fetched, the app seeds the server URL into history so it can be suggested next time:
await prefs.setStringList('previous_server_urls', urls);This is why the URL autocomplete in ServerSetupScreen can work even before the first successful login.
Step 3: Login (Authenticate) and create a session
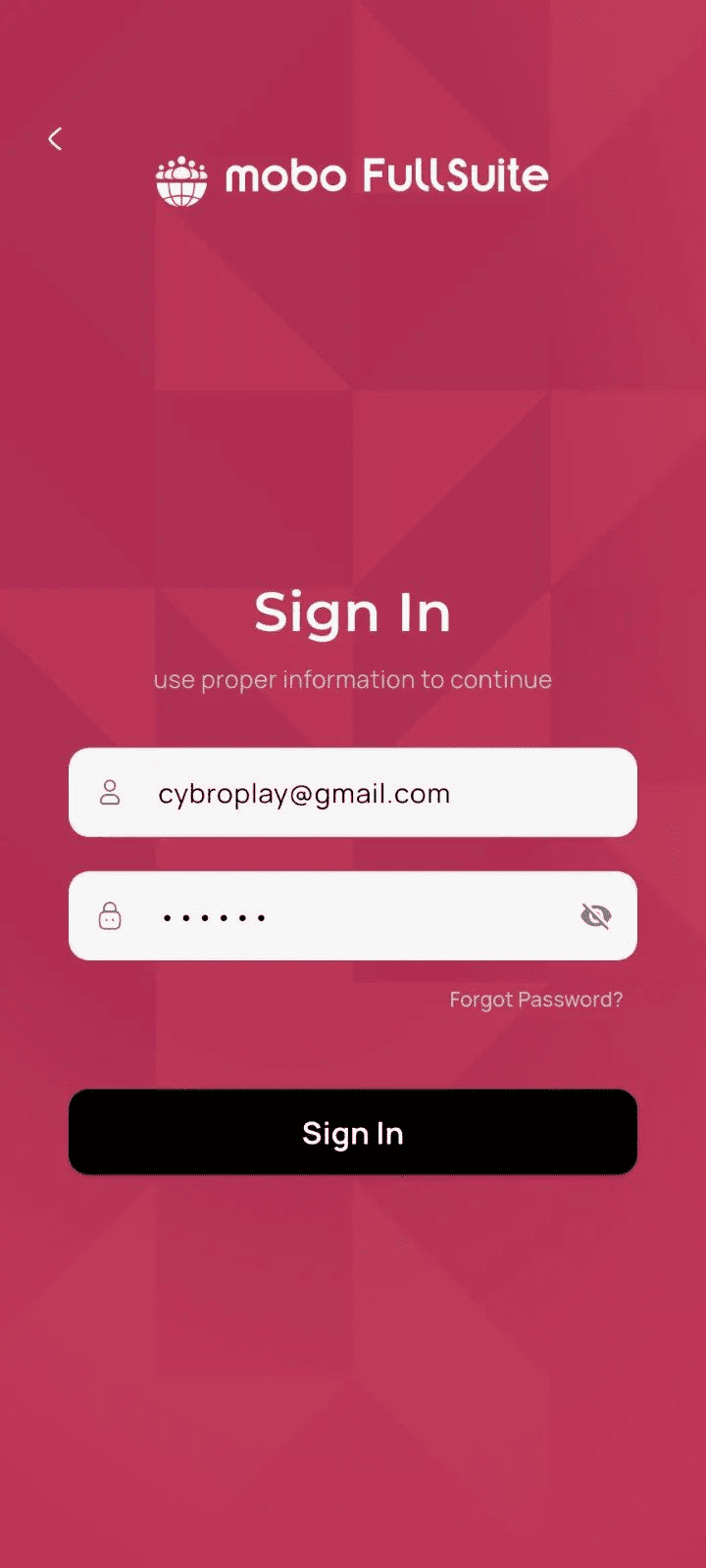
After choosing a database, the user enters:
- username/email
- password
In this project, login is initiated by:
- the login screen/provider
That calls:
- the session manager login method
The key odoo_rpc authentication call is:
final odooSession = await client.authenticate(
database,
userLogin,
password,
);
Login orchestration from the provider
In this app, the provider delegates login to the session manager:
final loginSuccess = await OdooSessionManager.loginAndSaveSession(
serverUrl: serverUrl,
database: database!,
userLogin: userLogin,
password: password,
);
What does authenticate() return?
It returns an OdooSession object (from odoo_rpc) which contains (among other fields):
- id (the session id, used like a token)
- userId
- userLogin
- companyId
This project wraps that into an app model called AppSessionData.
Step 4: Persist the session (AppSessionData)
The app-specific session model is:
- AppSessionData
It stores:
- the raw OdooSession
- serverUrl, database
- expiresAt
- selected/allowed company IDs
- and password (stored securely)
Saving session metadata to SharedPreferences
The session model stores non-sensitive session metadata:
await prefs.setString('sessionId', odooSession.id);
await prefs.setString('userLogin', odooSession.userLogin);
await prefs.setString('database', database);
await prefs.setString('serverUrl', serverUrl);
await prefs.setInt('userId', odooSession.userId);
await prefs.setBool('isLoggedIn', true);Storing password securely (not in SharedPreferences)
Passwords are stored via:
The session model stores the password using 2 keys (username + userId):
await SecureStorageService.instance.storePassword(
'session_password_username_${odooSession.userLogin}',
password,
);
await SecureStorageService.instance.storePassword(
'session_password_${odooSession.userId}',
password,
);
Restoring session from prefs (including HTTPS fallback)
When restoring a saved session, the app ensures a scheme exists (defaults to https:// if missing):
serverUrl = serverUrl!.trim();
if (!serverUrl.startsWith('http://') && !serverUrl.startsWith('https://')) {
serverUrl = 'https://$serverUrl';
}
And retrieves the password from secure storage (username first, then userId):
String? password = await SecureStorageService.instance.getPassword(
'session_password_username_$userLogin',
);
if (password == null || password.isEmpty) {
password = await SecureStorageService.instance.getPassword(
'session_password_$userId',
);
}
if (password == null || password.isEmpty) return null;
Step 5: Restore / reuse sessions
When the app needs a client later (e.g., on app restart), it calls:
That loads the saved session, then re-authenticates using stored credentials to obtain a fresh OdooSession:
final saved = await AppSessionData.fromPrefs();
final client = OdooClient(saved.serverUrl);
final odooSession = await client.authenticate(
saved.database,
saved.userLogin,
saved.password,
);
Why re-authenticate instead of trusting stored sessionId?
Mobo sessions can expire server-side. Re-authentication:
- ensures the session is valid
- avoids "invalid session" errors on the first RPC call
This project also includes a refreshSession() method to refresh when an auth error is detected.
Step 6: Create an authenticated OdooClient for RPC
The recommended way in this project is:
- the session manager
It
- loads the saved session
- checks expiry (expiresAt)
- refreshes the session if needed
- authenticates a new OdooClient when the cache is stale
Once you have the client, you can call Odoo models using callKw:
final result = await client.callKw({
'model': 'res.users',
'method': 'read',
'args': [
[session.userId],
['name'],
],
'kwargs': {},
});Recommended pattern: wrap calls with a session refresh
This project provides a wrapper that can refresh the session on auth errors:
final res = await OdooSessionManager.callWithSession((client) async {
return await client.callKw({
'model': 'res.users',
'method': 'read',
'args': [
[1],
['name'],
],
'kwargs': {},
});
});Step 7: Multi-account handling (SessionService)
This project supports storing multiple accounts and switching between them using:
What is stored?
Accounts are stored in SharedPreferences under:
stored_accounts
Sensitive passwords are stored in secure storage.
Storing an account after login
After successful authentication, the app stores the account for switching:
final currentSession = await OdooSessionManager.getCurrentSession();
if (currentSession != null) {
await sessionService.storeAccount(currentSession, password);
}
Storing password safely with multiple patterns
SessionService stores passwords using multiple key patterns for robust retrieval:
await secureStorage.storePassword(
'password_${session.userId}_${session.database}',
password,
);
await secureStorage.storePassword(
'password_${session.userLogin}_${session.database}',
password,
);
And retrieval tries both patterns:
List<String> passwordKeys = [
'password_${userId}_$database',
'password_${username}_$database',
];
for (String key in passwordKeys) {
final password = await secureStorage.getPassword(key);
if (password != null && password.isNotEmpty) {
return password;
}
}
return null;
The account storage stores profile data (name, userId, url, database, sessionId) and stores the password with multiple patterns for reliable retrieval.
Step 8: Making authenticated HTTP requests (using session_id cookie)
Sometimes you need raw HTTP (reports, downloads, etc.). The session id can be used via the Cookie header.
This project includes a helper for building authenticated headers:
final headers = {
'Cookie': 'session_id=${session.sessionId}',
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest',
'Referer': '${session.serverUrl}/web',
};Copy-only: session cookie header
If you're debugging with Postman/cURL, the essential part is:
Cookie: session_id=<SESSION_ID>
Common issues and fixes
1) SSL / certificate errors
If you get SSL errors and your server is local or doesn't have HTTPS configured:
- switch the protocol to HTTP:
http://192.168.1.50:8069
The app already shows a message like:
SSL certificate error. Try using HTTP instead of HTTPS, or contact your administrator.
2) "Server returned HTML instead of JSON"
Usually caused by:
- wrong URL
- reverse proxy returning an HTML page
- pointing to /web or a non-Odoo endpoint
Use the base host URL:
http://<host>:8069
(not a web page path)
3) Android emulator > localhost is not your PC
If you use Android emulator:
http://10.0.2.2:8069
If you use a physical device, use your LAN IP:
http://192.168.x.x:8069
mobo App Home Screen (After successful login)
Authenticating a Mobo mobile application with Odoo using the odoo_rpc package becomes reliable and maintainable when the process is structured around server configuration, session persistence, and controlled client creation. Instead of JWT-based authentication, Odoo uses a server session where a session_id acts as a token and is automatically reused for subsequent requests.
A typical flow involves validating and normalizing the server URL, fetching the database list, and authenticating with username and password to obtain an OdooSession. Persisting session metadata in SharedPreferences and storing sensitive credentials in Secure Storage allows the app to restore sessions securely and re-authenticate when needed, preventing expired-session errors.
Using a centralized Session Manager pattern ensures that authenticated OdooClient instances are created, refreshed, and reused transparently, while helper wrappers enable safe RPC calls with automatic session recovery. This architecture also supports multi-account management, secure password handling, and authenticated HTTP requests for downloads or reports.
Overall, combining odoo_rpc, structured session management, and secure local storage provides a clean, scalable approach to handling authentication, sessions, and API access in any Flutter app that integrates with Odoo.
To read more about How to Secure Odoo Credentials in Mobo Apps, refer to our blog How to Secure Odoo Credentials in Mobo Apps.