An Asset is any resource owned by a business or individual that has measurable value and is expected to provide future economic benefits. Assets help organizations operate, generate revenue, and grow. They can be physical items like machinery, buildings, and vehicles, or non-physical items like patents, trademarks, and software.
In Accounting, assets are recorded on the balance sheet and are categorized based on their nature and how long they provide value, such as Current Assets (short-term) and Non-current Assets (long-term). Understanding assets is essential because they form the foundation of financial statements and influence decisions related to investments, profitability, and long-term planning.
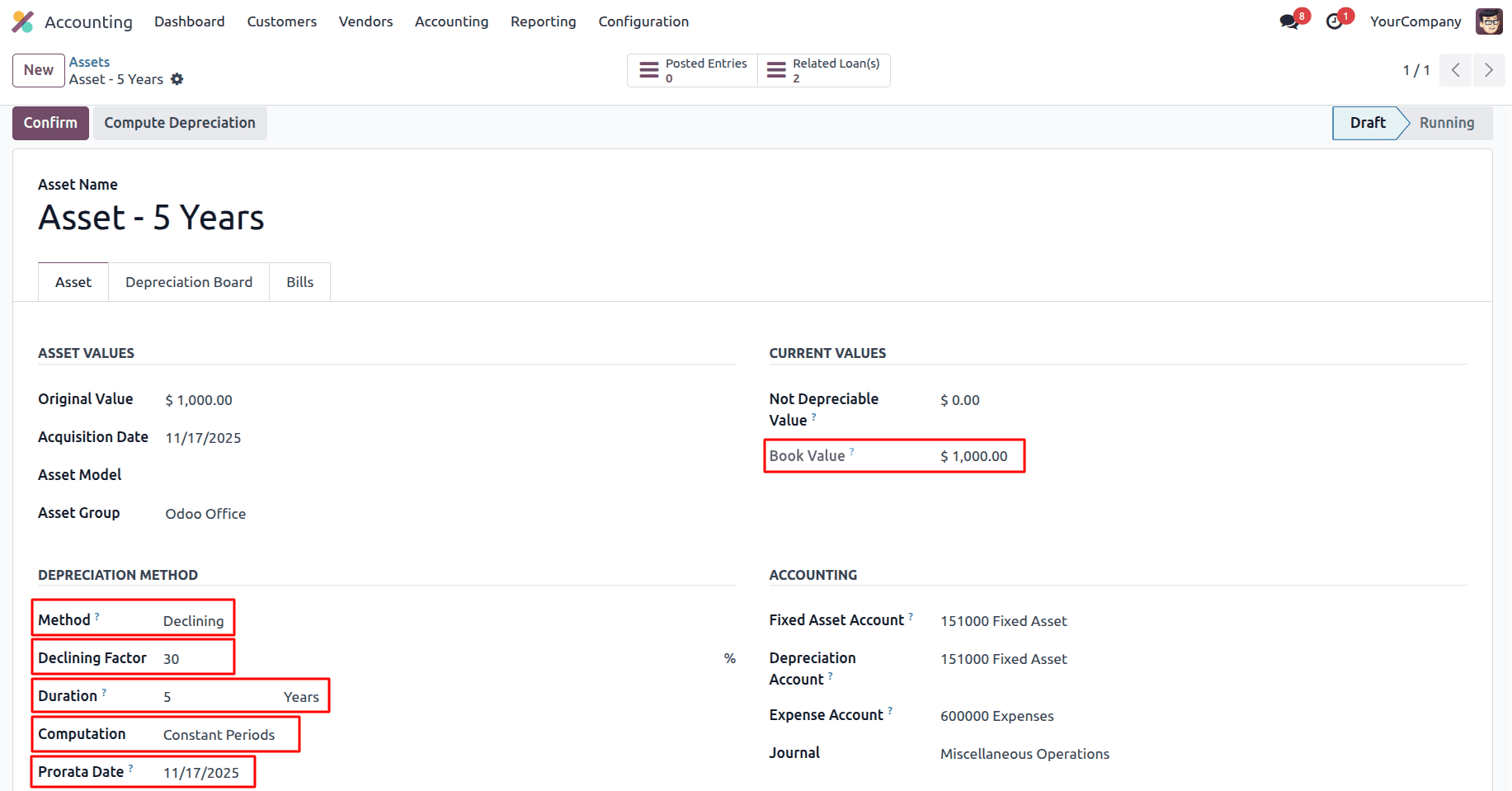
Asset depreciation is the accounting method used to allocate the cost of a physical asset over its useful life. Instead of recording the full cost upfront, depreciation spreads the expense across months or years—reflecting the gradual wear, usage, or obsolescence of the asset.
Odoo 18 includes three depreciation methods, each suited to different types of assets and accounting strategies:
- Straight Line Method
- Declining Balance Method
- Declining Balance then Straight Line Method
1. Straight Line Method
The asset’s cost is spread evenly across its useful life. Each depreciation period records the same amount. Useful when Asset usage is consistent over time (e.g., buildings, office furniture)
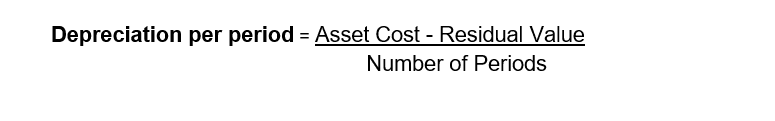
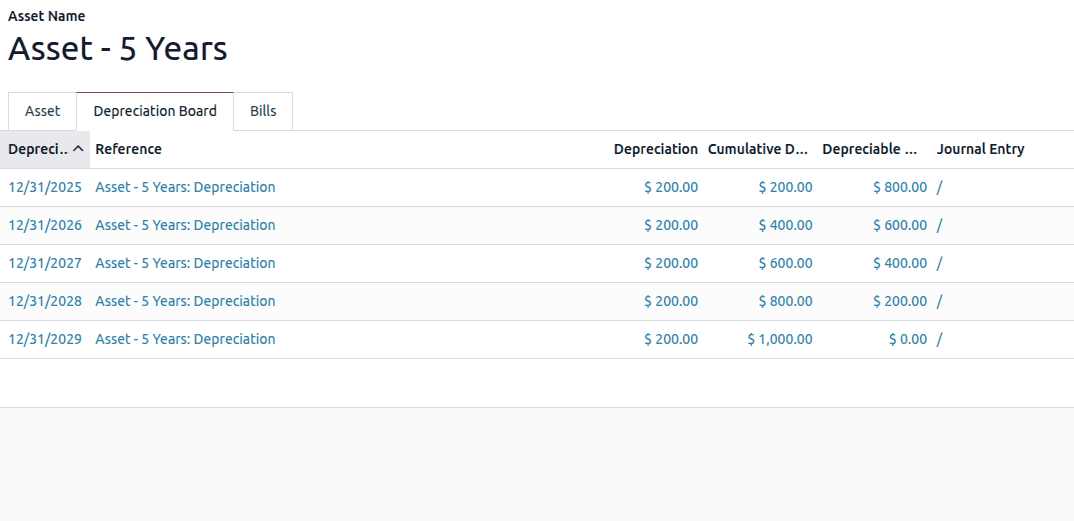
Computation based on No Prorata
Computation based on No Prorata using the Straight-Line method means depreciation is calculated evenly over time without adjusting for partial periods, regardless of when the asset is purchased or put into use.
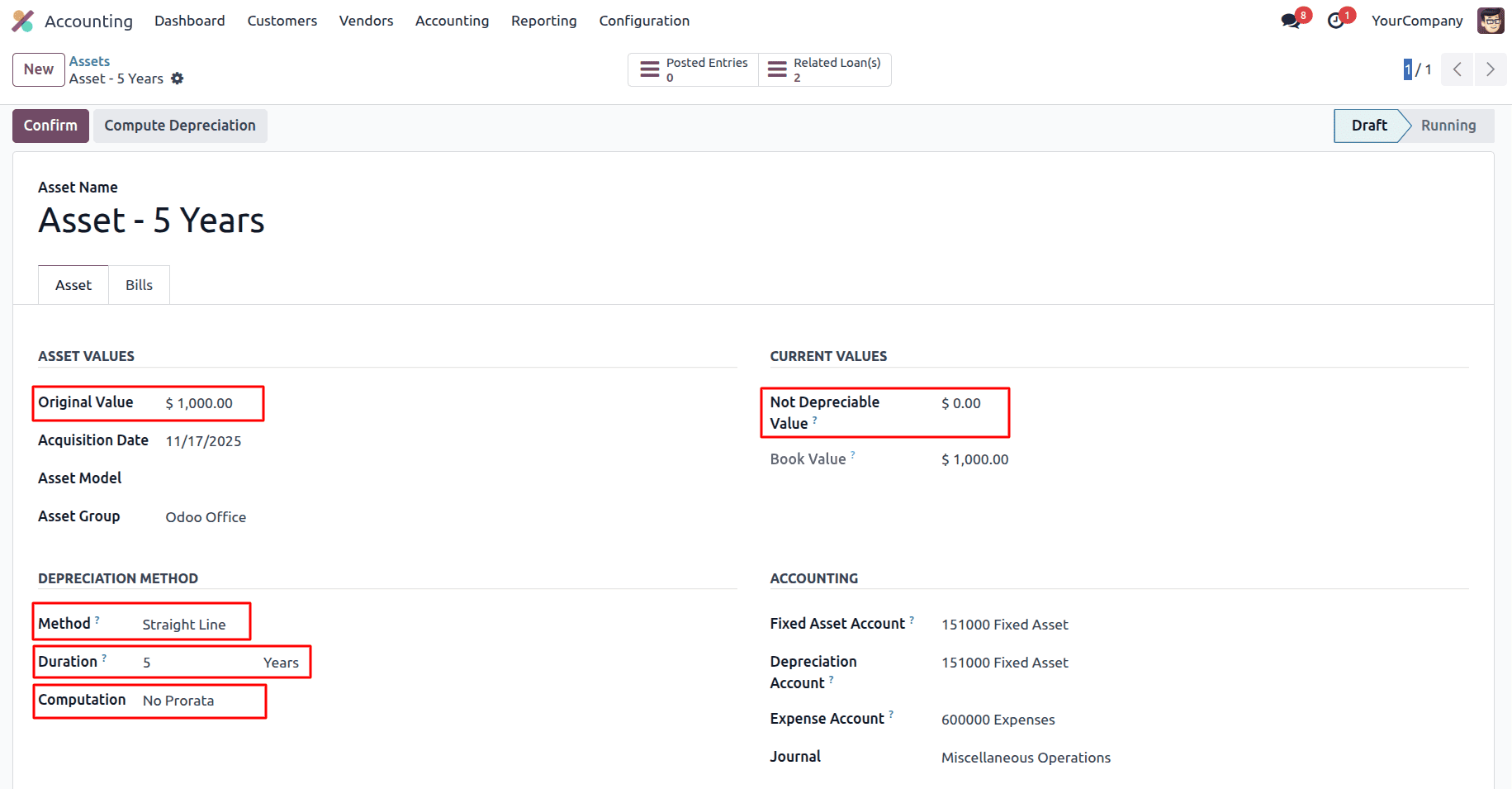
Residual value (Non Depreciable Value) is the estimated value of an asset at the end of its useful life — the amount you expect to recover either through sale or scrap.
Asset Cost (Original Value) is the total purchase price of the asset, including installation and delivery.
Number of Periods (Duration) is the total number of time units (months or years) over which depreciation will occur.
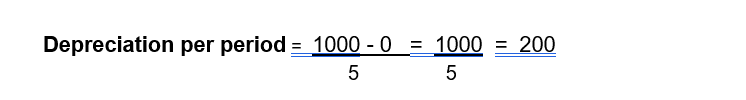
Depreciation value is the amount of an asset’s cost that is allocated as an expense for a specific accounting period.
Cumulative depreciation (also called accumulated depreciation) is the total depreciation recorded on an asset from the time it is put into use up to a specific date.
Depreciable value is the total amount of an asset’s cost that can be depreciated over its useful life.
Asset depreciation spreads the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life. Each depreciation period, an accounting journal entry is recorded to recognize the expense.
Computation based on Constant Periods
When Constant Periods is selected, Odoo calculates depreciation by dividing the asset’s depreciable value into equal amounts for each depreciation period. This defines a fixed depreciation amount per period.
When a Prorata Date is set, Odoo does not start depreciation from the beginning of the period. Instead, it starts from the specified date. As a result, the first depreciation amount is reduced and calculated only for the portion of the period remaining after the Prorata Date.
Fixed Asset Account records the original purchase cost of the asset and represents its gross value on the balance sheet. This account remains unchanged by depreciation.
Depreciation Account records the periodic depreciation expense of the asset, reflecting the consumption of its economic value over time and appearing in the profit and loss statement.
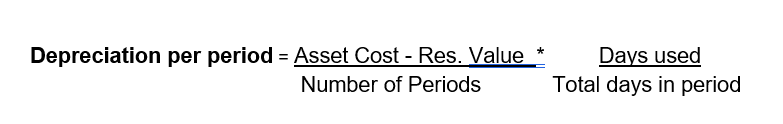
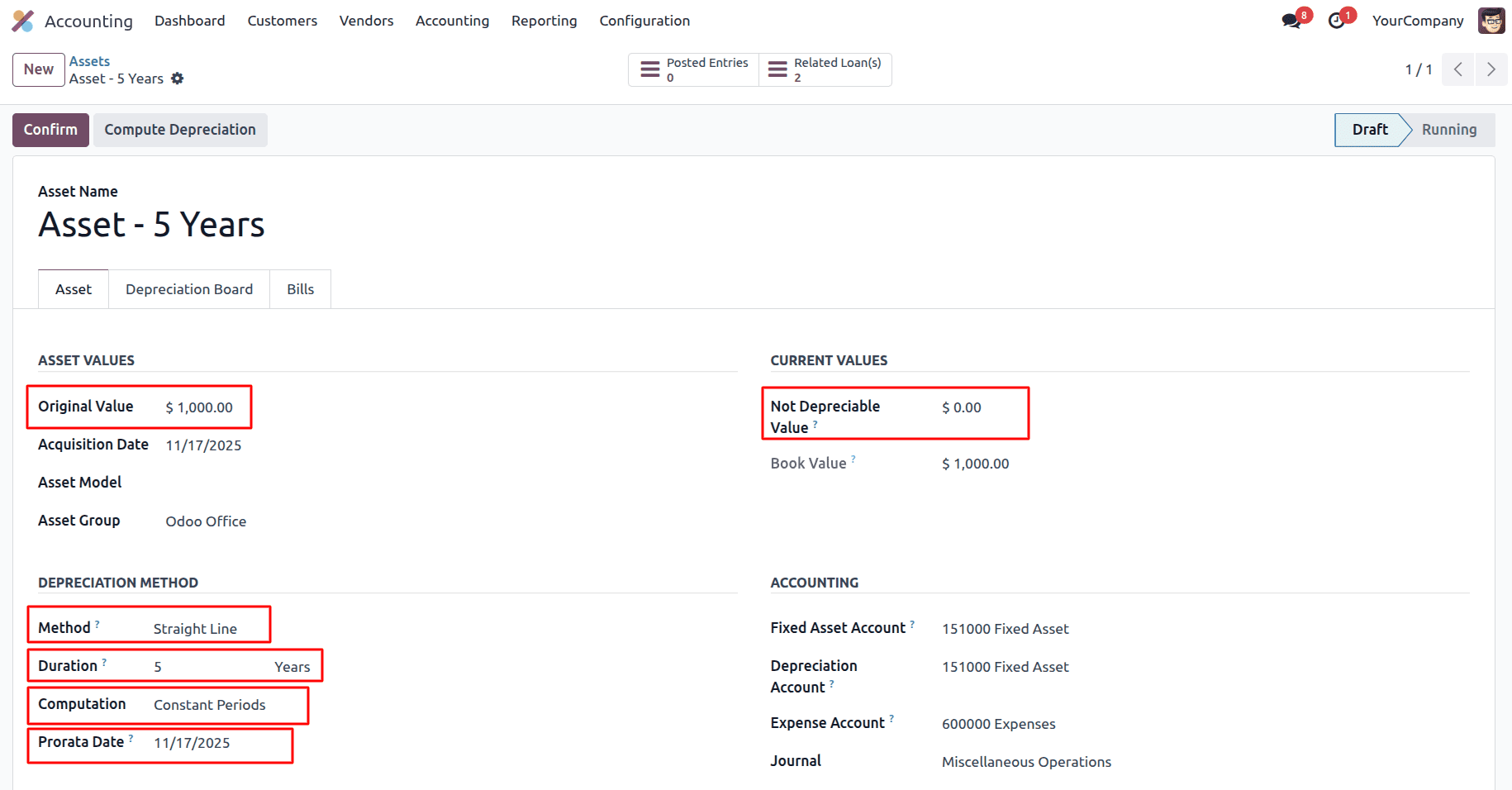
Days Used is the number of days the asset was used in the first year.
Total Days in Period is the total number of days in that year.

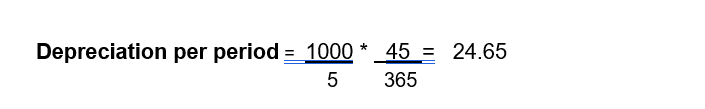
The first year will depreciate only ˜ 24.65 because the asset started late in the year (Nov 17), so you only depreciate the value for the remaining days of the year which is 45.
After that, each full year receives the normal annual depreciation of 200, because those years have a complete 12-month period. By the final year, the asset has already been depreciated for four full years plus a partial first year, so the remaining balance is less than 200; Odoo posted this leftover amount (about 175.56) in the last year to bring the asset’s book value to zero.
Computation based on days per period
When Computation Based on Days per Period is selected, Odoo calculates depreciation using a daily depreciation rate. Each depreciation period receives an amount proportional to the actual number of days in that period.
When a Prorata Date is set, it defines the exact date from which depreciation starts. Odoo excludes any days before this date in the first period.
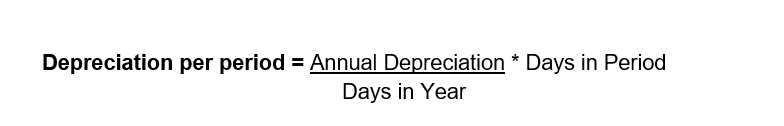
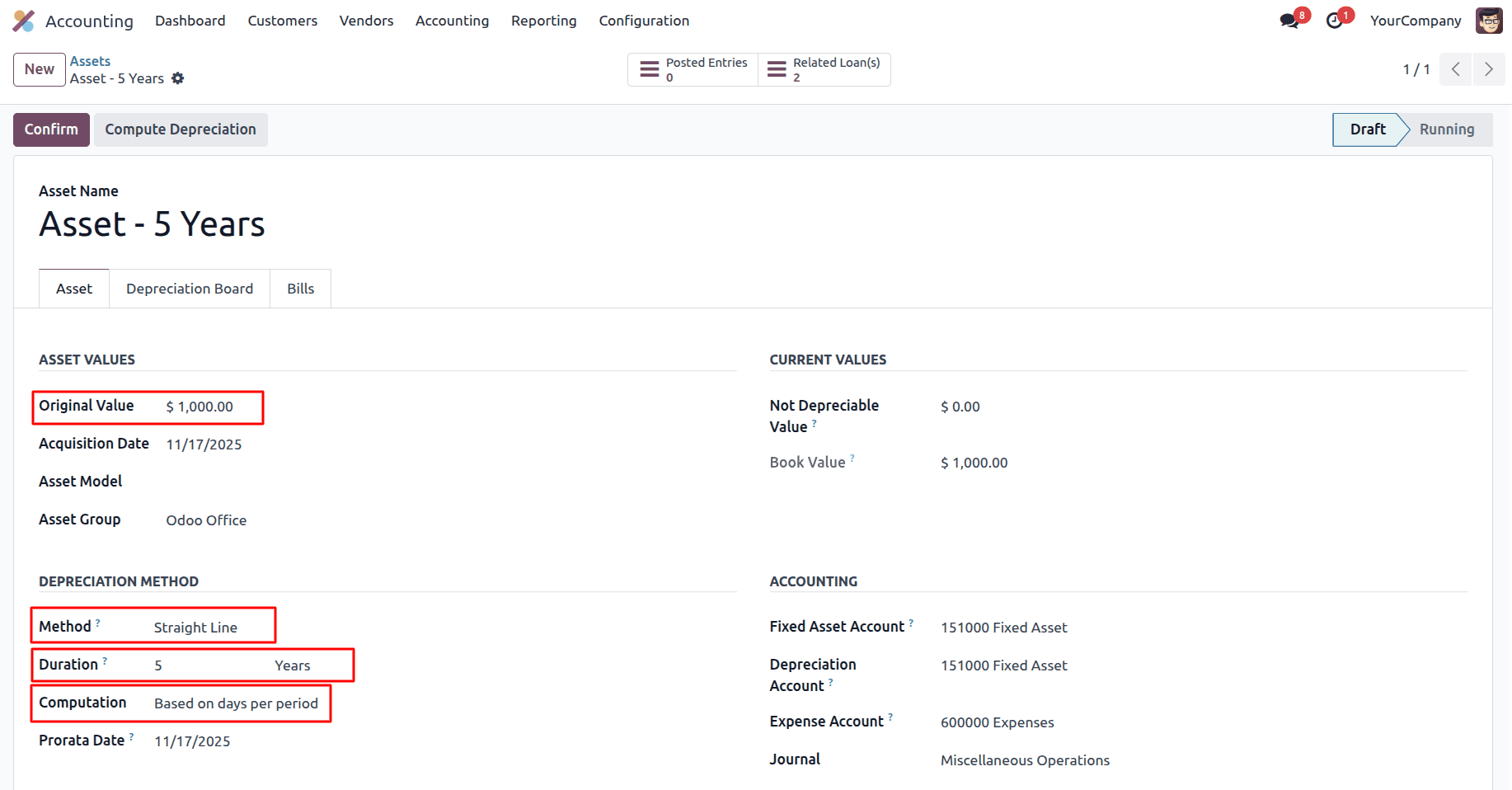
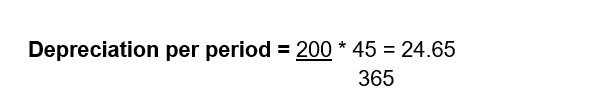
Depreciation using the days-per-period straight-line method means the asset loses value based on the exact number of days it is in use during each period. The annual depreciation is first calculated by dividing the depreciable amount by the useful life, and then this annual amount is converted into a daily rate by dividing it by the number of days in the year. Because your asset starts on November 17, it is used for only 45 days in the first year, so the depreciation for that year is the daily rate multiplied by those 45 days, resulting in a much smaller first-year depreciation. Each of the following years has a full 12-month period, so they receive the full annual depreciation amount. Finally, in the last year, instead of applying another full year of depreciation, only the remaining balance is depreciated so that the asset’s book value reaches exactly zero.
2. Declining Balance Method
A fixed percentage is applied to the remaining book value each period, leading to higher depreciation in the beginning and lower amounts later. Uses when Assets lose value quickly in the early years (e.g., electronics, vehicles).
In the Declining Balance Method, depreciation is calculated on the remaining (book) value of the asset at the beginning of each period — not on the original cost. This leads to higher depreciation expenses in the early years, and lower ones later on.
Computation based on No Prorata
Depreciation per period = Remaining Asset Value × Depreciation Rate
Depreciation rate is the percentage of an asset’s value that is depreciated (expensed) each period — typically annually.
Remaining Asset Value, also called book value or net book value, is the value of an asset after accounting for accumulated depreciation.
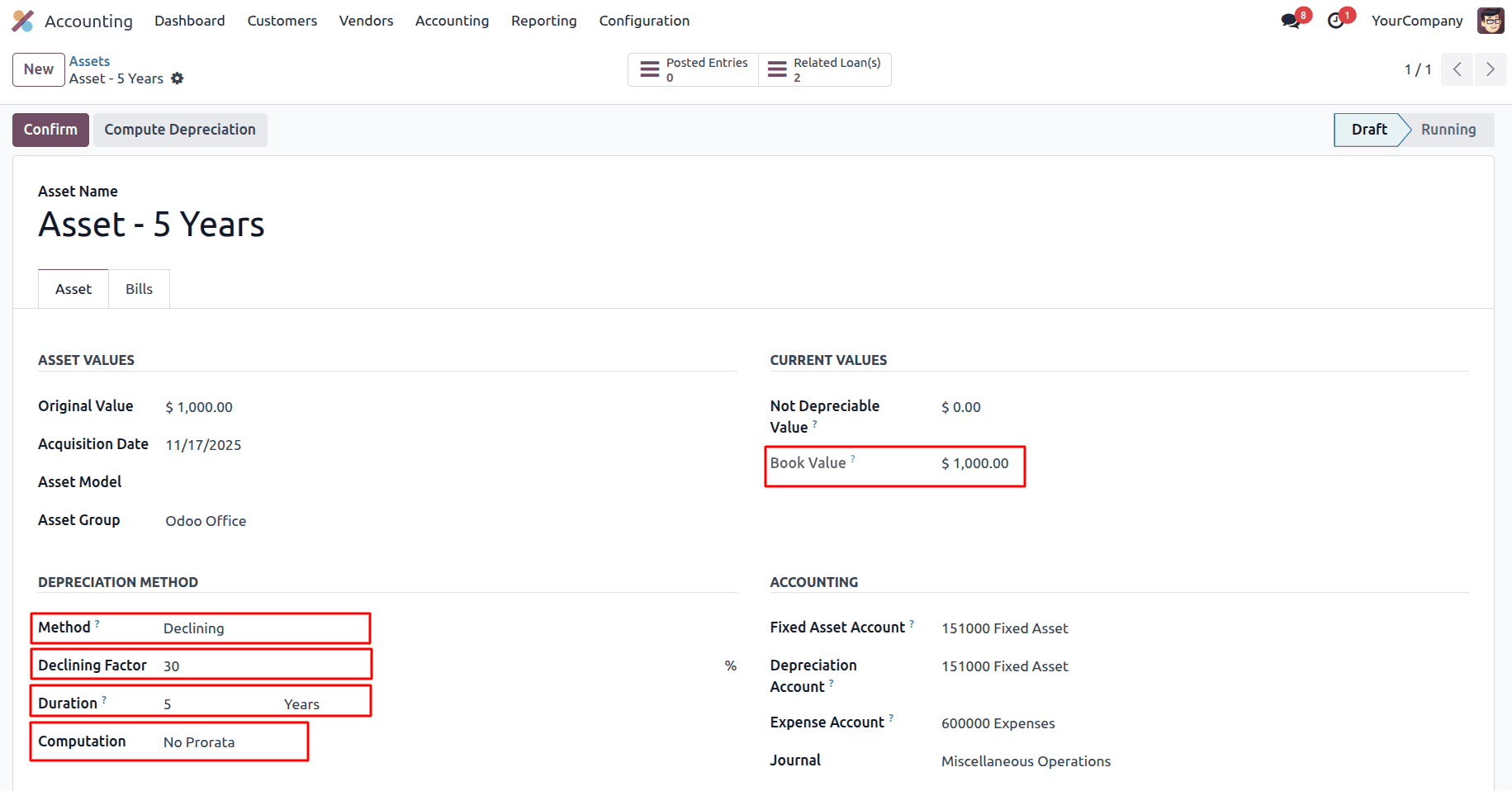
Depreciation per period = 1000 * (30/100) = 300
In the Declining balance method with a 30% declining factor, depreciation is calculated each year as a constant percentage of the asset’s remaining book value, not its original cost. Since prorata is not applied here, the first year receives the full depreciation percentage. With a cost of $1,000, the first year’s depreciation is 30%, or $300, leaving a book value of $700. The next year, depreciation is again 30%, but now applied to the new book value of $700, giving $210 and reducing the book value to $490.
Each following year repeats the same process: depreciation equals 30% × beginning book value for that year, so the amount decreases over time because the base value keeps shrinking. This creates a pattern where depreciation becomes smaller each year until the final period, where Odoo depreciates the remaining balance to bring the asset’s value down to zero. This declining method reflects how many assets lose more value in early years and less as they age.
Computation based on Constant Periods
In the Declining Balance method with Constant Periods, depreciation is calculated in each period by applying a fixed depreciation rate to the asset’s remaining book value. When a Prorata Date is set, depreciation does not start from the beginning of the first period, but from the specified date, resulting in a prorated first depreciation amount.

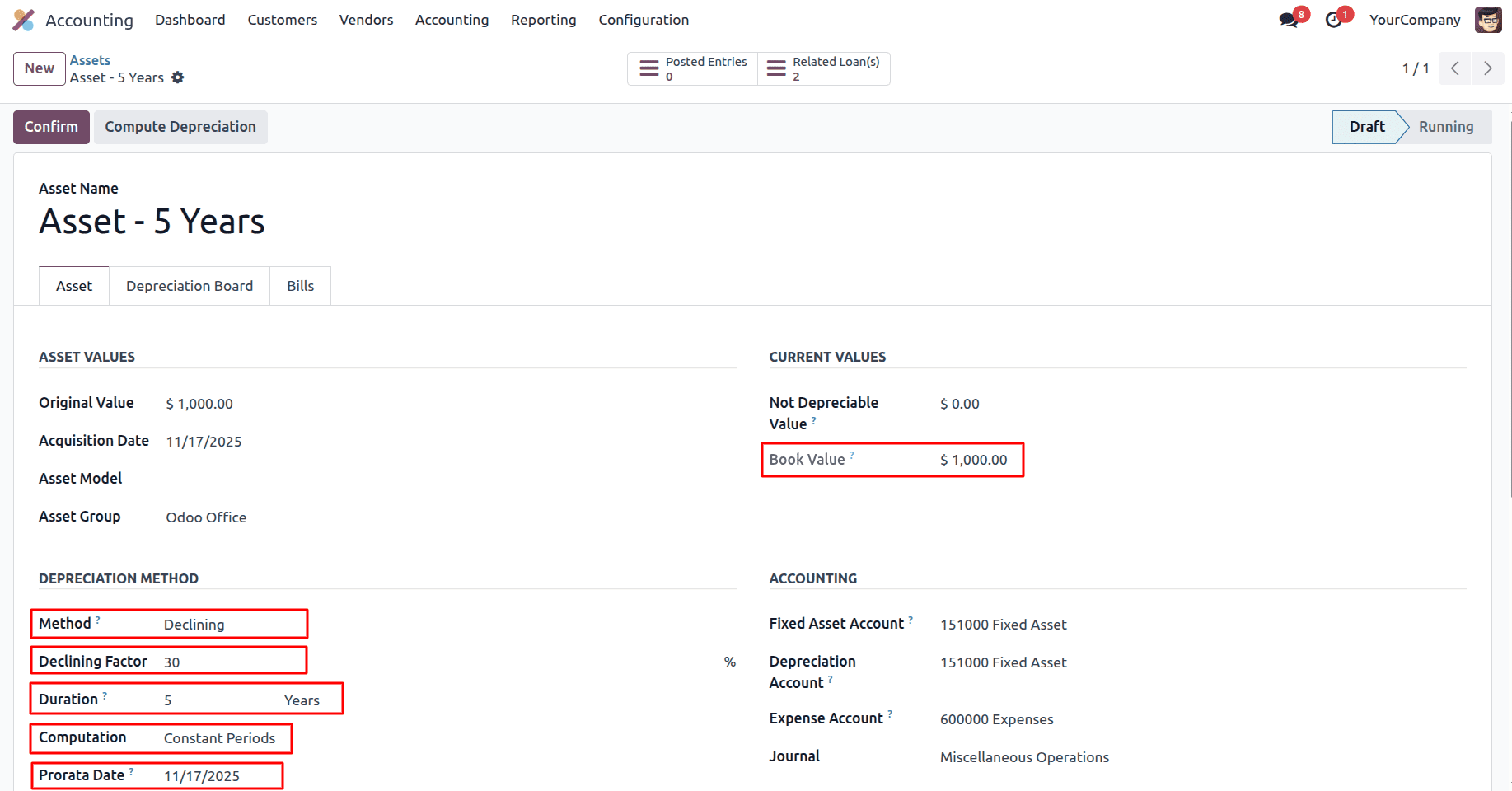
Depreciation per period = 1000 * (30/100) = 300 * (45/365) = 36.98
When using the Declining method with Constant Periods, Odoo creates the same number of depreciation years, but the amount reduces every year. The percentage (30%) is always applied to the remaining book value, not the original cost. Because the asset started on November 17, the first year is only for 45 days, so Odoo calculates the first depreciation as a small prorated amount. After that, every full year uses 30% of whatever value is left. So the second year is 30% of the lower amount, the next year is 30% of the new lower amount, and so on. Each year the depreciation gets smaller because the value keeps going down, until it reaches zero in the last period.
Computation based on days per period

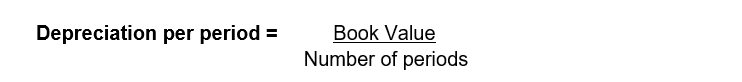
Depreciation per period = (300/365) * 45 = 36.98
In the declining method with computation based on days per period, depreciation is calculated on the remaining book value each period, not on the original cost. Since the method is based on days, the system first checks how many days belong to each depreciation period. Because the asset starts on November 17, the first period includes only the days from that date to the year-end, so the depreciation for that period is reduced accordingly. After the first period, each new period uses the updated (reduced) book value, and full-year periods receive the full declining-balance depreciation. This makes the depreciation amounts decrease every year while the first year is prorated based on the exact number of days used.
3. Declining Balance then Straight Line Method
Starts with declining balance, then automatically switches to straight-line when that approach results in higher depreciation. This hybrid method ensures full depreciation is achieved.
Uses when you want the efficiency of declining balance but also ensure full depreciation
- Start with Declining Balance
Use a fixed rate (e.g., 30%) to depreciate the remaining book value each year.
- Switch to Straight-Line
At a certain point, Odoo automatically switches to straight-line depreciation when:
- The straight-line amount per year is greater than the declining balance amount.
- This switch ensures full depreciation is achieved over the remaining life.
- Continue with Straight-Line
After the switch, depreciation is applied evenly over the remaining periods.
Computation based on No Prorata
At first, depreciation is calculated using a fixed declining rate (example: 30%) applied to the remaining book value.
Depreciation per period = Remaining Book Value * Deprecation Rate
Odoo automatically switches to straight-line when the straight-line amount becomes greater than the declining amount.
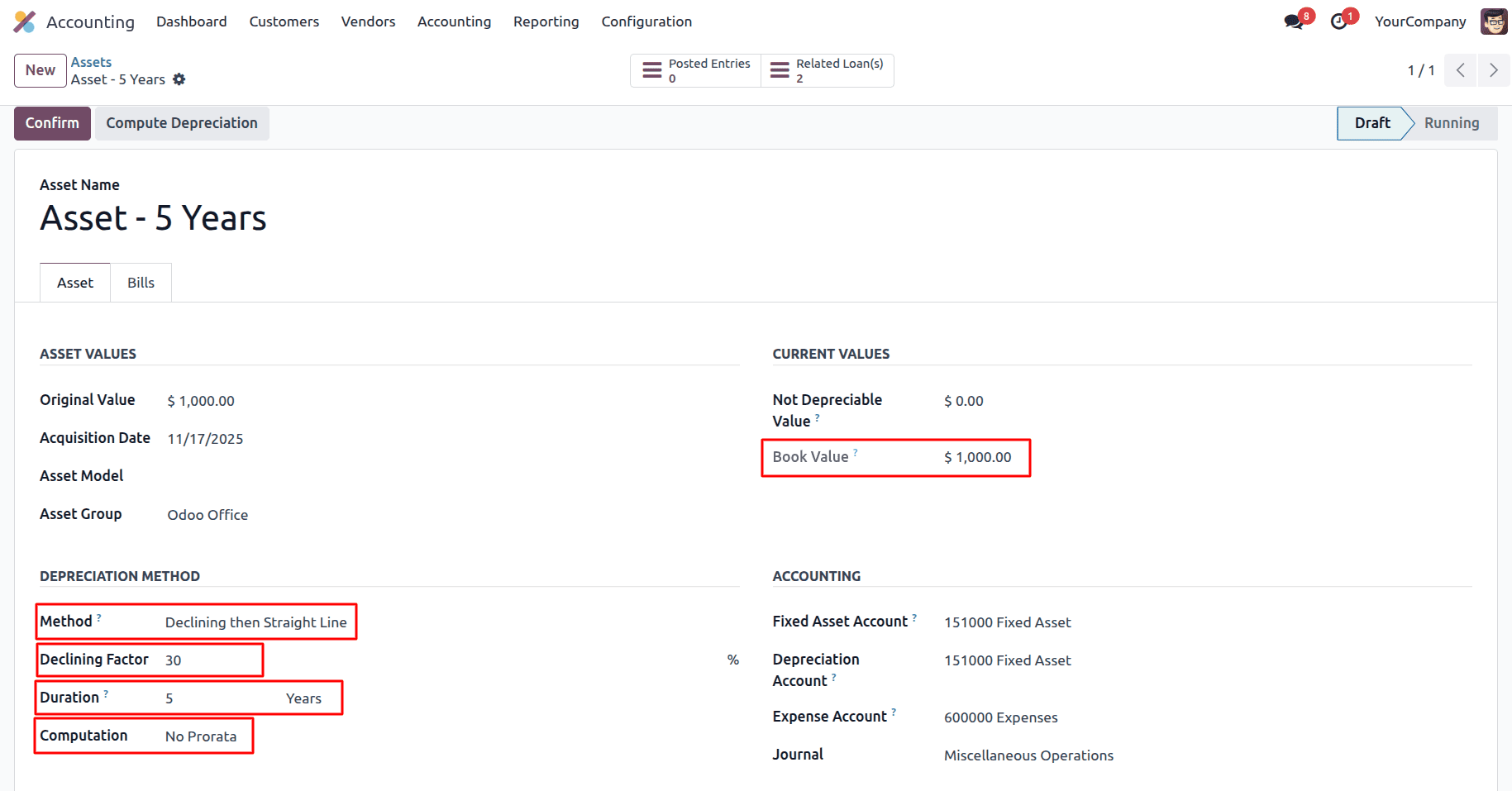
Year 1
Depreciation per period = 1000 * (30/100) = 300
Year 2
Depreciation per period = 700 * (30/100) = 210
Year 3
Depreciation per period = 490 * (30/100) = 147
The straight-line amount for the remaining life is now larger than the declining-balance amount, so it switches to straight-line. The straight-line figure it calculates is only used to decide that a switch should happen, not to determine the exact depreciation values.
Year 3
Depreciation per period = 1000/5 = 200
The depreciation expense becomes equal to the original asset cost divided by the total number of years, resulting in a consistent depreciation charge for each remaining year. This approach balances the need to reflect higher early expenses with the simplicity of straight-line depreciation for the later years.

Computation based on Constant Periods
In Declining then Straight Line with Computation based on Constant Periods and Prorata Date enabled, depreciation is calculated once per fixed period (monthly or yearly), starting with the declining balance method by applying the defined declining factor to the asset’s remaining book value. At each period, Odoo compares this declining depreciation with the straight-line depreciation calculated over the remaining duration and automatically switches to straight-line when it produces a higher amount. Since a Prorata Date is set, depreciation begins from that specific date rather than the start of the period, so the first depreciation amount is prorated according to the remaining time in that period, while all subsequent periods use the full depreciation amount determined by the active method.
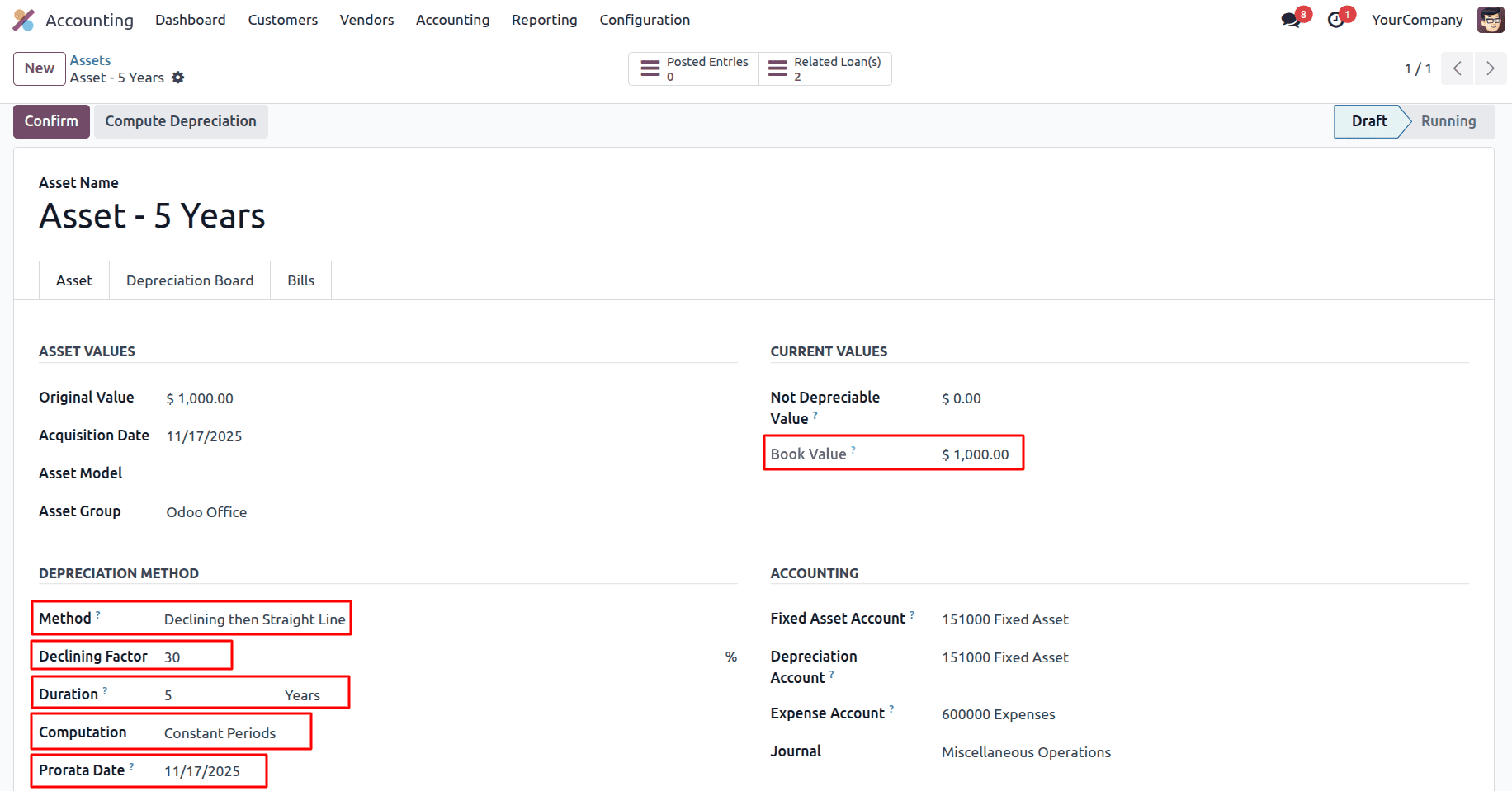
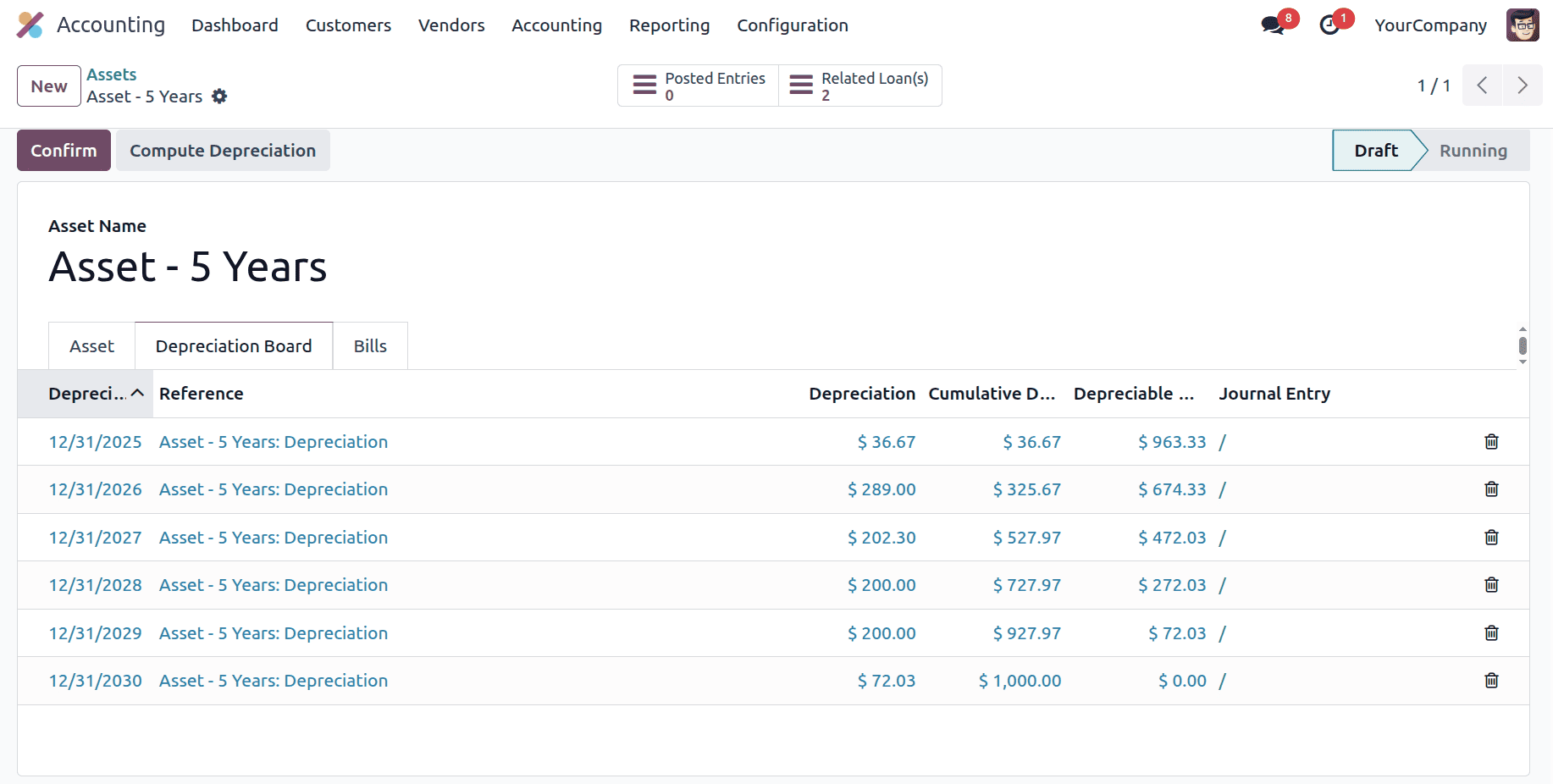
Year 1
Depreciation per period = (300/365) *45 = 36.986
Year 2
Depreciation per period = 963 * (30/100) = 289
Year 3
Depreciation per period = 674 * (30/100) = 202.2
Year 4
Depreciation per period = 472 * (30/100) = 141.6
Now the straight-line amount for the remaining life is larger than the declining-balance amount, so it switches to straight-line.
So,
Year 4
Depreciation per period = 1000/5 = 200
After the switch, each remaining year is depreciated evenly according to the straight-line formula, ensuring that the total depreciation equals the original asset cost and the asset is fully depreciated by the end of its useful life.

Computation based on days per period
In Declining then Straight Line with Computation based on Days per Period and Prorata Date enabled, depreciation is calculated using a daily rate rather than a fixed amount per period. Depreciation starts from the Prorata Date, so only the actual number of days from that date to the end of each period is considered. Initially, depreciation follows the declining balance method, applying the declining factor to the asset’s remaining book value and converting it into a daily amount, and at each period Odoo compares this with the straight-line depreciation calculated over the remaining useful life. When the straight-line method results in a higher daily depreciation, Odoo switches to straight-line for the remaining periods, while ensuring the total depreciation fully reduces the asset value within its defined duration.
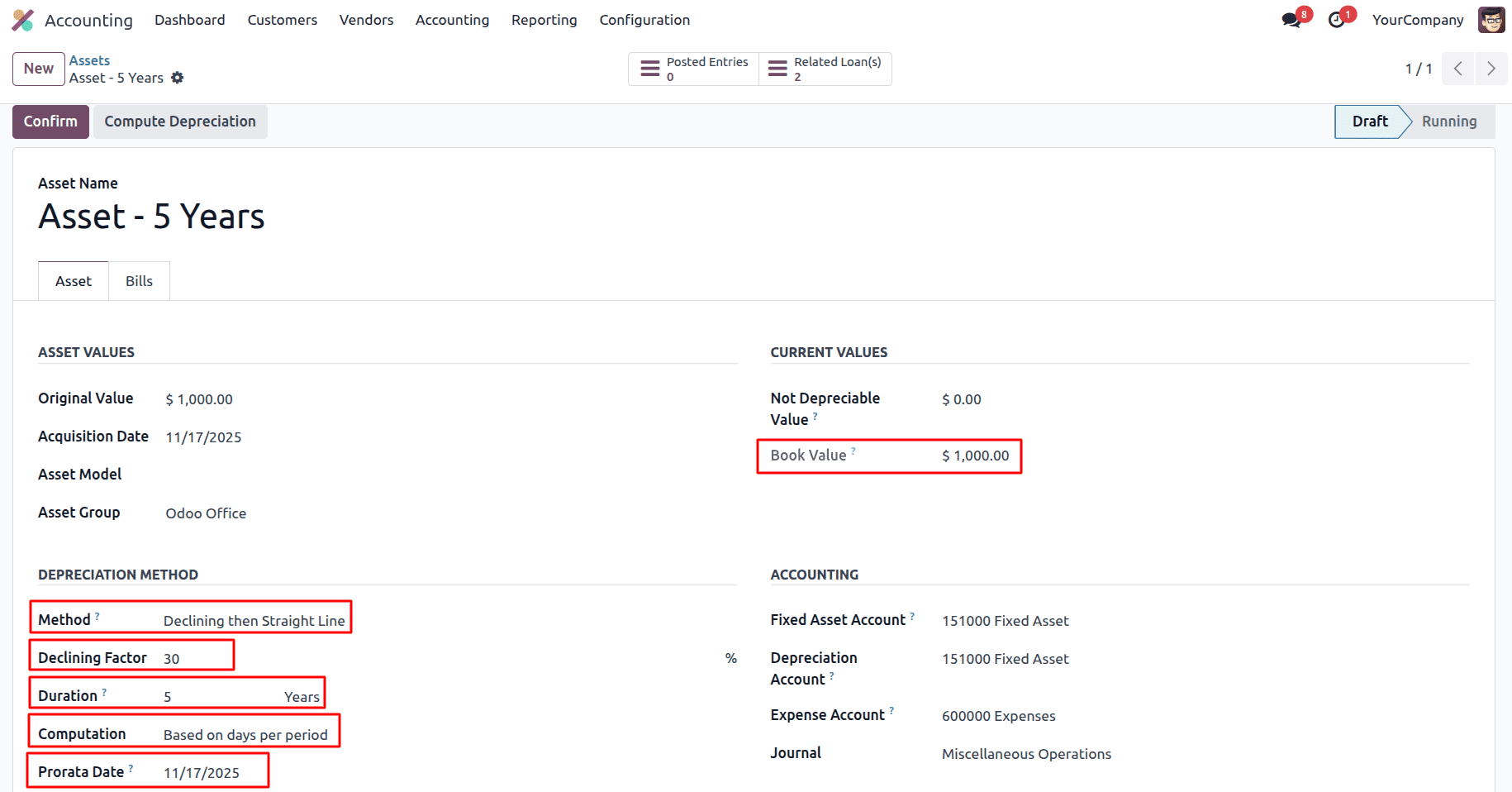
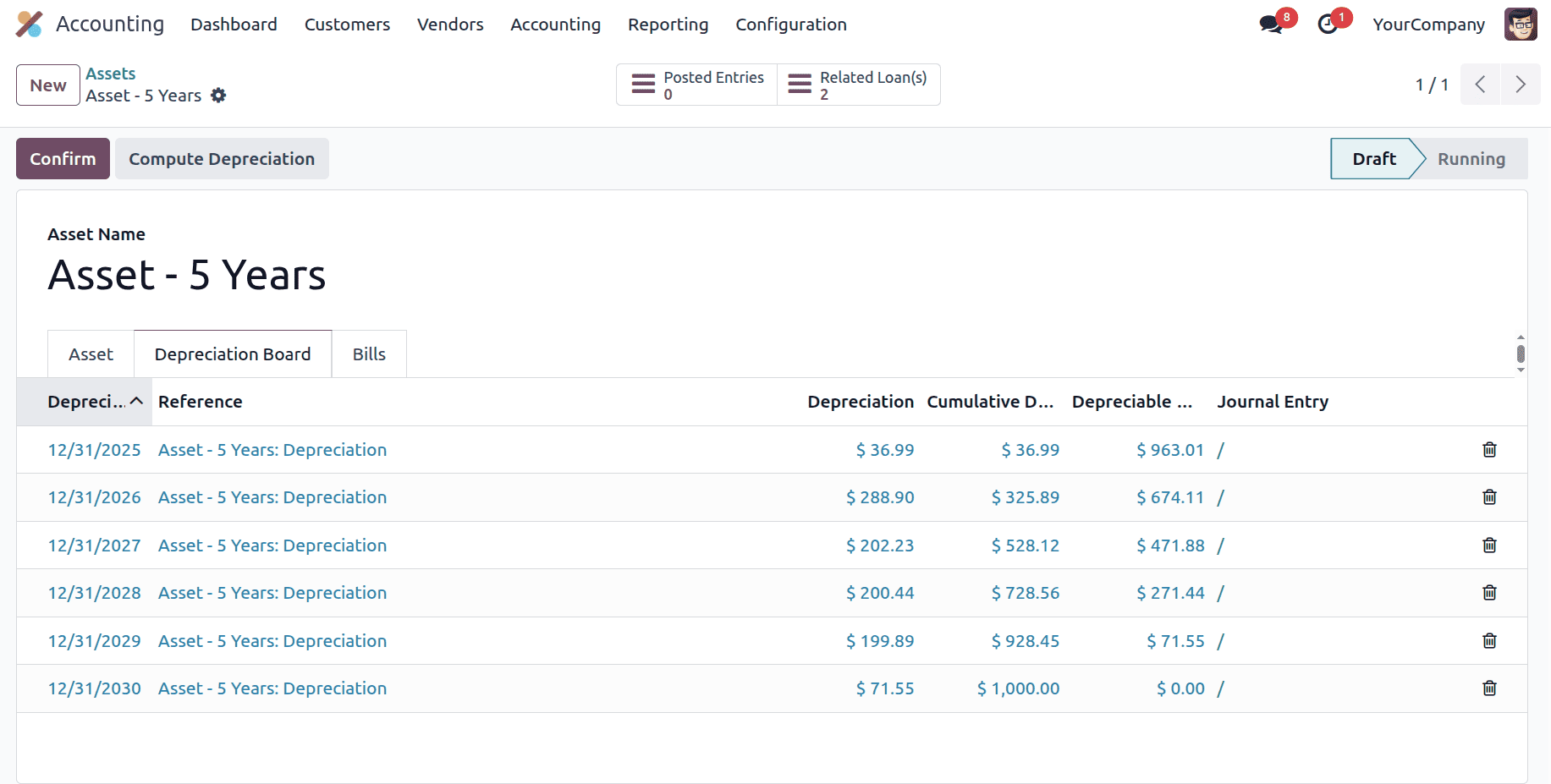
Year
Depreciation per period = (300/365) * 45 = 36.986
Year 2
Depreciation per period = 963 * (30/100) = 289
Year 3
Depreciation per period = 674 * (30/100) = 202.2
Year 4
Depreciation per period = 472 * (30/100) = 141.6
Now the straight-line amount becomes larger than the declining-balance amount, so it will switch to the straight-line method.
Year 4,
Since the 4th depreciation period falls in the year 2028, and 2028 is a leap year, Odoo considers that year to have 366 days when computing depreciation. Because your depreciation method is set to use prorata based on days per period, Odoo allocates the remaining asset value proportionally according to the number of calendar days in each year. Therefore, the year 2028 receives a slightly higher share of the remaining depreciation amount.
Asset depreciation is a critical aspect of accurate financial reporting and effective asset management. Odoo 18 provides flexible options to calculate depreciation based on different business needs: the Straight-Line method for evenly spreading costs, the Declining Balance method for higher early-year expenses, and the Declining Balance then Straight-Line method for a balanced approach that combines both strategies. By selecting the appropriate method, businesses can better match expenses with revenue, maintain accurate asset values on the balance sheet, and make informed decisions about investments, budgeting, and long-term planning. Proper use of Odoo’s depreciation tools ensures transparency, compliance, and optimized financial performance.
To read more about How to Manage Company Assets & Depreciation in Odoo 17 Accounting, refer to our blog How to Manage Company Assets & Depreciation in Odoo 17 Accounting.