In the Odoo framework, the ORM Cache decorator plays a key role in
managing in-memory caches.This guide provides an in-depth look at
how function caching operates within this system.
The ORM cache classes are defined in /odoo/tools/cache.py. To utilize
them in a record, import the necessary classes accordingly. To
access the ORM cache decorator, import it using from odoo import
tools. Odoo provides various types of in-memory cache decorators,
each of which is described in the following sections.
Orm cache
The orm cache decorator is one of the most commonly used and
easy-to-implement cache decorators. To apply it, you need to specify
the argument names the method depends on. Below is an example
demonstrating the use of the ormcache decorator.
@tools.ormcache('key')
def _check_data(self, key):
# some code
return result
During the initial call, the method runs and generates the result.
For subsequent calls with the same key, the cached result is
returned, skipping the method's execution
If a method's result depends on certain environmental attributes, it
should be defined to explicitly include those dependencies.
@tools.ormcache('self.env.uid', 'category_id')
def _get_default_values(self, category_id):
# Simulate some heavy computation or database query
values = self.env['my.category'].browse(category_id).mapped('default_values')
return values
This example method stores the cached result using the environment's
user and mode parameters as cache keys.
Ormcache_context
The ormcache_context decorator operates like ormcache but
additionally takes context parameters into account. To use it, you
need to specify both the method’s parameter names and the relevant
context keys. For example, if the method’s result depends on the
lang and tz keys in the context, you can apply ormcache_context as
follows:
@tools.ormcache_context('name', keys=('tz', 'lang'))
def _get_partner_country(self, name):
partner = self.env['res.partner'].with_context(lang=self._context.get('lang')).search([('name', '=', name)], limit=1)
return partner.country_id.name if partner.country_id else False
In this example, the cache depends on both the method's key arguments
and the values of the specified context keys.
Least Recently Used (LRU)
The ORM cache uses a Least Recently Used (LRU) strategy, where less
frequently accessed keys are automatically removed. However,
improper use can lead to inefficiencies—for example, if method
arguments are highly dynamic, Odoo will repeatedly attempt cache
lookups before proceeding with the actual computation. To observe
cache activity, you can send the SIGUSR1 signal to the running Odoo
process.
kill -SIGUSR1
Replace the process ID (e.g., 674269). After the command is executed,
check the logs to view the current status of the ORM cache.
kill -SIGUSR1 674269
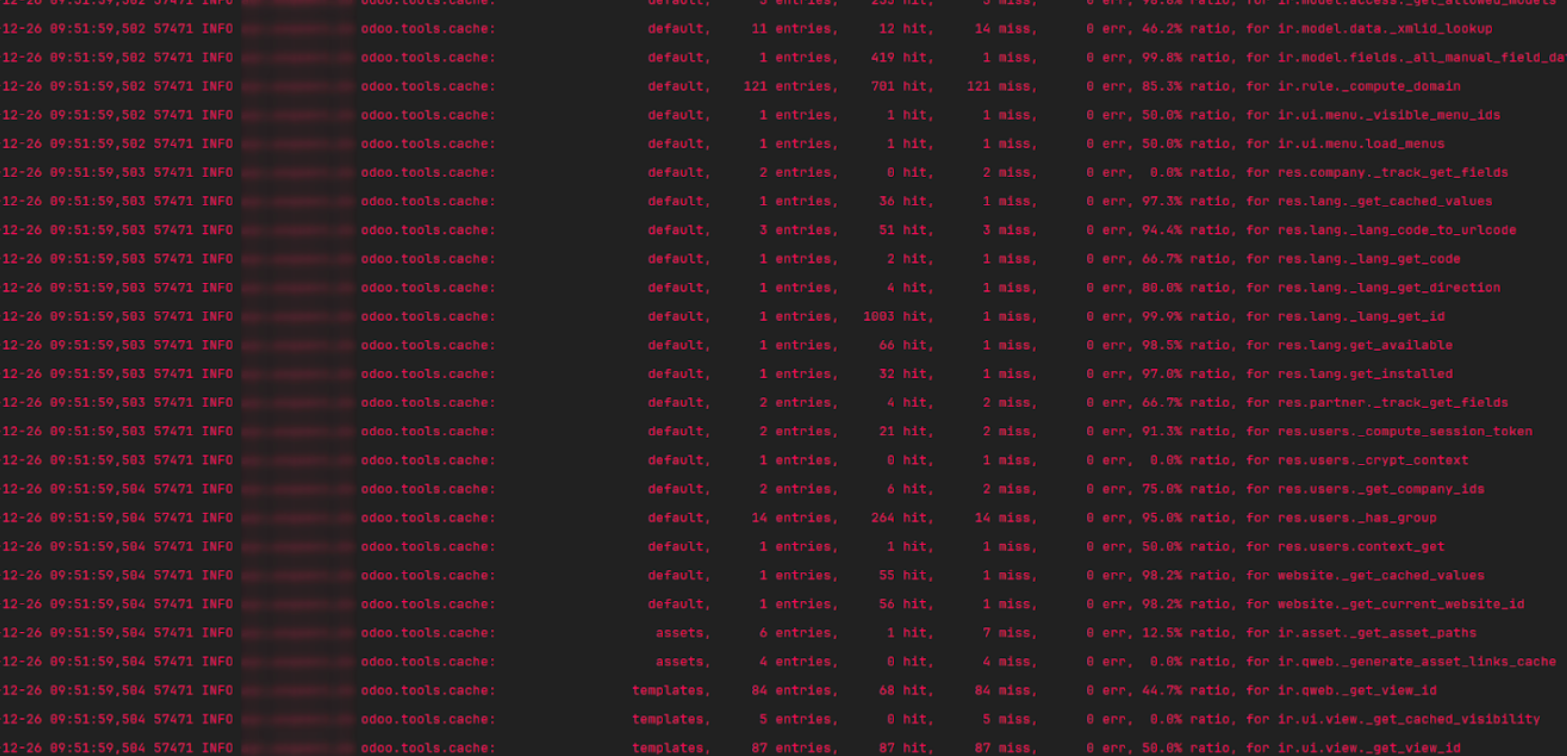
The cache percentage indicates the ratio of cache hits to misses,
representing how effectively the cache retrieves stored results. A
consistently low hit/miss ratio suggests that using the ORM cache in
the method may not be efficient and should be reconsidered.