XML-RPC is a remote procedure call protocol that uses XML to encode
its calls and HTTP as a transport mechanism. This allows
applications running in different environments (e.g., Windows,
Linux, MacOS) to communicate over the internet.
It’s particularly useful in Odoo when integrating third-party systems
or building automated scripts, offering a lightweight, standard way
to interact with Odoo’s backend using method calls.
How Odoo Handles XML-RPC
Odoo exposes two XML-RPC endpoints that remain unchanged in Odoo 18:
- /xmlrpc/2/common – Used for general info and authentication.
- /xmlrpc/2/object – Used for data manipulation (e.g., create,
read, update, delete).
Authenticating with API Key in Odoo 18
Starting with Odoo 17 and continuing in Odoo 18, API Keys offer a
secure way to authenticate without using plain-text passwords in
scripts.
To generate an API key:
1. Enable Developer Mode.
2. Go to your User Preferences (My Profile section).
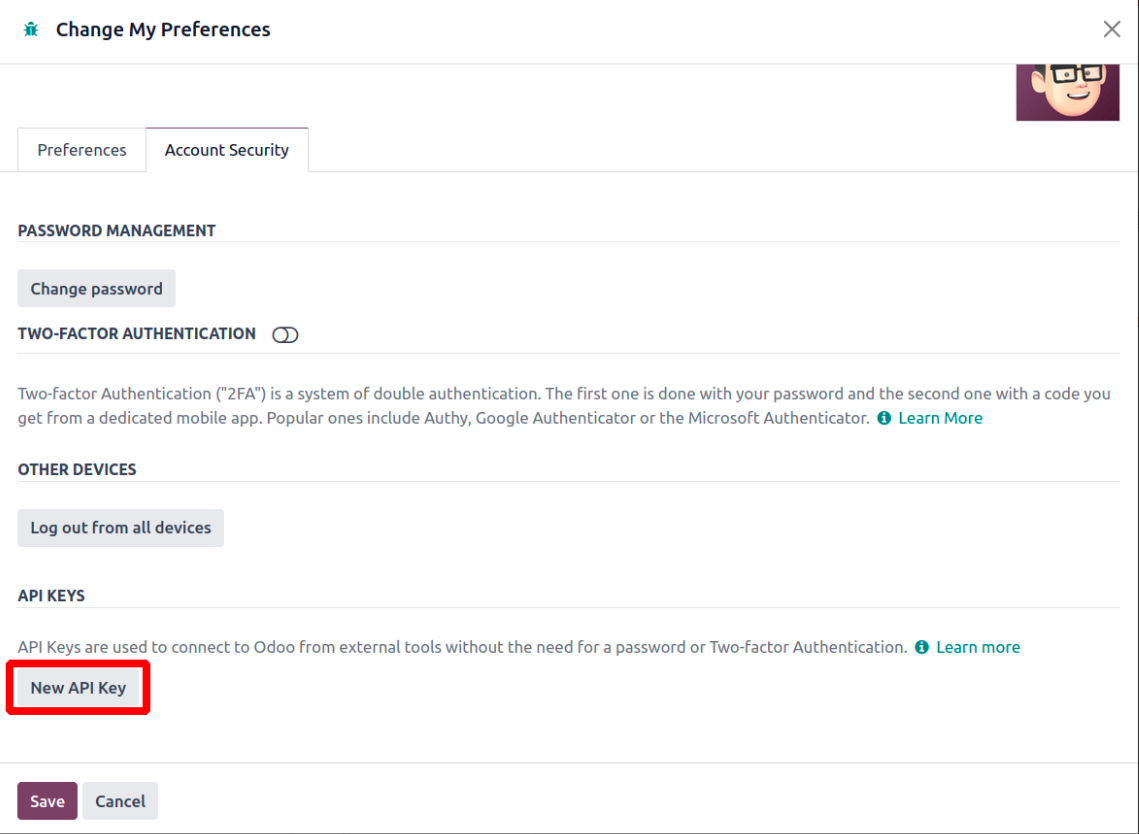
3. Open the Account Security tab.
4. Click New API Key and provide a label for the key.
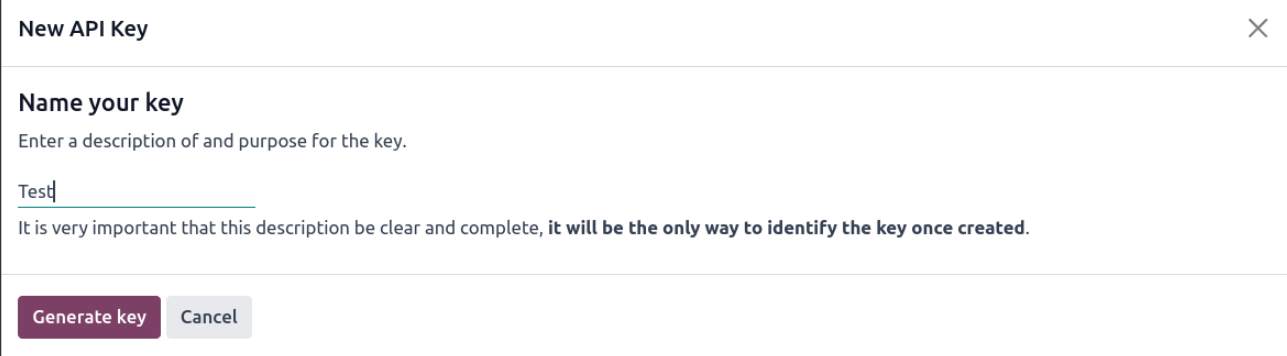
5. Enter a description and purpose of the key.
6. Odoo will generate an API Key for you. Store it securely.
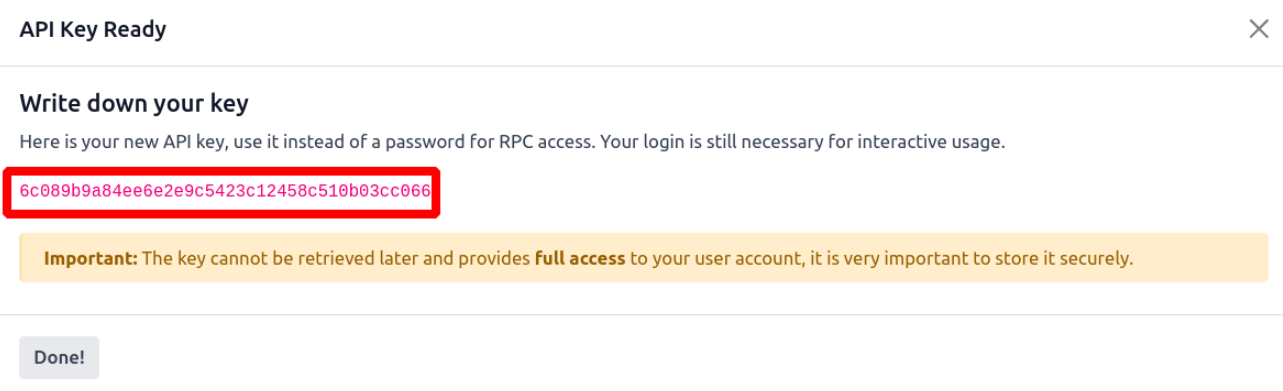
API keys offer the same access level as your password but cannot be
used for UI login. Always treat them with care.
Connecting to Odoo via XML-RPC in Python
import xmlrpc.client
url = 'http://localhost:8069'
db = 'your_db_name'
username = 'admin'
api_key = 'generated_api_key_here'
common = xmlrpc.client.ServerProxy(f'{url}/xmlrpc/2/common')
uid = common.authenticate(db, username, api_key, {})
The authenticate() function returns the user ID (uid) which will be
used for further operations.
Working with Models Using /xmlrpc/2/object
After authentication, we can interact with models via the object
endpoint:
models = xmlrpc.client.ServerProxy(f'{url}/xmlrpc/2/object')
Now, using models.execute_kw(), we can perform various operations.
Search Records
Basic Search
partner_ids = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', True]]])
With Limit
partners = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', True]]], {'limit': 1})
With Offset
partners = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', True]]], {'limit': 1})
Count Records
count = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'search_count', [[['is_company', '=', True]]])
Read Records
partner_id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', True]]], {'limit': 1})
partner_data = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'read', [partner_id])
Read with Specific Fields
partner_data = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'read', [partner_id], {'fields': ['name', 'email']})
Search and Read (Combined)
partner_data = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'search_read', [[['is_company', '=', True]]], {'fields': ['name', 'email'], 'limit': 1})
This method is more efficient when both searching and fetching fields
are required.
Create a Record
new_partner_id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'create', [{'name': 'New Partner', 'email': 'partner@example.com'}])
Update a Record
update_result = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'write', [[new_partner_id], {'name': 'Updated Partner Name'}])
Returns True if the record was updated successfully.
Delete a Record
delete_result = models.execute_kw(db, uid, api_key, 'res.partner', 'unlink', [[new_partner_id]])
Returns True if the deletion was successful.