Data fields
In Odoo, a model serves as a blueprint that defines the structure and
behavior of data entities. Essentially, each model represents a
database table, and its attributes (called fields) correspond to the
table's columns. A model class contains field definitions and the
logic to manage the data.
To begin creating a custom model, we place the Python file in the
appropriate directory, such as:
models > university_student.py
1. Below is a custom model designed to manage student data within a
university student management system
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from datetime import date
from odoo import models, fields, api
from dateutil.relativedelta import relativedelta
class UniversityStudent(models.Model):
"""Model to store student information."""
_name = "university.student"
_description = "University Student Records"
_inherit = ['mail.thread', 'mail.activity.mixin']
# This is the sequential ID shown at the top of the form
student_id = fields.Char(
string='Student ID', required=True, copy=False, readonly=True,
default=lambda self: 'New'
)
# This links to a res.partner record for the student's name and contact info
student_name = fields.Many2one('res.partner', string="Student Name", required=True)
# Personal Information
birth_date = fields.Date(string='Date of Birth')
student_age = fields.Integer(string='Age', compute='_compute_student_age', store=True)
gender_type = fields.Selection([
('male', 'Male'),
('female', 'Female'),
('other', 'Other')
], string='Gender')
blood_type = fields.Selection([
('A+', 'A+'), ('A-', 'A-'),
('B+', 'B+'), ('B-', 'B-'),
('AB+', 'AB+'), ('AB-', 'AB-'),
('O+', 'O+'), ('O-', 'O-')
], string='Blood Type')
# Contact & Family
country_id = fields.Many2one('res.country', string='Country')
father_name = fields.Char(string="Father's Name")
mother_name = fields.Char(string="Mother's Name")
mobile_phone = fields.Char(string='Mobile Phone', related='student_name.mobile', readonly=False)
landline = fields.Char(string='Landline', related='student_name.phone', readonly=False)
# Academic History One2many relationship
enrollment_history = fields.One2many(
'university.enrollment.history',
'student_id',
string='Enrollment History'
)
@api.depends('birth_date')
def _compute_student_age(self):
"""Calculate age from birth date."""
for record in self:
if record.birth_date:
today = date.today()
birth = record.birth_date
record.student_age = today.year - birth.year - (
(today.month, today.day) < (birth.month, birth.day))
else:
record.student_age = 0
class UniversityEnrollmentHistory(models.Model):
"""Stores the academic history for a student."""
_name = "university.enrollment.history"
_description = "Student Enrollment History"
student_id = fields.Many2one('university.student', string='Student Reference')
course_level = fields.Char(string='Course Level', required=True)
department = fields.Char(string='Department', required=True)
academic_session = fields.Char(string='Academic Session', required=True)
Fields in a model class, declared as attributes, determine the
specific kind of data the model will handle and contribute to its
overall data structure. The range of non-relational field types
offered is presented below
Char: Stores single-line text values (names, codes,
titles).
Text: Handles multi-line text content (descriptions,
notes).
Selection: Creates dropdown lists with predefined
options.
Binary: Manages file storage and binary data
(images, documents).
Html: Stores HTML-formatted rich text content.
Boolean: Handles True/False values for flags and
toggles.
Date: Stores date values only (YYYY-MM-DD format).
Datetime: Stores combined date and time values
(YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS format).
Date Field Utilities
- fields.Date.to_date(string) - Converts string to date object
- fields.Date.to_string(date) - Converts date object to string
- fields.Date.today() - Returns current date
- fields.Date.context_today(record, timestamp) - Returns
context-aware date
Datetime Field Utilities
- fields.Datetime.to_datetime(string) - Converts string to
datetime object
- fields.Datetime.to_string(datetime) - Converts datetime object
to string
- fields.Datetime.now() - Returns current datetime
- fields.Datetime.context_timestamp(record, timestamp) - Adjusts
datetime to user's timezone
Float: Stores decimal numbers and floating-point
values.
Monetary: Handles currency amounts with proper
formatting and conversion.
Many2one: Links current model to a single record in
another model (many-to-one relationship).
One2many: Creates inverse Many2one relationships,
linking one record to multiple related records.
Many2many: Establishes bidirectional many-to-many
relationships between models.
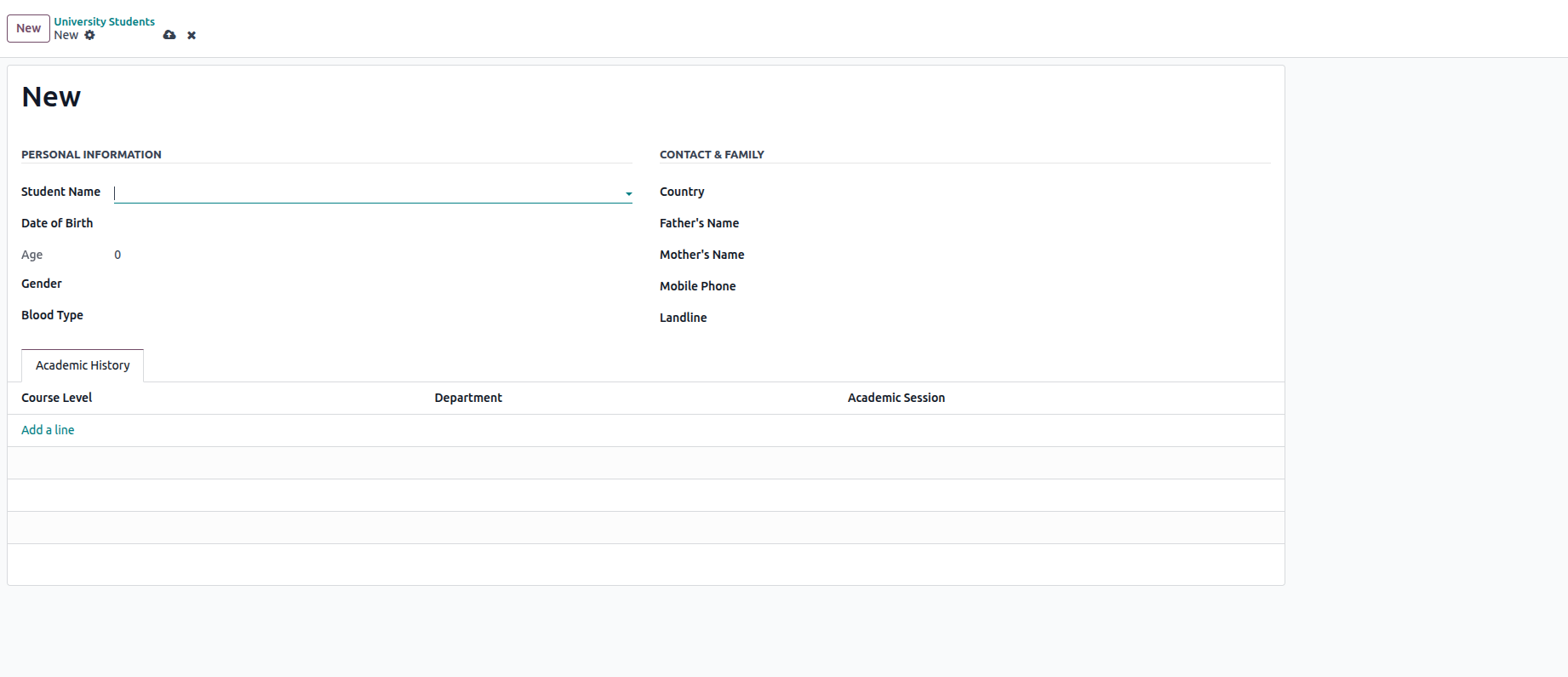
2. With the new fields now part of our model structure, the following
phase requires setting up the form view to showcase these fields in
the interface. The code example provided illustrates how to render
these fields for user interaction.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<odoo>
<record id="university_student_form_view" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">university.student.form</field>
<field name="model">university.student</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<form>
<sheet>
<div class="oe_title">
<h1>
<field name="student_id" readonly="1"/>
</h1>
</div>
<group>
<group string="Personal Information">
<field name="student_name"
widget="res_partner_many2one"
context="{'res_partner_search_mode': 'customer'}"
options='{"always_reload": True}'/>
<field name="birth_date"/>
<field name="student_age"/>
<field name="gender_type"/>
<field name="blood_type"/>
</group>
<group string="Contact & Family">
<field name="country_id"/>
<field name="father_name"/>
<field name="mother_name"/>
<field name="mobile_phone"/>
<field name="landline"/>
</group>
</group>
<notebook>
<page string="Academic History">
<field name="enrollment_history">
<list editable="bottom">
<field name="course_level" required="1"/>
<field name="department" required="1"/>
<field name="academic_session" required="1"/>
</list>
</field>
</page>
</notebook>
</sheet>
</form>
</field>
</record>
<!-- Tree View -->
<record id="university_student_tree_view" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">university.student.list</field>
<field name="model">university.student</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<list>
<field name="student_id"/>
<field name="student_name"/>
<field name="student_age"/>
<field name="gender_type"/>
<field name="country_id"/>
</list>
</field>
</record>
<!-- Action -->
<record id="university_student_action" model="ir.actions.act_window">
<field name="name">University Students</field>
<field name="res_model">university.student</field>
<field name="view_mode">list,form</field>
</record>
<menuitem id="menu_university" name="University" sequence="1"/>
<!-- Menu -->
<menuitem id="university_student_menu"
name="Students"
parent="menu_university"
action="university_student_action"/>
</odoo>
3. Following the module upgrade process, the modified form view
appears in the user interface.