In Odoo, relational fields are used to define links between different
models, enabling access to and interaction with related records.
These relationships play a vital role in real-world business
applications where connecting various models is crucial for
implementing specific workflows and processes. Odoo provides three
primary types of relational fields to establish these connections:
- Many2one
- One2many
- Many2many
Many2one Field
The Many2one field defines a many-to-one association
between two models. This means that several records in one model can
be connected to a single record in another model. It is typically
used when you want to assign a "parent" record from another model to
the current one.
This field is declared with the suffix _id and creates a reference
from the current model to another model (known as the comodel).
Here's the general syntax:
field_id = fields.Many2one('comodel_name', 'Field Label')
comodel_name: Refers to the technical name of the related model.
Example
To connect the product.product model with the product.category model
using a field named Category, you can define a Many2one field as
follows:
class Category(models.Model):
_name = 'product.category'
name = fields.Char(string='Category Name')
class Product(models.Model):
_name = 'product.product'
name = fields.Char(string='Product Name')
category_id = fields.Many2one('product.category', string='Product Category')
To retrieve the name of a product category from a related model that
has a character field called 'name', you can use the syntax
category_id.name.
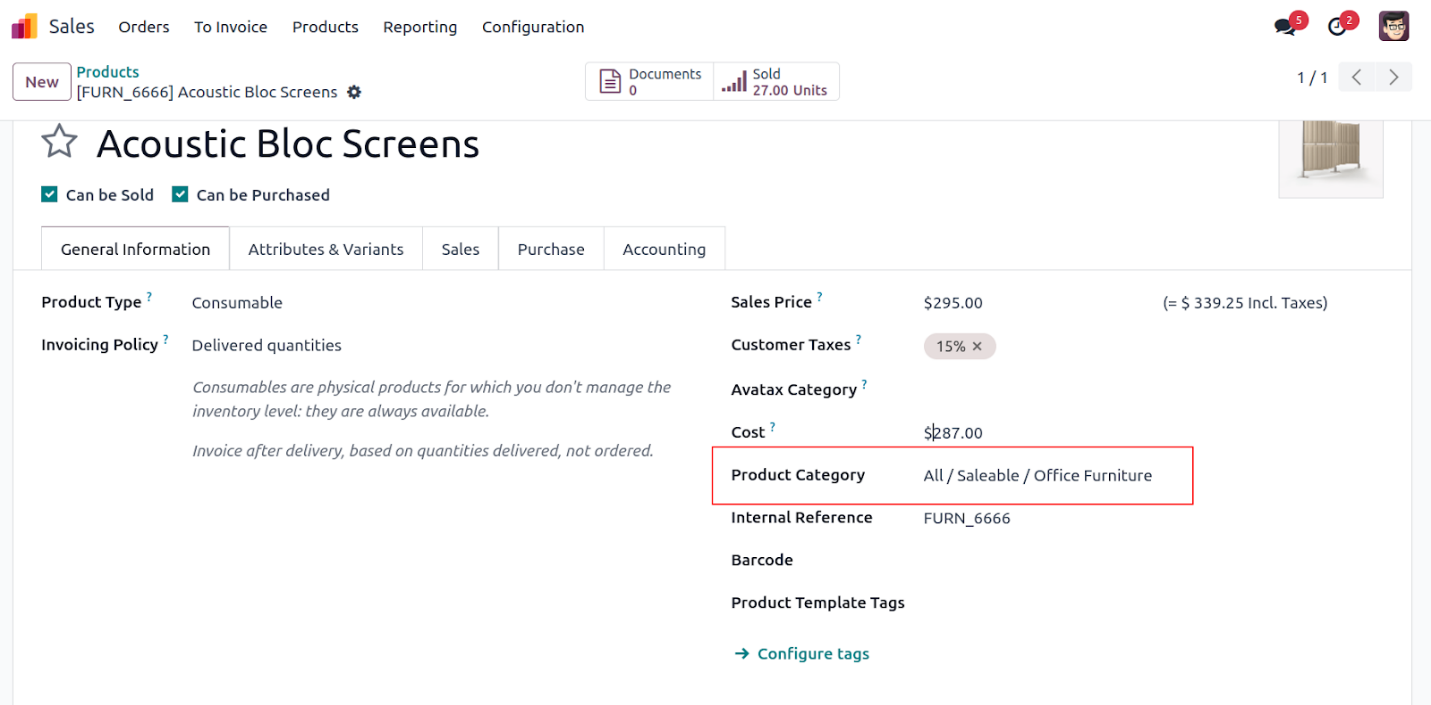
In this case, the 'Product Category' field represents a Many2one
relationship.
One2many fields:
The One2many field creates a one-to-many link between two models. It
is used when a single record in one model is associated with
multiple records in another. Essentially, this is the reverse of a
Many2one relationship. This field helps connect a parent record to
several child records, enabling structured data representation.
By convention, One2many fields typically use the _ids suffix.
For example,
from odoo import models, fields
class SaleOrder(models.Model):
_name = 'sale.order'
name = fields.Char(string='Order Reference')
order_lines = fields.One2many('sale.order.line', 'order_id', string='Order Lines')
class SaleOrderLine(models.Model):
_name = 'sale.order.line'
name = fields.Char(string='Description')
quantity = fields.Integer(string='Quantity')
order_id = fields.Many2one('sale.order', string='Order')
In the sale.order model, the order_lines field is a
One2many field that connects to the
sale.order.line model. Each record in the
sale.order.line model represents an individual line
item in the order and includes an order_id field, which is a
Many2one reference pointing back to the
sale.order model.
Since order_lines holds multiple records, it functions like a list,
allowing you to iterate over its contents using a loop.
for line in self.order_lines:
print(line.name)
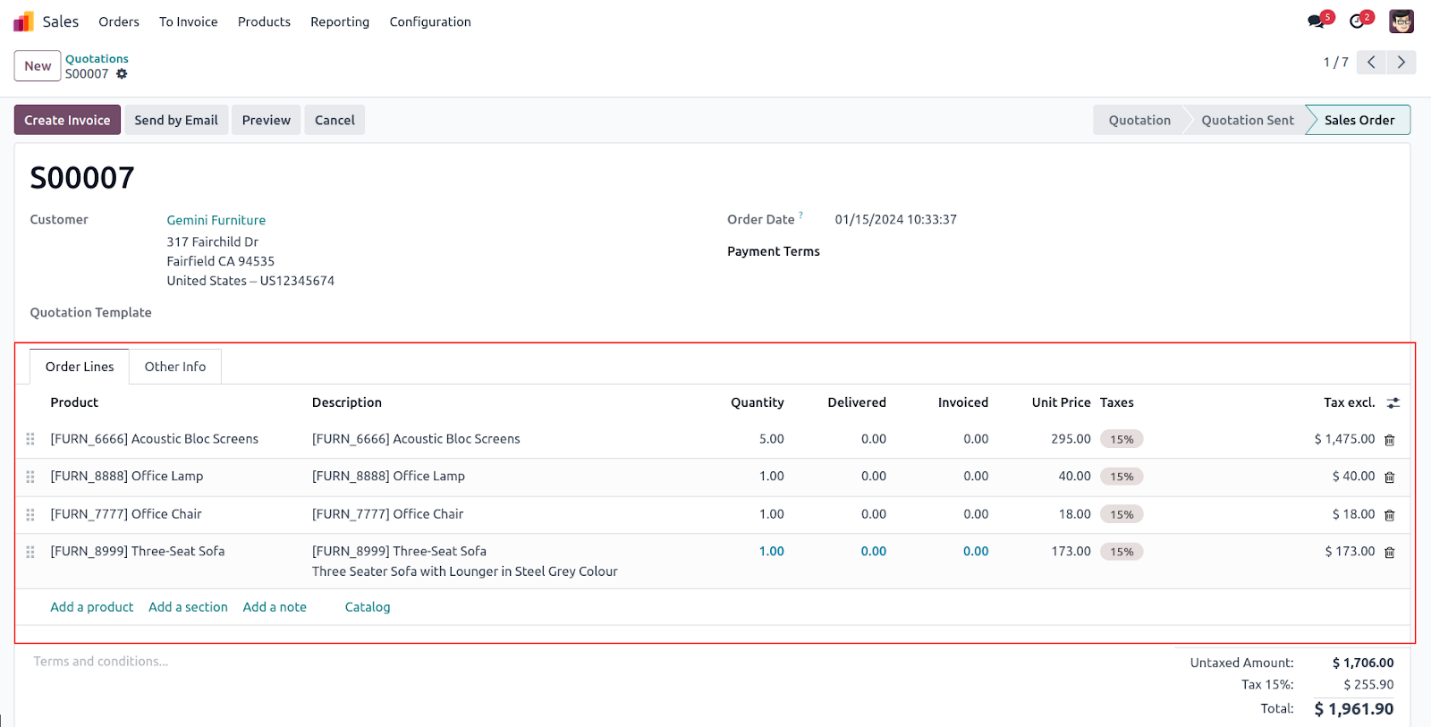
This is a list of sale order lines associated with a sales order,
displayed through a One2many field in the sale.order model.
Many2many fields:
The Many2many field defines a bidirectional many-to-many relationship
between two models. This type of field is used when multiple records
in one model need to be linked with multiple records in another.
By convention, Many2many fields use the _ids suffix.
field_ids = fields.Many2many('comodel_name', string='Field Name')
comodel_name: The technical name of the related model.
The values in a Many2many field act like a list, which means you can
iterate through them using a loop:
for rec in self.field_ids:
print(rec.name)
Optional Parameters:
Many2many fields support additional optional arguments:
- relation: The name of the database table that
stores the relationship.
- column1: Refers to the field that links back to
the current model in the relation table.
- column2: Refers to the field that links to the
related model in the relation table.
These parameters provide more control over how the relational table
is structured in the database.
For example,
from odoo import models, fields
class Product(models.Model):
_name = 'product.product'
name = fields.Char(string='Product Name')
tag_ids = fields.Many2many(
'product.tag', 'product_tag_rel', 'product_id', 'tag_id',
string='Product Template Tags'
)
class Tag(models.Model):
_name = 'product.tag'
name = fields.Char(string='Tag Name')
The product.product model represents individual products and includes
a Many2many field named tag_ids, which links to the product.tag
model. The product.tag model defines various tags that can be
assigned to products and contains a corresponding Many2many field
called product_ids, pointing back to the product.product model.
In this case, the tag_ids field in the product.product model
establishes the many-to-many relationship with the crm.tag (or
product.tag) model. In the database, this relationship is maintained
through an intermediate table named product_tag_rel, which contains
two columns: product_id and tag_id, representing the linkage between
products and their associated tags.
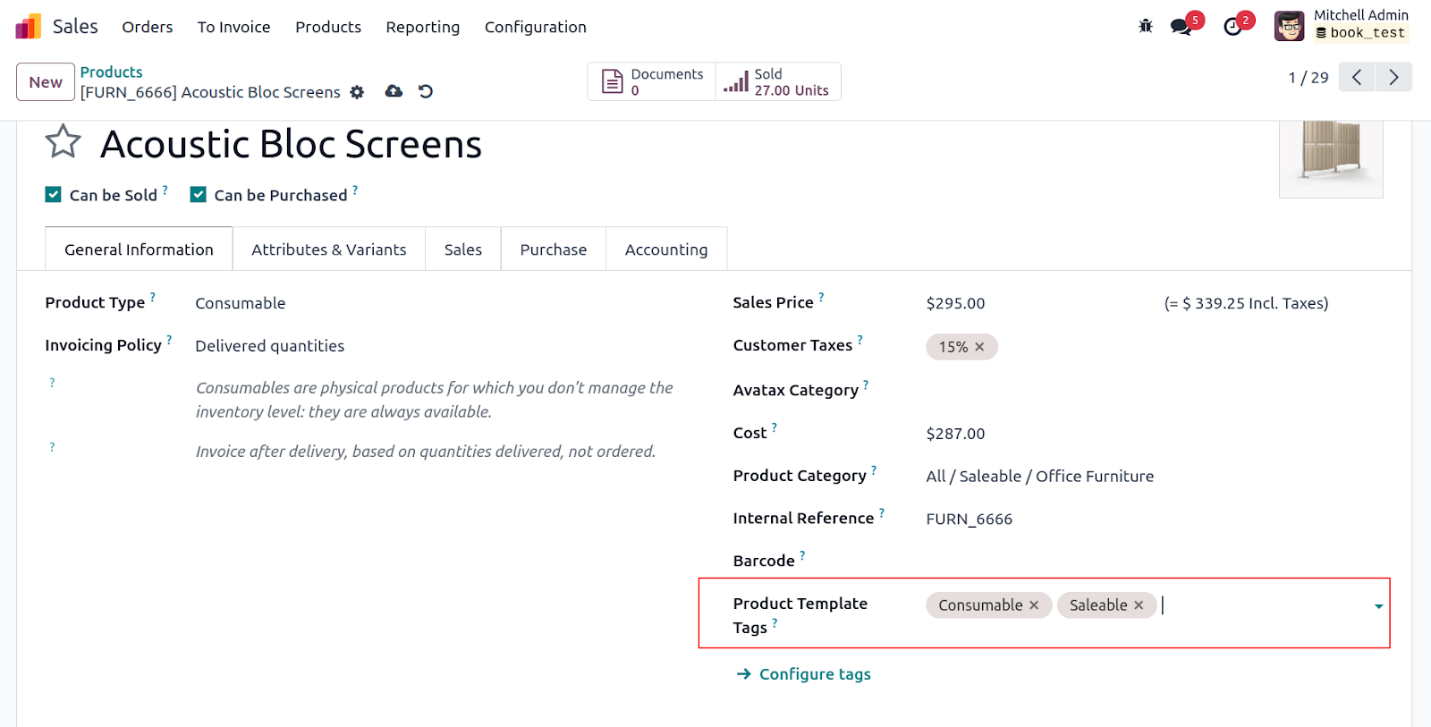
These are the tags linked to the product template, retrieved through
a Many2many field in the product model, using the Many2many tags
widget.