Building robust APIs is essential for seamless integration between business applications. Odoo 19, a leading open-source ERP platform, provides powerful capabilities for creating REST controllers that enable external systems to interact with your Odoo instance. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of building and implementing REST controllers in Odoo 19, from basic setup to handling different authentication scenarios.
Introduction
REST controllers in Odoo 19 allow you to expose your business logic through HTTP endpoints, making it possible for third-party applications to access and manipulate data within your Odoo system. Whether you need to integrate with mobile applications, external services, or custom dashboards, REST controllers provide a flexible and scalable solution. By following this guide, you'll learn how to create effective REST controllers, manage authentication, and build reliable API endpoints.
Step 1: Import Required Modules
To begin building REST controllers in Odoo 19, you'll need to import essential Python modules. Start with the core dependencies for handling HTTP requests and JSON data:
from odoo import http
from odoo.http import request
import json
The http module provides the controller framework, request allows you to access incoming request data, and json enables you to work with JSON payloads. These modules are fundamental for creating REST endpoints in Odoo 19.
Step 2: Define the Controller Class
Create a Python class that inherits from http.Controller. This class will serve as the foundation for your REST endpoints and contain all the route handlers for your API.
class MyRestController(http.Controller):
"""
REST Controller for handling API requests in Odoo 19.
This controller manages various API endpoints for data manipulation.
"""
pass
The controller class acts as a container for all your API routes and methods. You can define multiple routes within a single controller class, organizing your API endpoints logically.
Step 3: Create API Routes with Decorators
In Odoo 19, routes are defined using the @http.route() decorator. This decorator specifies the URL endpoint, request type, and authentication method. Here's how to structure a basic route:
@http.route('/api/v1/endpoint', type='jsonrpc', auth='public')
def my_api_endpoint(self, **kwargs):
"""
API endpoint for handling requests.
"""
return {'status': 'success', 'message': 'API endpoint reached'}The type='jsonrpc' parameter indicates that the request and response will be in JSON format. The auth parameter determines whether authentication is required. These parameters are crucial for defining how your endpoint behaves.
Step 4: Handle Request Parameters
To work with incoming request data in your API endpoints, access the request object provided by Odoo. Request parameters can be retrieved from the kwargs or directly from the request object:
@http.route('/api/v1/data', type='jsonrpc', auth='user', methods=['POST'])
def process_data(self, **kwargs):
"""
Process incoming request data.
"""
data = request.get_json_data()
name = data.get('name')
email = data.get('email')
return {
'status': 'success',
'received': {
'name': name,
'email': email
}
}The request.get_json_data() object contains the parsed JSON data from the incoming request. This allows you to extract and process parameters sent by client applications.
Two Scenarios for REST Controllers in Odoo 19
Odoo 19 supports two primary authentication scenarios for REST controllers: authenticated endpoints that require user login and public endpoints that are accessible without authentication. The approach you choose depends on your security requirements and use case.
Case 1: With Authentication (auth='user')
In this scenario, the REST controller endpoint requires users to authenticate before accessing the API. This ensures that only authorized users can interact with sensitive business data.
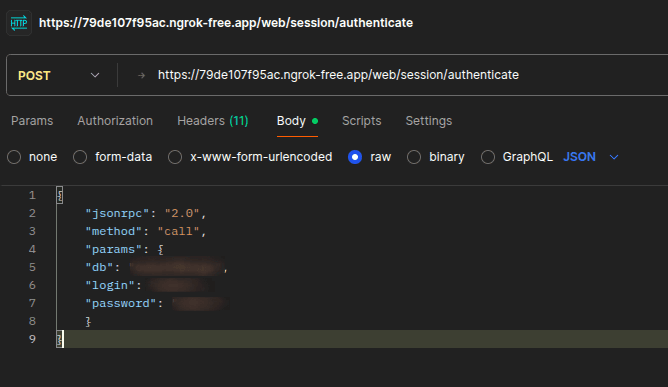
Before calling any authenticated endpoint if you are using external applications (like scripts, mobile apps, or integrations), you must first obtain a valid session by authenticating. Follow these steps:
- Send authentication request to /web/session/authenticate with your database name, username, and password
- Use the session cookie for all subsequent API calls
Once authenticated, you should include the session cookie with each request.
When building secure REST APIs in Odoo, authentication is crucial to protect sensitive data and ensure only authorized users can access your endpoints. This guide demonstrates how to create authenticated API endpoints that require valid user sessions.
Step 1: Configure Authenticated Routes
When creating authenticated endpoints, use the auth='user' parameter. This restricts access to logged-in users only:
@http.route('/api/v1/products', type='jsonrpc', auth='user', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def manage_products(self, **kwargs):
"""
Authenticated endpoint for managing products.
Only accessible to logged-in users.
"""
if request.httprequest.method == 'GET':
return self._get_products()
elif request.httprequest.method == 'POST':
return self._create_product()The auth='user' parameter ensures that Odoo validates the user's session before allowing access to this endpoint. If the user is not authenticated, Odoo will return an authentication error.
Step 2: Implement Authenticated Request Handlers
Build the logic to handle authenticated requests. You can access the current user through the request object and perform operations on their behalf:
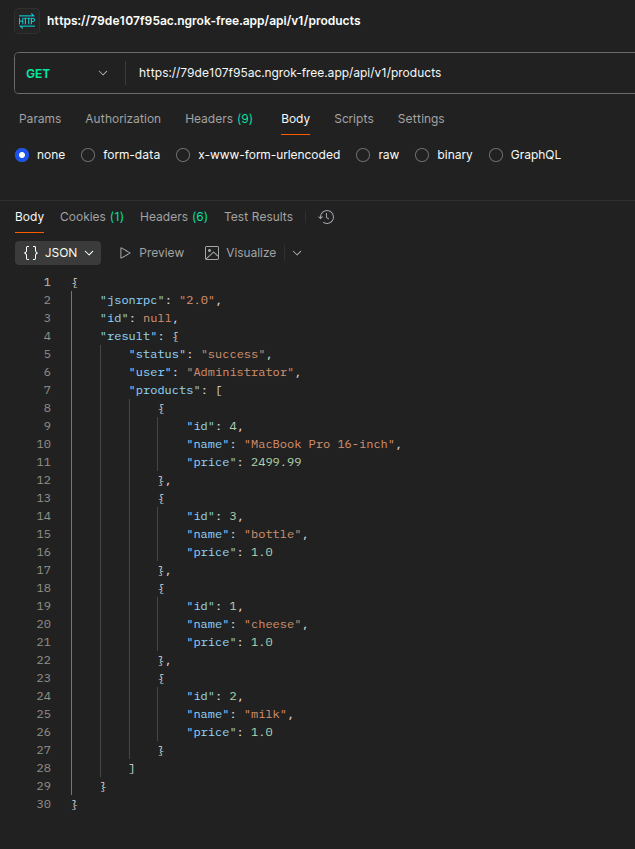
Retrieving Products from Odoo
The _get_products function fetches all products from Odoo's product.template model and returns them in a structured JSON format:
def _get_products(self):
"""Retrieve products for the authenticated user."""
try:
user = request.env.user
products = request.env['product.template'].search([])
product_data = [{
'id': product.id,
'name': product.name,
'price': product.list_price,
} for product in products]
return {
'status': 'success',
'user': user.name,
'products': product_data
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'status': 'error',
'message': str(e)
}
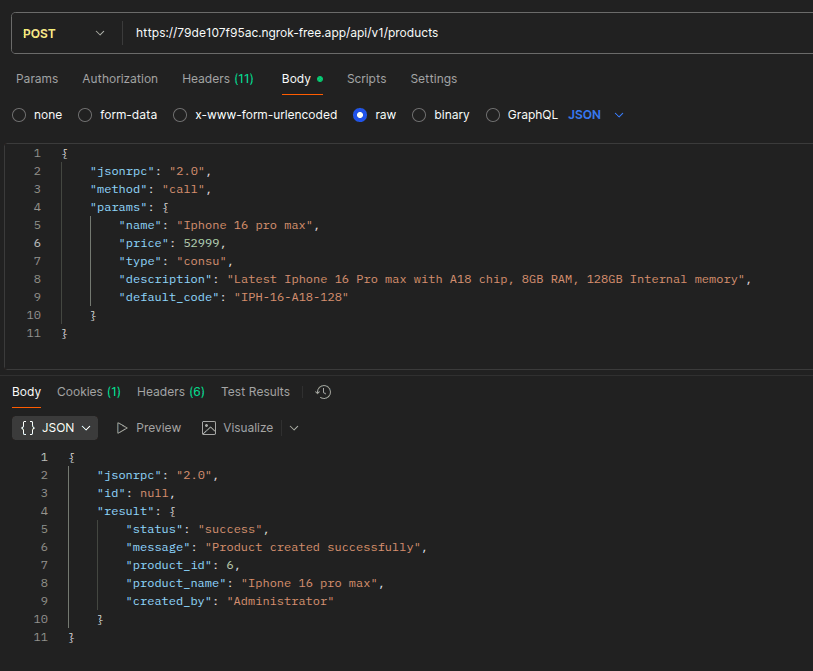
Creating Products in Odoo
The _create_product function creates a new product record in Odoo's inventory system:
def _create_product(self):
"""
Create a new product in Odoo's product catalog.
This function validates input data and creates a new product.template record
with the provided details like name, price, type, description, etc.
"""
data = request.get_json_data()
try:
product_data = data.get('params')
user = request.env.user
if not product_data.get('name'):
return {
'status': 'error',
'message': 'Product name is required'
}
product = request.env['product.template'].create({
'name': product_data.get('name'),
'list_price': product_data.get('price', 0.0),
'type': product_data.get('type', 'consu'),
'description': product_data.get('description', ''),
'default_code': product_data.get('default_code', ''),
})
return {
'status': 'success',
'message': 'Product created successfully',
'product_id': product.id,
'product_name': product.name,
'created_by': user.name
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'status': 'error',
'message': f'Failed to create product: {str(e)}'
}
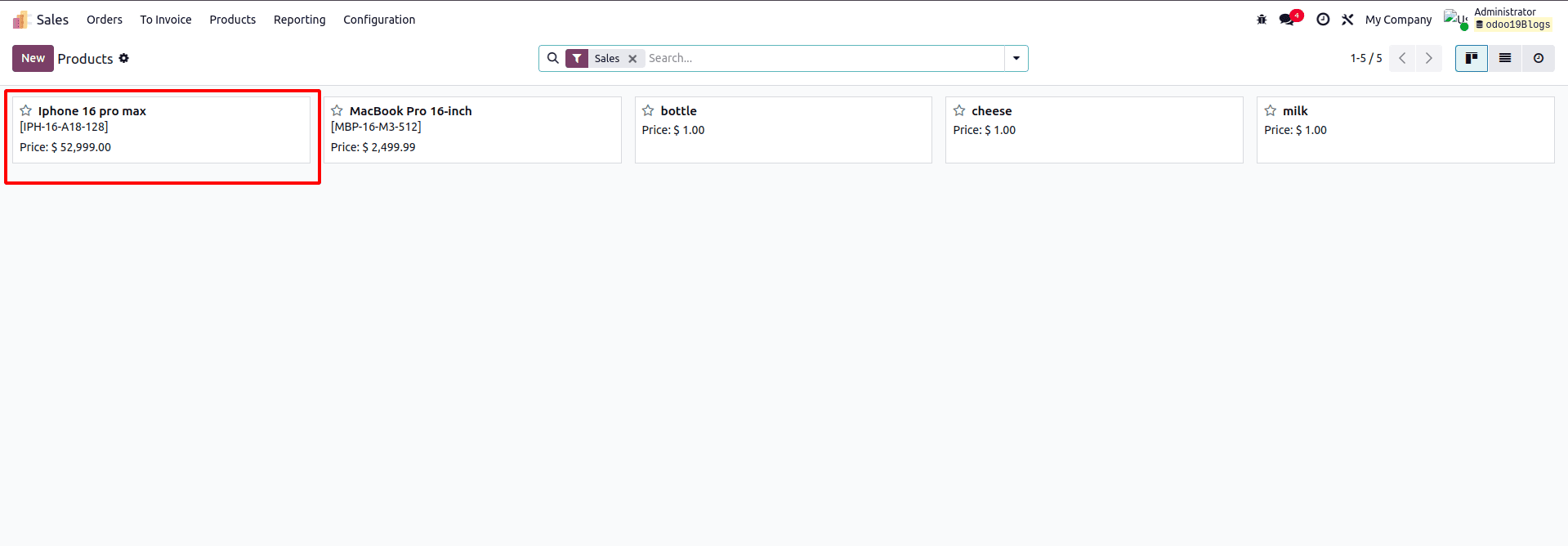
Case 2: Without Authentication (auth='public')
In this scenario, the REST controller endpoint is publicly accessible without requiring user authentication. Use this approach for endpoints that provide general information or services that don't involve sensitive data.
@http.route('/api/v1/products', type='jsonrpc', auth='public', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def manage_products(self, **kwargs):
"""
Authenticated endpoint for managing products.
Only accessible to logged-in users.
"""
if request.httprequest.method == 'GET':
return self._get_products()
elif request.httprequest.method == 'POST':
return self._create_product()Conclusion
You now understand how to build REST controllers in Odoo 19 to expose your business logic through HTTP APIs. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create authenticated endpoints for sensitive operations and public endpoints for general information sharing. REST controllers provide a powerful mechanism for integrating Odoo with external applications, enabling real-time data synchronization, mobile app backends, and third-party service integrations. Whether you choose to implement authenticated or public endpoints depends on your specific security requirements and use case. Leverage the flexibility of Odoo 19's REST controller framework to build scalable, maintainable APIs that drive your business forward.
To read more about How to Configure Odoo REST API Module in Odoo 18, refer to our blog How to Configure Odoo REST API Module in Odoo 18.