In Odoo 19, sequence numbers help keep your records organized by giving each document its own unique and easy-to-track identifier. You’ve probably seen them on invoices, sales orders, purchase orders, and many other records that rely on clear numbering. What makes Odoo even more flexible is that you can customize these numbers by adding your own prefixes, suffixes, date formats, or padding—so the sequence matches the way your business likes to work.
In this guide, we’ll look at how you can set up custom prefixes and suffixes in Odoo 19. To make things easier to understand, we’ll use a simple example from a Hospital Management module, where every OP ticket automatically gets a neatly formatted reference number generated from the sequence you configure.
Step 1: Define the Model
To begin, we first create the model where our sequence will be applied. In this example, we’re working within the hospital_management module and setting up a model to represent OP tickets. This model will act as the foundation for generating unique identifiers. Once the structure is in place, we’ll configure a sequence that automatically assigns a distinct reference number each time a new OP ticket is created, ensuring proper tracking and consistency throughout the system.
from odoo import api, fields, models
class HospitalManagement(models.Model):
_name = 'hospital.management'
_description = 'Sample Model'
_inherit = ['mail.thread', 'mail.activity.mixin']
name = fields.Char(string='Name', required=True)
reference_number = fields.Char(string='Sequence',copy=False,default="New",readonly=True, required=True)
description = fields.Text(string='Description')
date = fields.Date(string='Date')
active = fields.Boolean(string='Active', default=True)
state = fields.Selection([
('draft', 'Draft'),
('confirmed', 'Confirmed'),
('done', 'Done')
], string='State', default='draft', tracking=True)
@api.model_create_multi
def create(self, vals):
"""Create records using provided values."""
for rec in vals:
code = self.env['ir.sequence'].next_by_code('hospital.registration')
rec['reference_number'] = code
res = super().create(vals)
return res
Explanation of the Code:
- reference_number – This is a character field with the default value set to "New". It is used to store the unique identification number generated for each ticket.
- create – By overriding this method, the system guarantees that every newly created record is automatically given a unique reference number by pulling the next value from the configured sequence.
Step 2: Define the Sequence in XML
With the model prepared, the next step is to define the sequence that will generate unique numbers for the hospital.management records. This configuration needs to be added inside an XML file located in your module’s data directory.
Create a new file named ir_sequence_data.xml and include the following code to set up the sequence for your OP ticket records.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<odoo>
<record id="ir_sequence_hospital_registration" model="ir.sequence">
<field name="name">Op Ticket Reference Numbers</field>
<field name="code">hospital.registration</field>
<field name="prefix">OP/</field>
<field name="suffix">/%(year)s</field>
<field name="padding">5</field>
<field name="number_next">1</field>
<field name="number_increment">1</field>
<field name="company_id" eval="False"/>
</record>
</odoo>
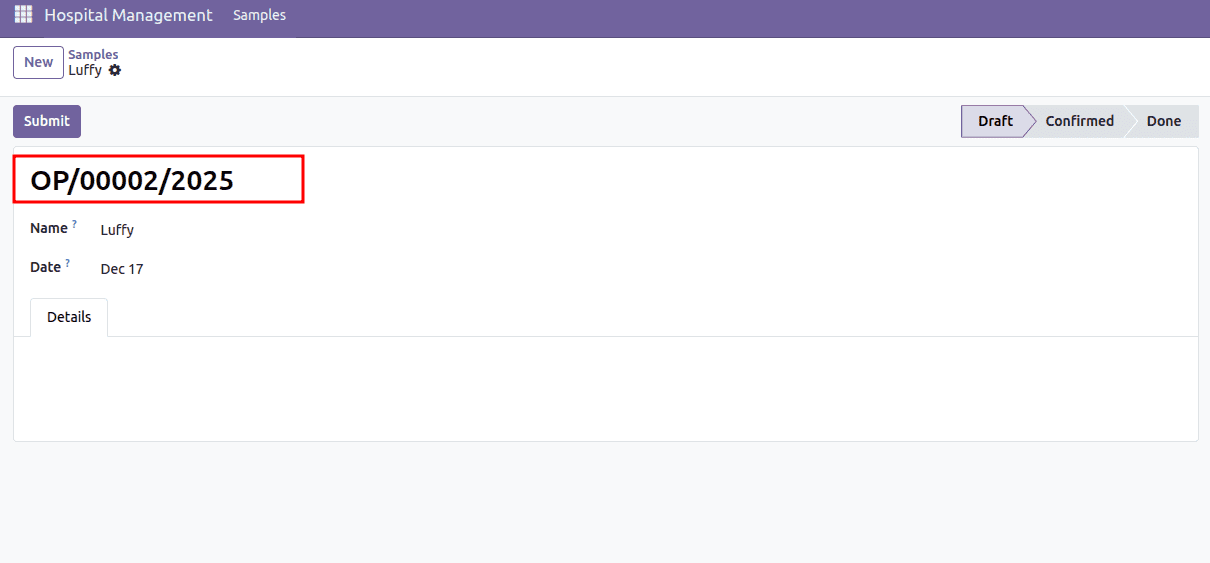
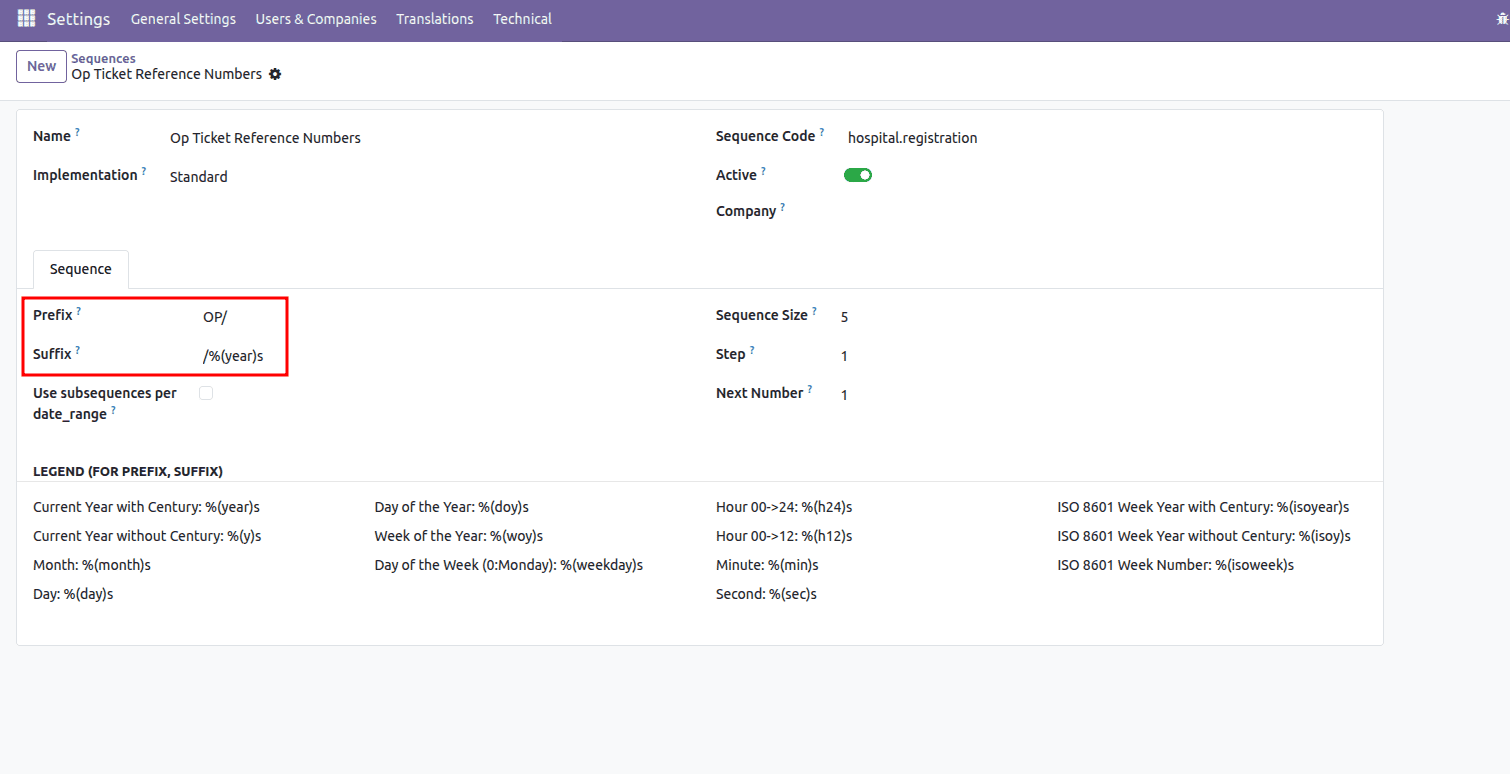
In this sequence definition, the prefix and suffix fields control how the final reference number is formatted. The prefix "OP/" ensures that every generated number begins with this text, making it easy to identify the record as an OP ticket at a glance. The suffix "/%(year)s" automatically appends the current year to the end of the sequence using Odoo’s date-based placeholders. When combined with the padded number in between, the final output follows a structure like OP/00001/2025, giving each record a clean, consistent, and meaningful reference format.
Example:
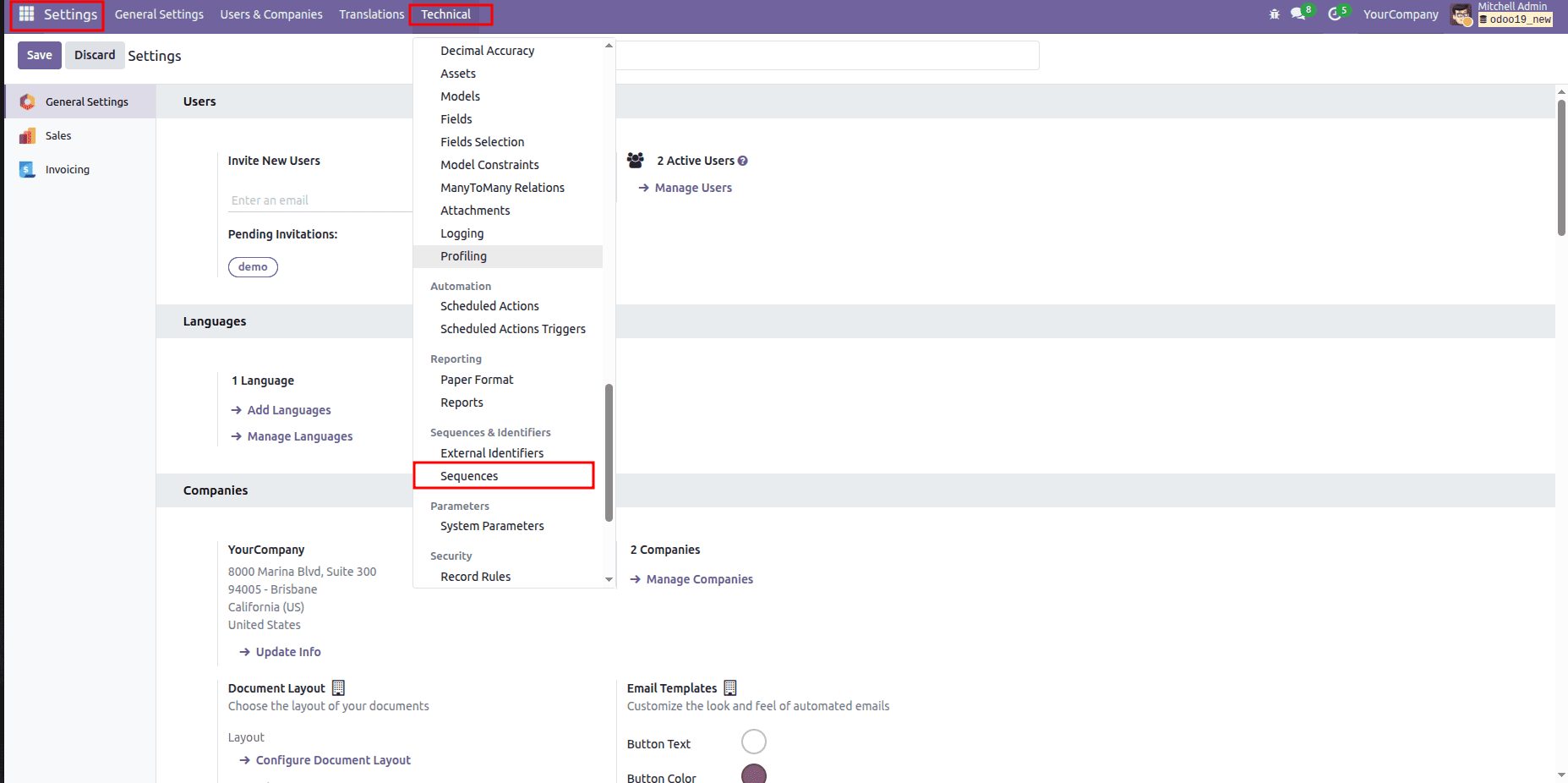
Alternatively, you can manage this sequence directly from the Odoo interface by navigating to Settings > Technical > Sequences. There, you’ll see the sequence record created from your XML file, and you can easily review or modify its configuration without touching the code. This makes it simple to adjust prefixes, suffixes, padding, or any other sequence settings whenever needed.
Inside the Sequence menu, you can see the sequence record that was created.
Configuring custom prefixes and suffixes in Odoo 19 is a straightforward yet effective way to create clean, meaningful, and well-structured document references. Whether you choose to set them up through the interface or define them in XML, this approach gives your records a consistent identity and makes them easier to track across different workflows. By adopting customized sequence formatting, you improve clarity, enhance auditing, and support smoother day-to-day operations—ultimately building a more organized and professional system for managing your data.
To read more about How to Create Sequence Numbers in Odoo 18, refer to our blog How to Create Sequence Numbers in Odoo 18.