QUnit is the primary JavaScript testing framework used in Odoo for
validating frontend (UI) behaviors. It helps ensure the reliability
of custom widgets, views, and frontend logic by allowing developers
to simulate interactions and assert expected results.
In Odoo 18, the testing system is more modular and robust, supporting
better mocking, view simulation, and DOM testing using the new OWL
framework and modern testing utilities.
QUnit is used to:
- Test views and widgets
- Simulate frontend behavior
- Mock RPC calls
- Validate DOM rendering
- Automate regression testing for JS changes
Steps to Add QUnit Tests in Odoo 18
1. Create the Test JS File
Inside your custom module, create a test folder under static. Then
add your test file. For example:
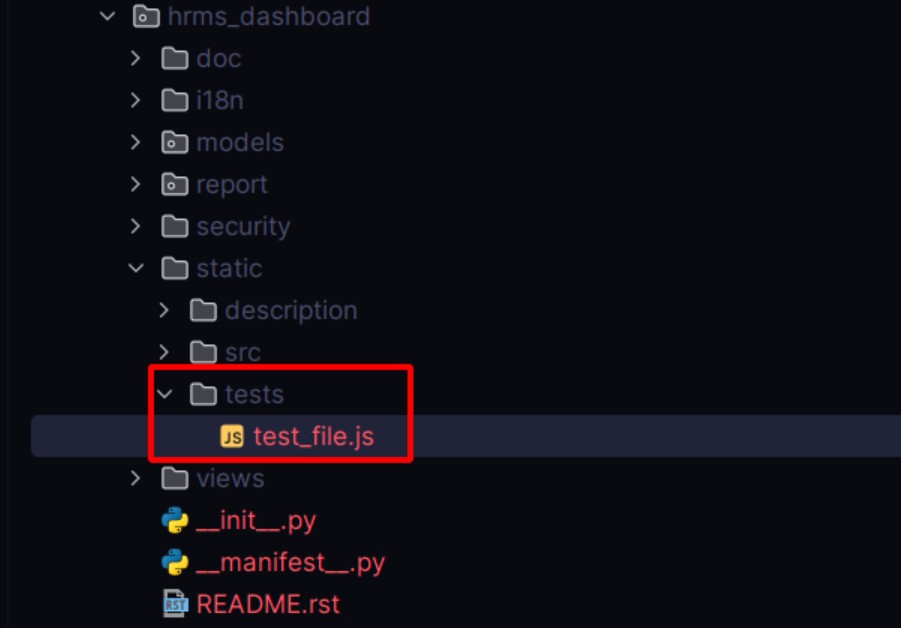
2. Register the Test in __manifest__.py
Add your JS test file under the web.qunit_suite_tests key in the
manifest:
'assets': {
'web.qunit_suite_tests': [
'your_module/static/tests/test_hr_leave.js',
],
}
3. Write the QUnit Test Case
Below is an example that tests if the form view for hr.leave is
rendered properly:
/** @odoo-module **/
import { getFixture } from "@web/../tests/helpers/utils";
import { makeView, setupViewRegistries } from "@web/../tests/views/helpers";
let makeViewParams, target;
QUnit.module("HR Leave Form View", (hooks) => {
hooks.beforeEach(() => {
makeViewParams = {
type: "form",
resModel: "hr.leave",
arch: ``,
serverData: {
models: {
"hr.leave": {
fields: {
id: { string: "ID", type: "integer" },
display_name: { string: "Name", type: "char" }
},
records: [
{ id: 1, display_name: "Test Record" }
],
},
},
},
};
target = getFixture();
setupViewRegistries();
});
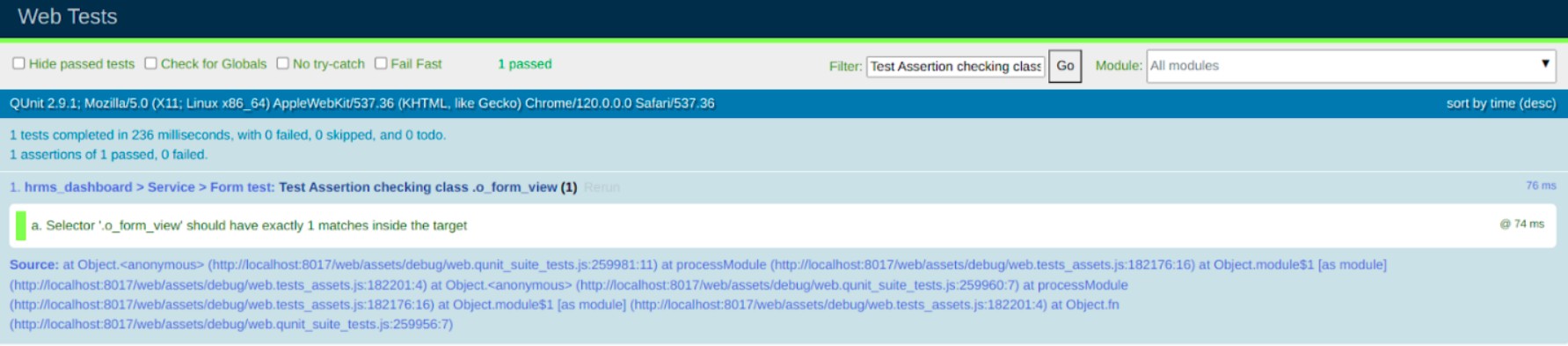
QUnit.test("Form view should render with .o_form_view class", async function (assert) {
await makeView(makeViewParams);
assert.containsOnce(target, ".o_form_view");
});
});
- makeView creates a simulated view.
- assert.containsOnce(...) checks that .o_form_view is present
exactly once in the rendered output.
- getFixture() defines where the DOM should render.
4. Run Your Test
You can run QUnit tests by:
- Navigating to: /web/tests
- Or by clicking Run JS Tests from the Developer Tools (in Debug
Mode)
Using Helper Functions in QUnit
Writing frontend tests in Odoo often means simulating complex
behaviors like view rendering, server communication, and user
interactions. To make this process easier and more reliable, Odoo
provides a suite of helper functions. These helpers allow developers
to mock data, interact with the DOM, and construct views in a
controlled, test-friendly environment.
These functions are especially useful when testing frontend modules
that depend on views, RPC calls, or widget rendering.
Mock Test Functions
Many views and widgets in Odoo communicate with the server using RPC
methods like read, search_read, or name_get. In testing, we don’t
want to hit the actual server, so we use mock objects.
You can provide mock model data via the serverData object in your
test setup. This simulates model behavior and lets you define
specific fields and records to return
DOM Helpers
Odoo’s test suite includes DOM utilities that safely simulate user
actions like clicks, input events, and more. These helpers ensure
that elements are in a valid state before interacting with them,
which prevents common test flakiness.
Create Helpers (createView, makeView)
Creating views is a core part of frontend tests. Odoo provides
makeView and createView functions to programmatically render views
(form, list, kanban, etc.) in a test-safe environment.
Custom QUnit Assertions
To improve readability and consistency of your test validations, Odoo
extends QUnit with custom assertion methods:
- assert.containsOnce(el, selector): Verifies the selector appears
exactly once.
- assert.containsN(el, selector, n): Verifies the selector appears
n times.
- assert.containsNone(el, selector): Verifies the selector does
not exist.
- assert.strictEqual(actual, expected, message): Checks equality.