Odoo 18 offers Python code-based server actions as one of the most
powerful automation tools. These actions allow you to inject Python
logic directly into the system without needing to write a full
module. You can create validations, automate field updates, or
interact with records—all through the front end.
Getting Started with Python Code Server Actions
- Enable Developer Mode.
- Navigate to Settings > Technical > Automation > Automated
Actions.
- Click New to create an automated action.
Let’s look at a basic example that checks if an email is entered when
creating a contact. If not, it raises a warning:
if not record.email:
raise UserError("Please add an email.")
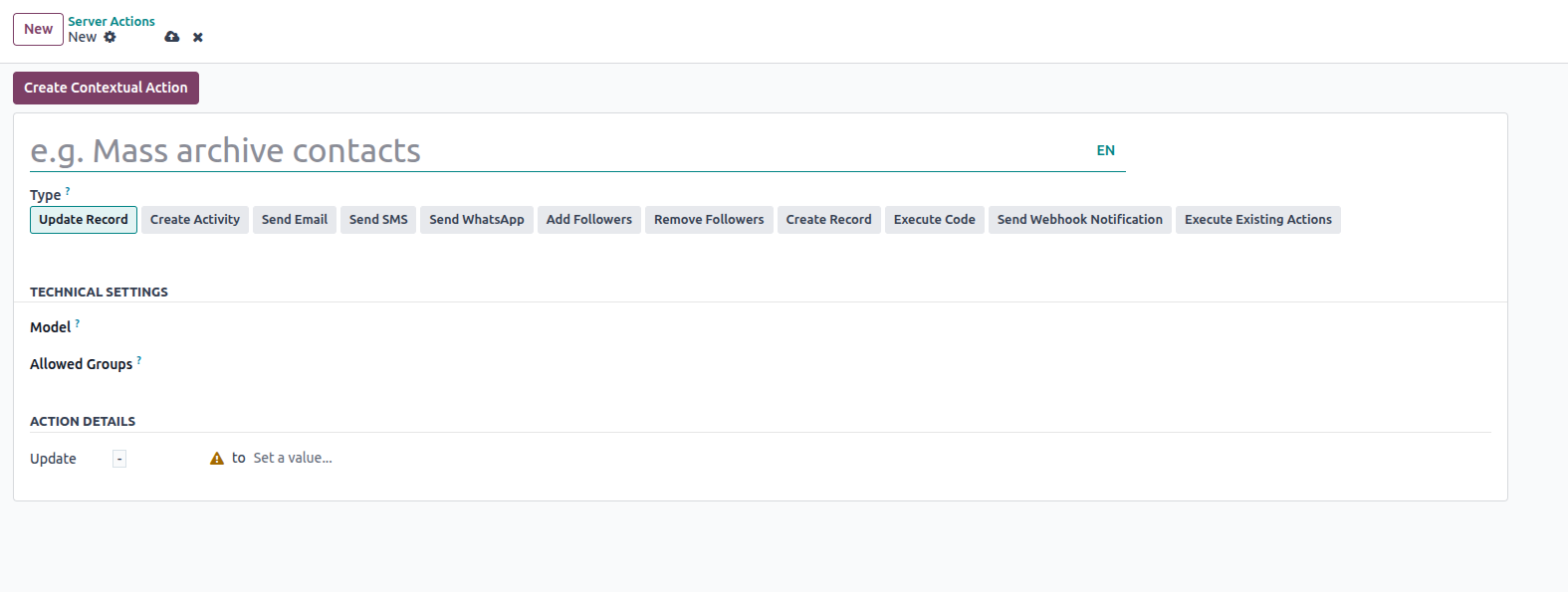
Key Fields in Automated Actions
When setting up a Python code server action, these fields are
important:
- Model: The database model the action targets (e.g., res.partner
for contacts).
- Trigger: When the action should be triggered—on creation,
update, deletion, or time-based.
- Apply On: Filters or conditions to limit which records are
affected.
- Python Code: Custom Python logic to execute.
What Happens After Saving?
In the above example, if someone tries to create a contact without
providing an email address, the system will block it and display the
error message defined in the Python code. This is a powerful way to
enforce business rules.
Time-Based Automated Actions
In addition to field-triggered actions, Odoo allows time-based
triggers. These are perfect for sending reminders, triggering
updates, or scheduling tasks in the future or before a certain date.
Setting Up a Time-Based Action
- Go to Settings > Technical > Automation > Automated Actions.
- Create a new record.
- Set Trigger to "Based on Time Condition".
Important fields to configure:
- Model: Where the action will apply.
- Action To Do: What kind of operation (e.g., Send Email).
- Trigger Date: Field from the model that will serve as a
reference date.
- Delay: Specify how many days/hours before or after the trigger
date the action should fire (negative delay means before).
- Email Template: Select if you're sending an email.

Event-Based Automated Actions
Odoo also supports actions based on specific events, such as changes
to fields or updates made by users. This is especially useful for
enforcing access control and business validations.
Use Case: Restricting Project Status Updates
Let’s say you want only the project manager or project leader to
update a project's status. You can achieve this by writing Python
logic in an automated action.
Example condition:
if record.user_id != env.user:
raise UserError("Only the assigned Project Manager can update this.")

Creating the Update-Based Action
1. Navigate to Automated Actions.
2. Create a new action with:
- ● Model: e.g., project.project
- ● Trigger: On Update
- ● Fields to Trigger the Action: Choose the status field (e.g.,
stage_id)
- ● Apply On: Filter if needed (e.g., project_stage_id != 'done')
- ● Action to Do: Execute Python Code
- ● Python Code: Use the logic above to check user access.

- Fields That Trigger the Action: Only updates to these fields
will activate the action.
- Apply On: A domain filter that limits which records the rule
will apply to.
- Prior to Updating the Domain: Conditions to validate before the
record is changed.
- What to Do: Select "Execute Python Code" and write your logic.
If a user who isn't assigned as the project manager tries to make
changes, they’ll see the error message and the update will be
blocked.
