Error management in Odoo 19 is essential for maintaining system stability and ensuring smooth business operations. With the platform’s increased modularity and advanced automation features, handling exceptions efficiently has become even more critical. Proper implementation of error logging, structured debugging, and user-friendly notifications helps developers quickly identify, trace, and resolve issues without disrupting workflow continuity. By leveraging Odoo’s built-in logging framework and adopting best practices in exception handling, organizations can significantly enhance application reliability and overall user experience.
In Odoo 19, various exceptions handle specific runtime scenarios. ValidationError ensures data consistency by enforcing business rules, while UserError alerts users about invalid actions. AccessError and AccessDenied control security by blocking unauthorized operations or logins. MissingError occurs when a requested record is deleted or unavailable, and RedirectWarning guides users toward necessary actions before proceeding. Lastly, CacheMiss is an internal exception raised when a record’s field value is missing from cache, typically handled automatically by Odoo’s framework. Let’s go through the errors one by one.
1. Validation Error
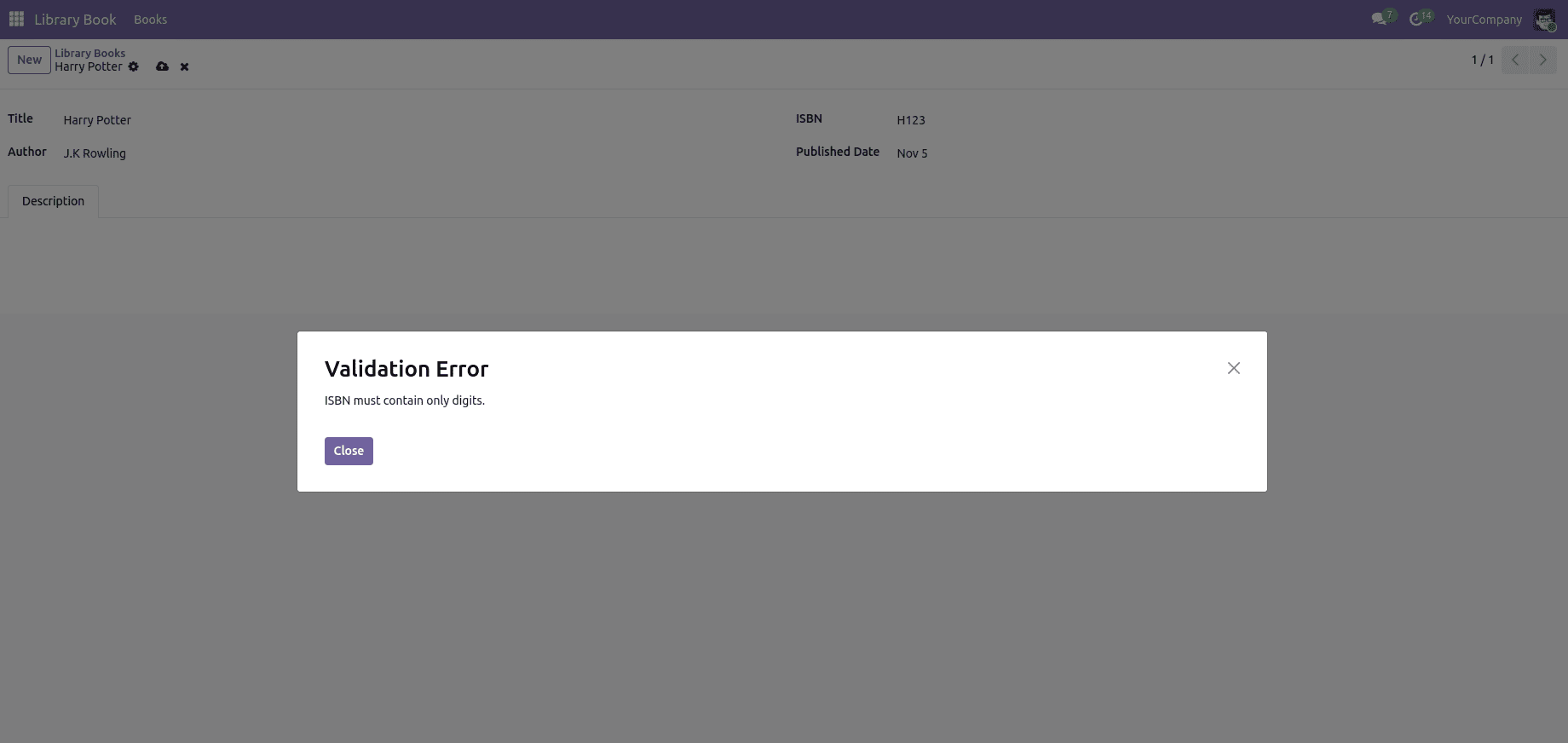
A ValidationError in Odoo 19 is raised when data fails to meet defined business or logical constraints. It ensures that records maintain consistency and accuracy before being saved. For instance, if a required field is left empty or an invalid value is entered, Odoo triggers this error to prevent the transaction, prompting the user to correct the data before proceeding.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from odoo import api, fields, models
from odoo.exceptions import ValidationError
class LibraryBook(models.Model):
_name = 'library.book'
_description = 'Library Book'
name = fields.Char(string='Title', required=True)
author = fields.Char(string='Author')
isbn = fields.Char(string='ISBN')
description = fields.Text(string='Description')
published_date = fields.Date(string='Published Date')
active = fields.Boolean(string='Active', default=True)
@api.constrains('isbn')
def _check_isbn_format(self):
"""ValidationError: Raised when ISBN is not a valid ISBN."""
for record in self:
if record.isbn and not record.isbn.isdigit():
raise ValidationError("ISBN must contain only digits")
2. User Error
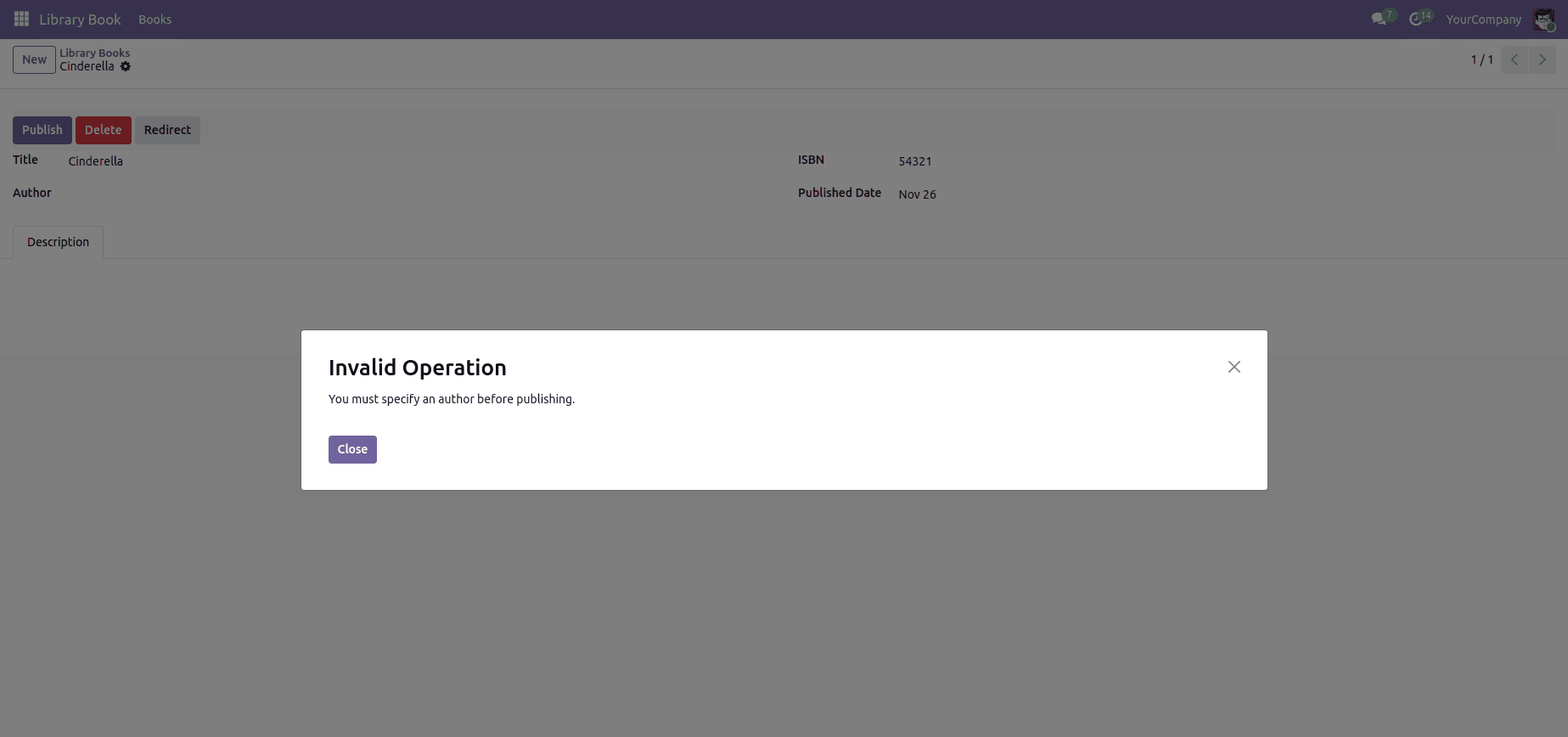
In Odoo 19, a UserError is raised when a user performs an invalid or restricted action that violates business logic or workflow rules. It’s primarily used to communicate clear, user-friendly error messages that guide the user to correct the issue. For example, if a required field is missing or an operation is not permitted under certain conditions, Odoo interrupts the process and displays the message defined in the UserError, ensuring proper validation without causing system-level crashes.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from odoo import fields, models
from odoo.exceptions import UserError
class LibraryBook(models.Model):
_name = 'library.book'
_description = 'Library Book'
name = fields.Char(string='Title', required=True)
author = fields.Char(string='Author')
isbn = fields.Char(string='ISBN')
description = fields.Text(string='Description')
published_date = fields.Date(string='Published Date')
active = fields.Boolean(string='Active', default=True)
def action_publish(self):
"""UserError: Prevent publishing without author"""
for record in self:
if not record.author:
raise UserError("You must specify an author before publishing")
3. Access Error
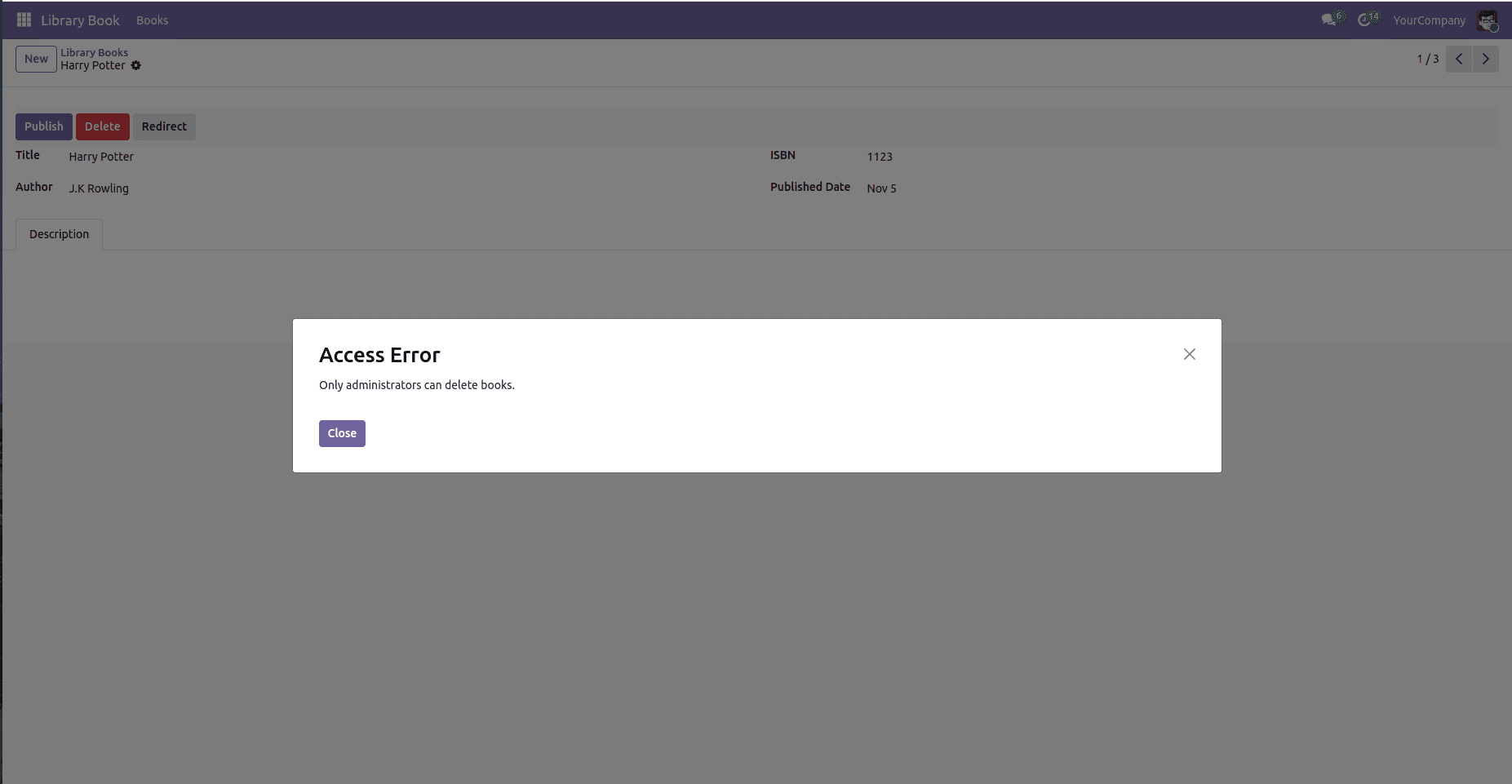
In Odoo, an AccessError occurs when a user attempts to perform an operation for which they lack the necessary access rights or permissions. This typically happens when reading, writing, creating, or deleting a record that’s restricted by Odoo’s security rules, such as record rules or access control lists (ACLs). The AccessError ensures that sensitive data and restricted operations are protected from unauthorized users. For example, if a regular user tries to delete a record that only administrators can remove, Odoo raises an AccessError to prevent the action and maintain data security.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from odoo import fields, models
from odoo.exceptions import AccessError
class LibraryBook(models.Model):
_name = 'library.book'
_description = 'Library Book'
name = fields.Char(string='Title', required=True)
author = fields.Char(string='Author')
isbn = fields.Char(string='ISBN')
description = fields.Text(string='Description')
published_date = fields.Date(string='Published Date')
active = fields.Boolean(string='Active', default=True)
def action_delete_book(self):
"""AccessError: Restrict deletion to admins."""
if not self.env.user.has_group('base.group_system'):
raise AccessError("Only admins can delete books")
self.unlink()
4. Missing Error
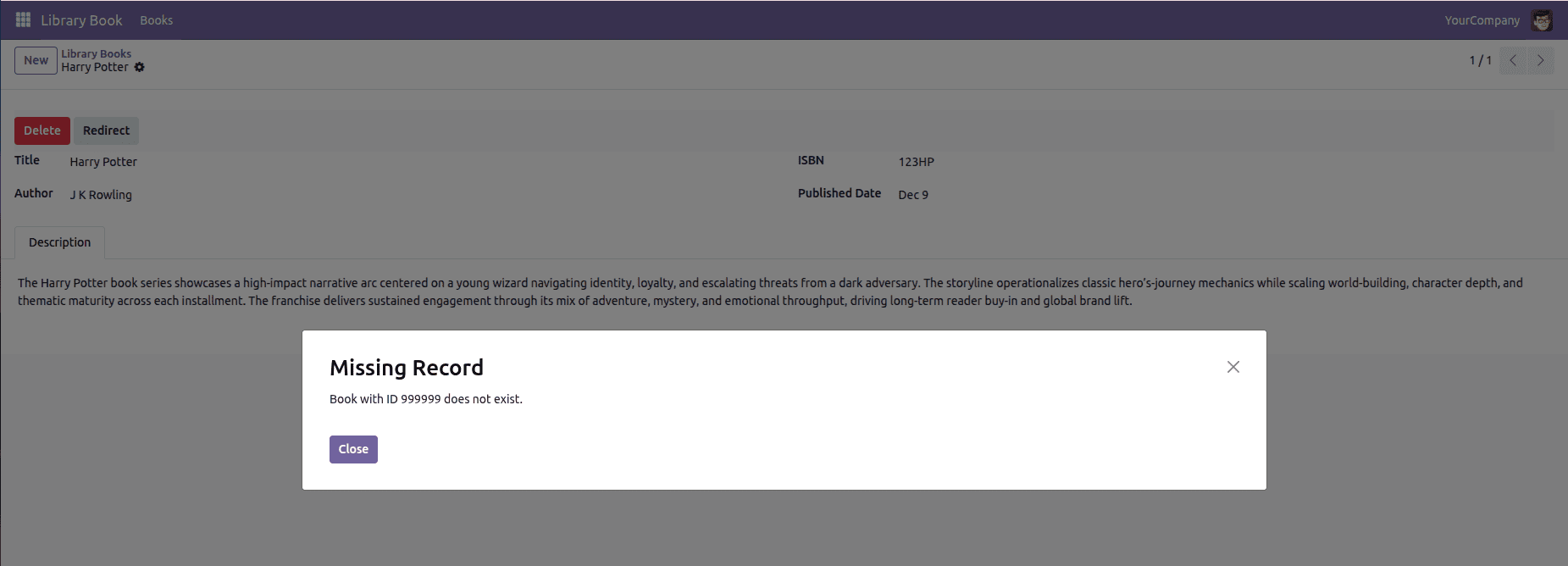
In Odoo 19, a missing error can show up when the system tries to access an ID that doesn’t exist. Instead of stopping and warning the user, it sometimes continues without showing any message. This makes the issue easy to miss, so proper checks need to be added to ensure the system warns the user when an invalid or missing ID is used.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from odoo import fields, models
from odoo.exceptions import MissingError
class LibraryBook(models.Model):
_name = 'library.book'
_description = 'Library Book'
name = fields.Char(string='Title', required=True)
author = fields.Char(string='Author')
isbn = fields.Char(string='ISBN')
description = fields.Text(string='Description')
published_date = fields.Date(string='Published Date')
active = fields.Boolean(string='Active', default=True)
def action_delete_book(self):
if not self.browse(999999).exists():
raise MissingError("Book with id 999999 does not exist.")
self.browse(999999).unlink()
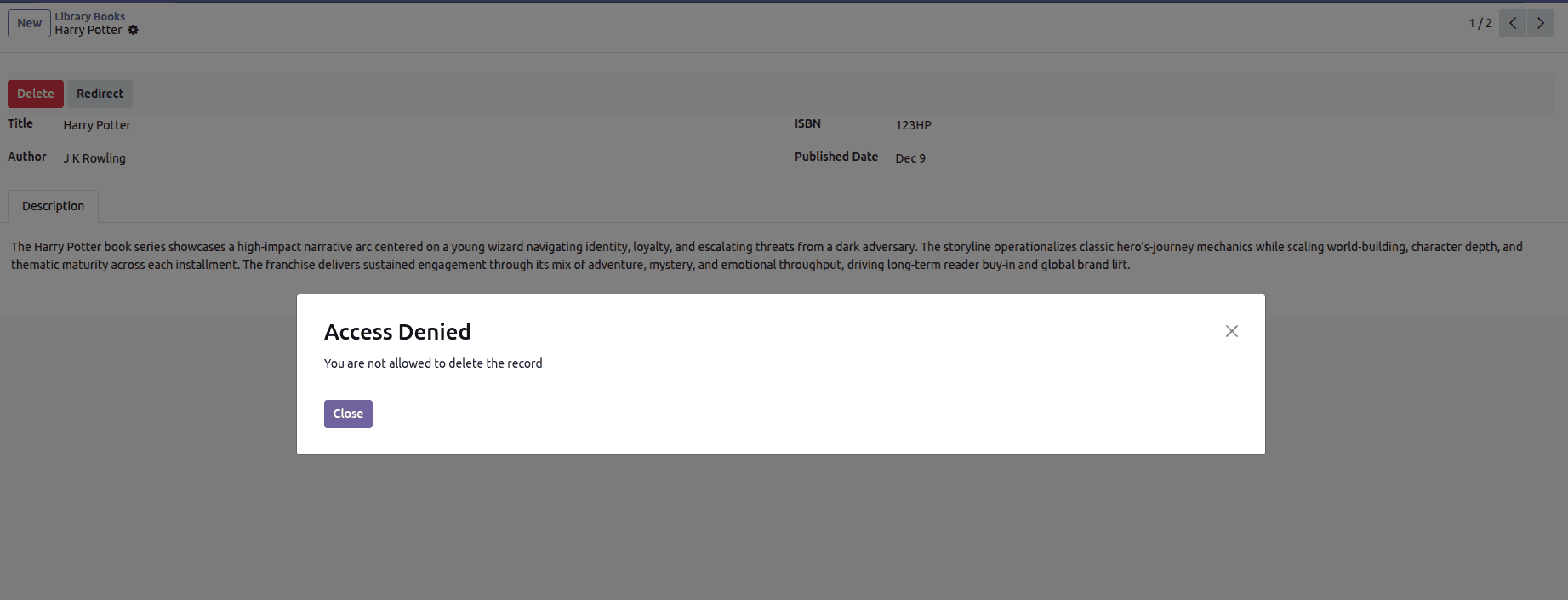
5. Access Denied
In Odoo 19, an access denied issue can occur when a user tries to open or modify something they don’t have permission for. Instead of letting the action go through, the system blocks it and shows an access denied message. This usually happens when the record, model, or menu requires higher rights than the user has. Adding the right permissions or adjusting the access rules helps prevent this from happening.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from odoo import fields, models
from odoo.exceptions import AccessDenied
class LibraryBook(models.Model):
_name = 'library.book'
_description = 'Library Book'
name = fields.Char(string='Title', required=True)
author = fields.Char(string='Author')
isbn = fields.Char(string='ISBN')
description = fields.Text(string='Description')
published_date = fields.Date(string='Published Date')
active = fields.Boolean(string='Active', default=True)
def action_delete_book(self):
""" Button function to delete the books """
if not self.env.is_admin():
raise AccessDenied("You are not allowed to delete books.")
return {'type': 'ir.actions.act_window_close'}
6. CacheMiss
A CacheMiss in Odoo 19 occurs when the ORM attempts to read a field value that isn’t available in the current prefetch cache. This can happen when the cache was invalidated, when only a subset of fields was prefetched, or when another operation cleared the cached data for that record. When the value isn’t found, Odoo raises a CacheMiss internally to trigger a safe, automatic fetch from the database. It’s not an error that the user sees — it’s a normal internal mechanism that ensures the ORM always returns up-to-date and consistent data.
country = env['res.country'].browse(1)
# First access ? cache hit (no SQL query)
print(country.name)
# Invalidate the cached field
country.invalidate_recordset(['name'])
# Second access ? cache miss (ORM refetches from DB)
print(country.name)
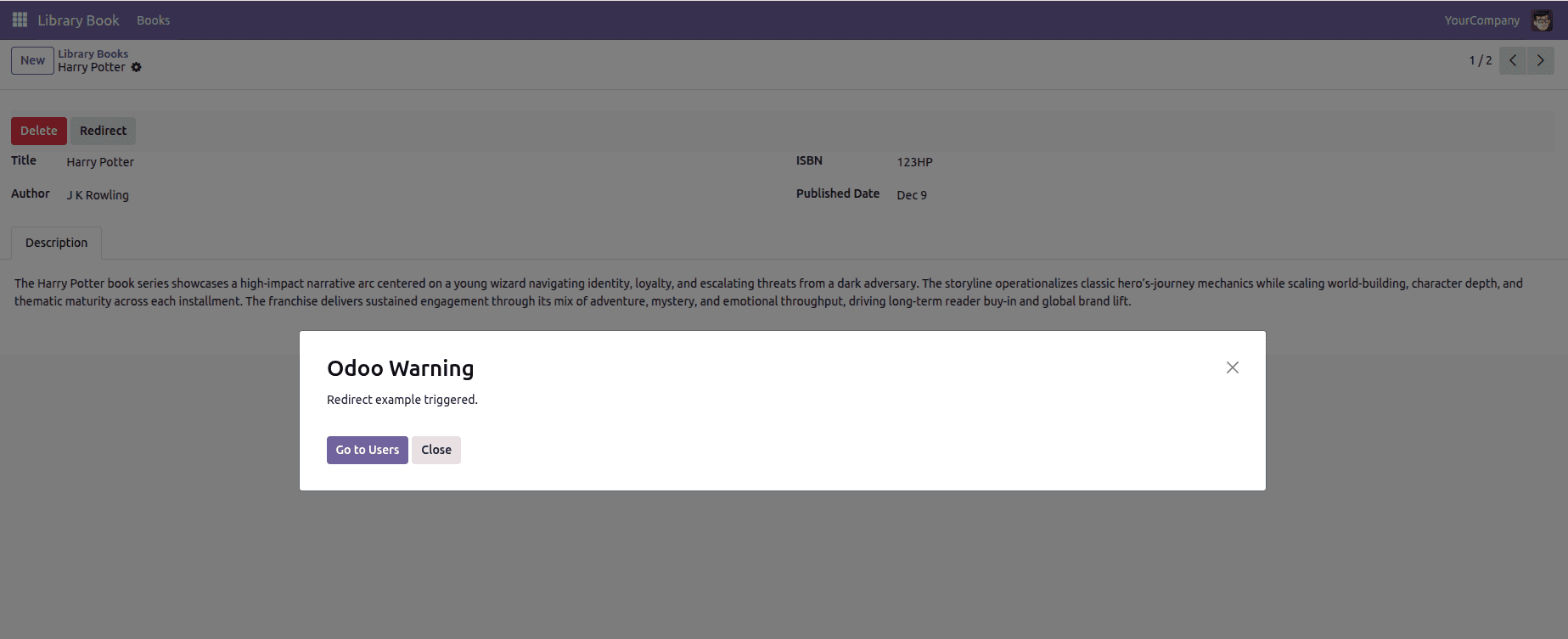
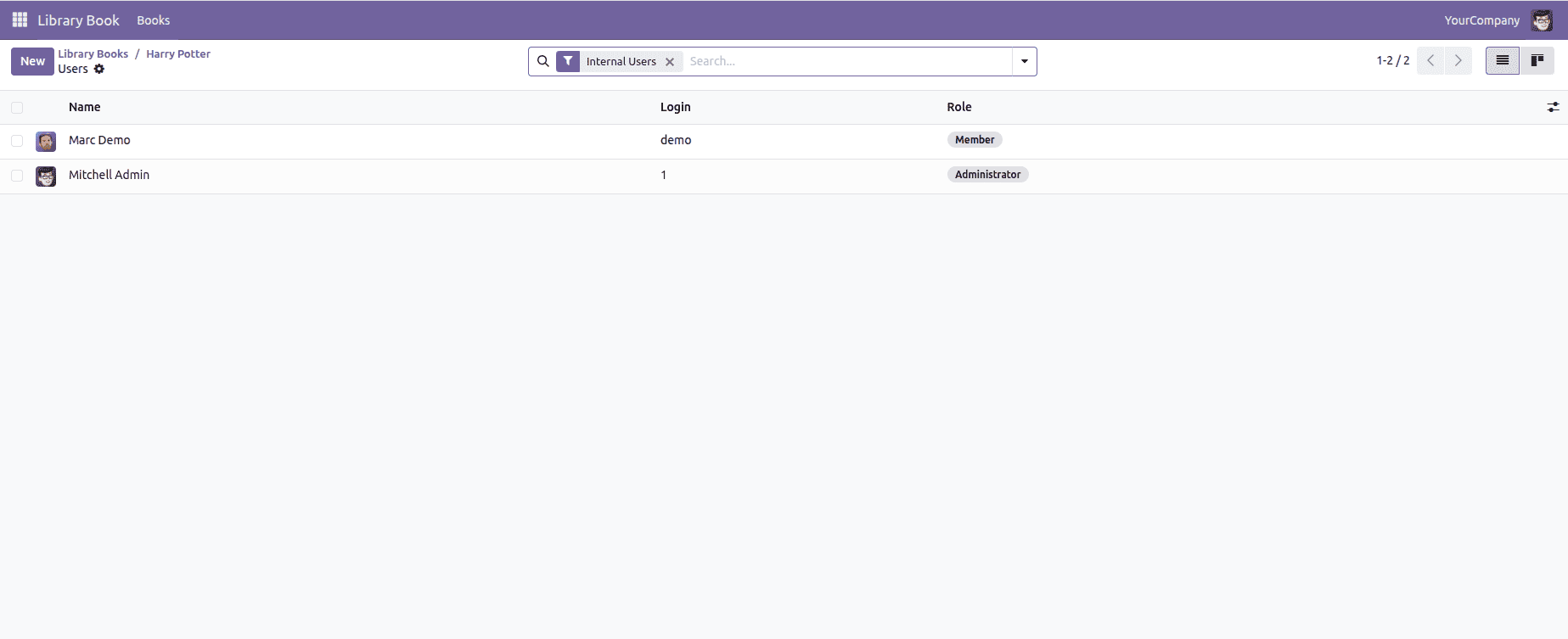
7. Redirect Warning
A redirect warning in Odoo 19 is triggered when the system intentionally reroutes the user to a specific action instead of completing the current operation. In the example below, the redirect is fired directly from the library.book model through a demo method that raises a RedirectWarning and pushes the user toward the Users menu. This pattern is typically used when the workflow requires the user to review or update related records before proceeding, and the platform proactively navigates them to the appropriate screen to close the gap.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from odoo import fields, models
from odoo.exceptions import RedirectWarning
class LibraryBook(models.Model):
_name = 'library.book'
_description = 'Library Book'
name = fields.Char(string='Title', required=True)
author = fields.Char(string='Author')
isbn = fields.Char(string='ISBN')
description = fields.Text(string='Description')
published_date = fields.Date(string='Published Date')
active = fields.Boolean(string='Active', default=True)
def redirect_to_author(self):
"""RedirectWarning: Suggest user go to related author record."""
raise RedirectWarning(
"Redirect example triggered.",
self.env.ref("base.action_res_users").id,
"Go to Users"
)
Odoo 19’s error-management framework drives disciplined workflow control by surfacing precise, context-aware exceptions such as access denials, redirect warnings, missing-record errors, and cache-miss recoveries. Each mechanism ensures the system maintains data integrity, guides users toward corrective actions, and prevents inconsistent states from propagating through business flows. The result is a tighter, more predictable execution layer that safeguards both user operations and backend reliability.
To read more about Error management in Odoo 18, refer to our blog, Error management in Odoo 18.