Managing inventory can quickly become overwhelming without a clear structure, especially as your product range grows. In Odoo 18, product categories offer a powerful way to bring order and clarity to your inventory operations. By grouping products into logical categories, businesses can simplify stock management, enhance search and filtering capabilities, and generate more insightful reports.
In this blog, we’ll delve into how product categories function in Odoo 18, how to configure them effectively, and best practices for utilizing them to streamline your inventory management process.
You can access the product categories under the Configuration tab inside the Inventory Module. You can create a new category by clicking on the New button.
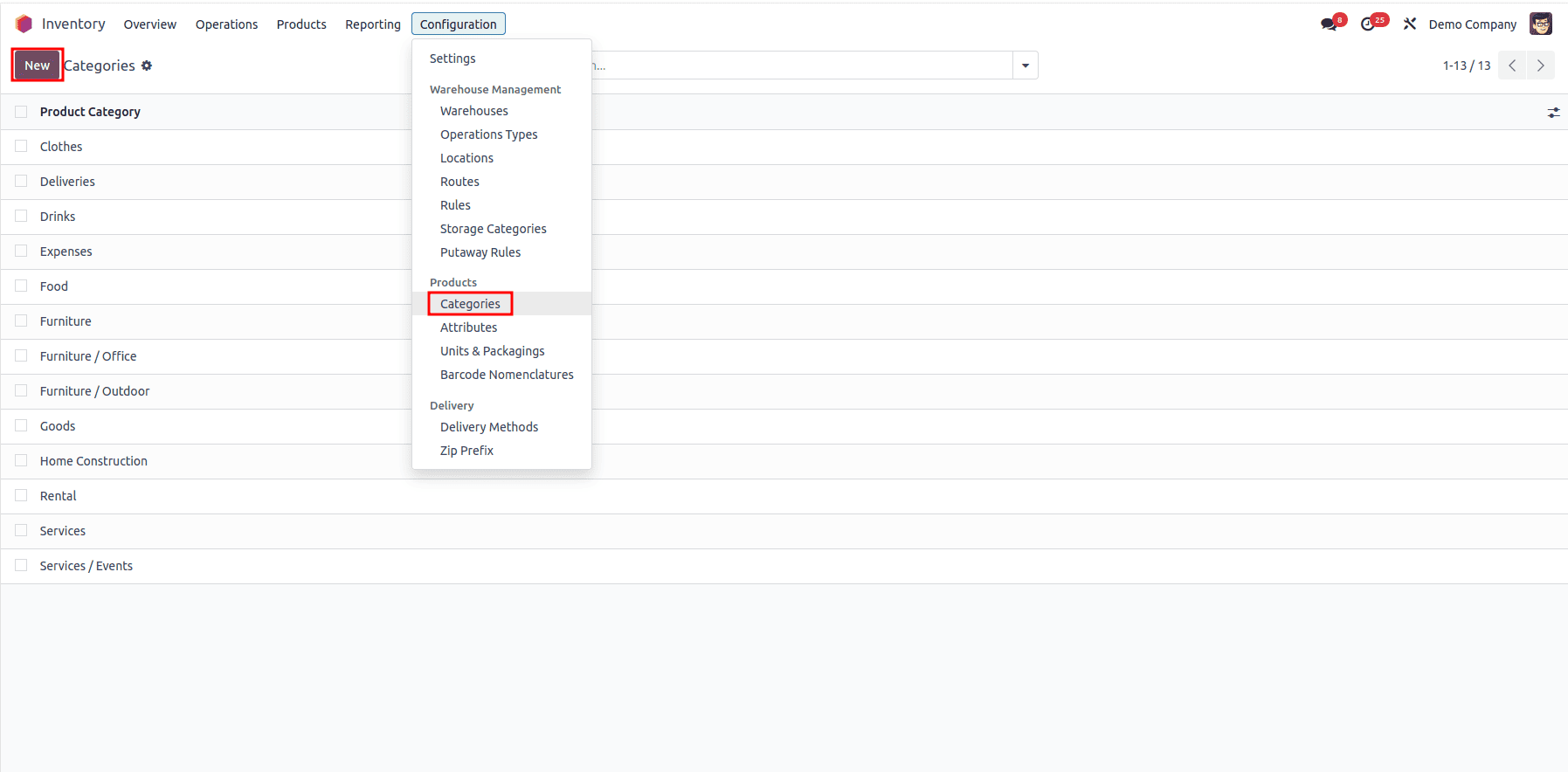
When setting up a new product category, start by specifying the category name and a clear description. Then, add any relevant attributes that help define and differentiate this category from others. The Parent Category feature helps you create a hierarchical structure for your product categories. Think of it as creating folders within folders. Each AVATAX Category maps a product category to a specific tax code recognized by Avalara.
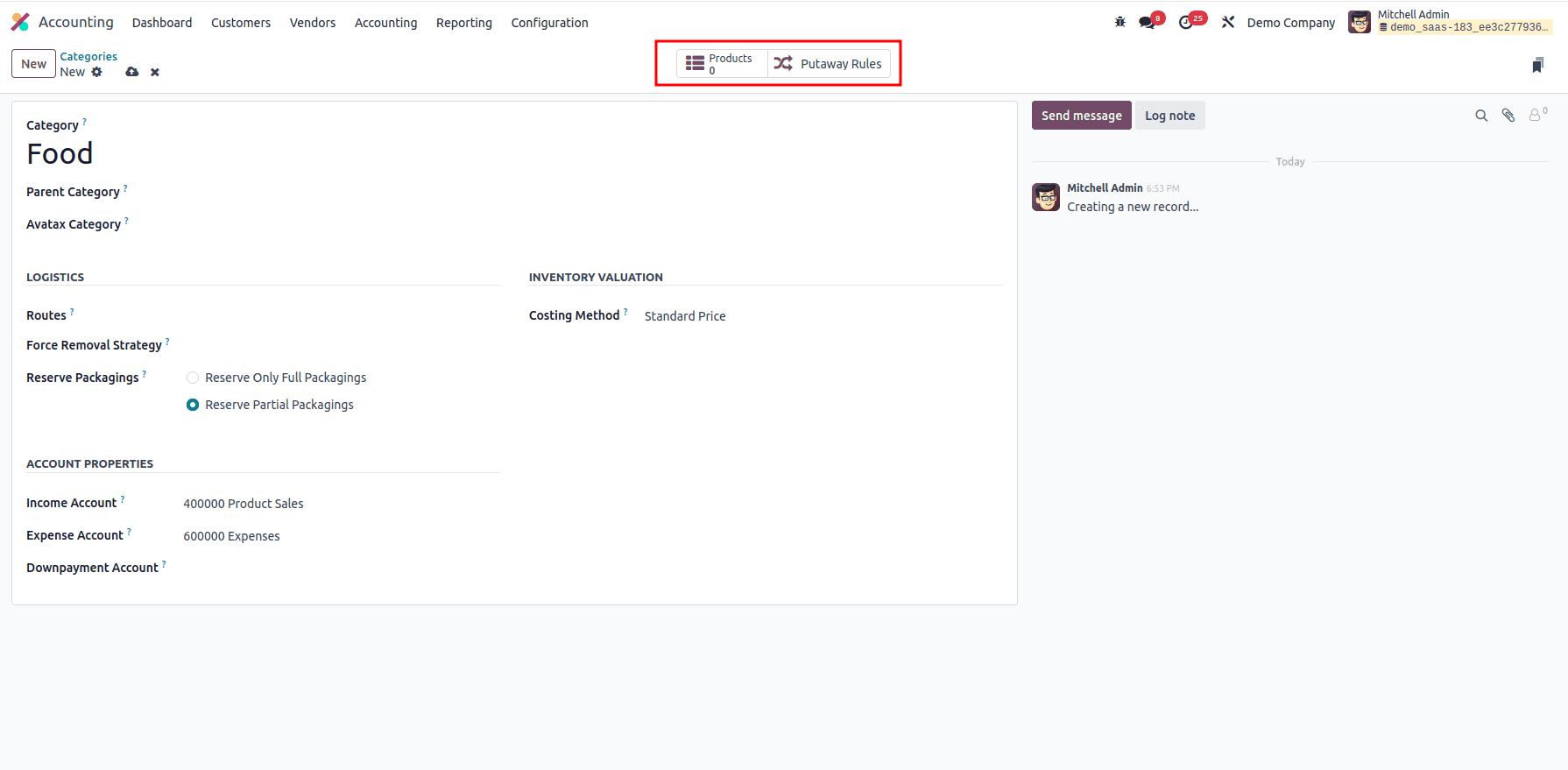
The smart tabs at the top display the number of products in the category and the putaway rules defined for it.
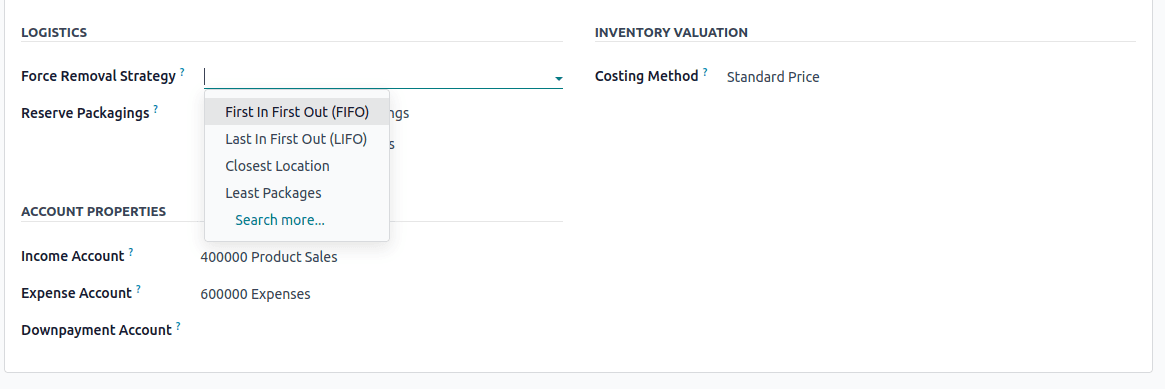
Force Removal Strategy deals with removal strategies in warehouse operations. A removal strategy decides how stock is picked when fulfilling delivery orders, manufacturing orders, or internal transfers. Odoo supports several out-of-the-box strategies:
- FIFO (First In, First Out): The items received first in the warehouse are the ones that are shipped out first.
- LIFO (Last In First Out): The items that were received last in the warehouse are the ones that get shipped out first.
- FEFO (First Expiry First Out): The items that will expire first are the ones that should be shipped out first. In order to see this option, you need to enable the ‘Expiration Dates’ feature inside Inventory > Configuration > Settings.
- Closest Location: It instructs Odoo to select products from the location that is physically closest to the source location or the shipping dock, based on the warehouse location hierarchy. In Odoo, the location hierarchy is in alphabetical order.
- Least Packages: Odoo will pick products from the location that contains the fewest number of packages (or pallets, boxes, etc.) containing the item. Thereby maintaining organized stock by not opening multiple packages.
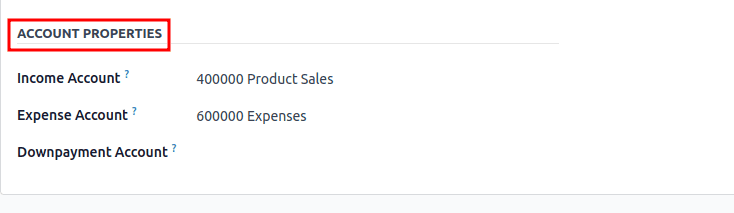
Income Account : This is where all the revenue from selling a product gets recorded. Every time a sale happens, Odoo posts the transaction to this account. It helps you keep a close eye on your earnings and understand exactly how much revenue each product line is generating.
Expense Account : This account captures the costs related to purchasing or producing the product, whether it's raw materials, supplier purchases, or manufacturing costs. It’s essential for calculating the true cost of goods sold and understanding your profit margins.
Downpayment Account : This account is used to temporarily hold customer prepayments. Sometimes customers pay you in advance, before the product is delivered or the service is rendered. Instead of immediately recognizing the income, Odoo records it as a liability (since you haven’t delivered the product yet). Once the order is fulfilled, the amount is transferred to the Income Account.
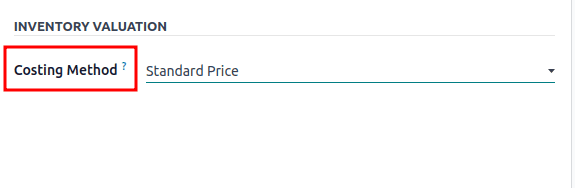
Costing Method: Determine how product costs are calculated and updated over time.
There are three main costing methods to track product costs in inventory management.
- Standard Costing
- Average Cost (AVCO)
- FIFO (First In, First Out)
Standard Costing
- A fixed cost is manually set for each product.
- Purchase orders do not change the product cost.
- Useful when costs remain stable for long periods.
Example:
- You set a product’s cost at $300.
- Even if you buy it for $100, inventory valuation will still use $300.
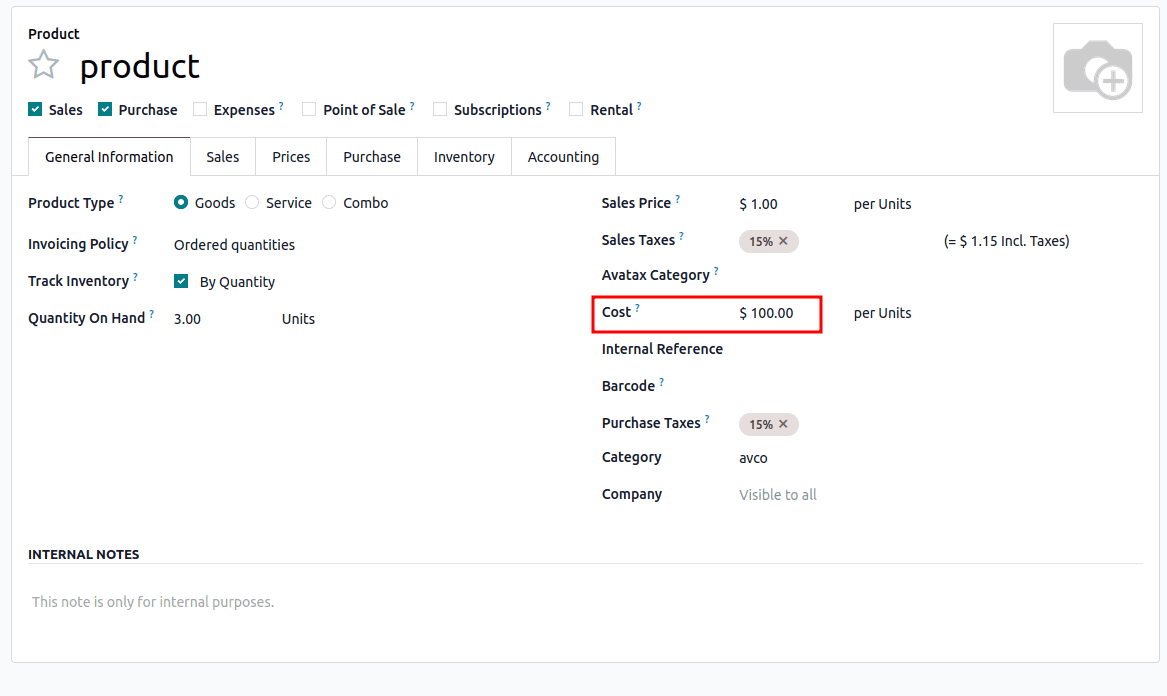
Average Cost (AVCO)
- Cost is calculated as the average of all purchase prices.
- Updates automatically with each new purchase.
- When selling, the cost remains the same until new stock arrives.
Example:
- Buy 3 product at $100 > Avg cost = $10
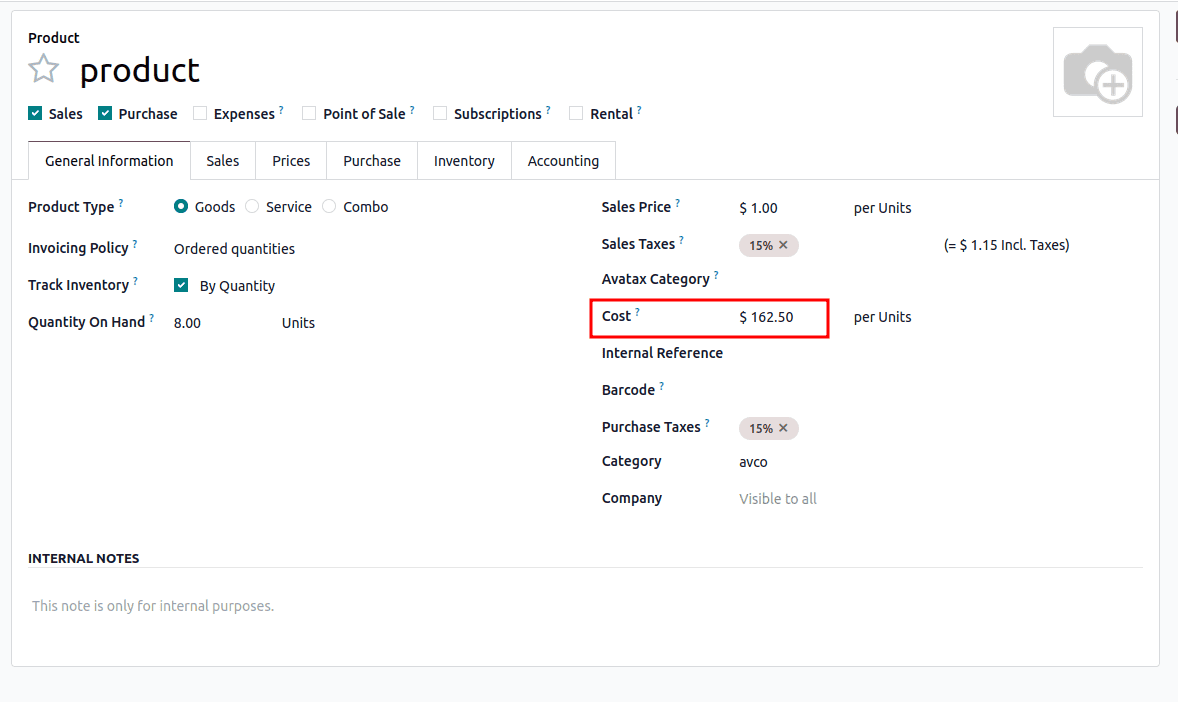
- Later buy 5 products at $200 > New avg cost = $162.5
- Calculation: (3×100 + 5×200)/8 = 162.5
- Later sell 1 product > New avg cost = $162.5
- Calculation: (3×100 + 5×200)/8 = 162.5
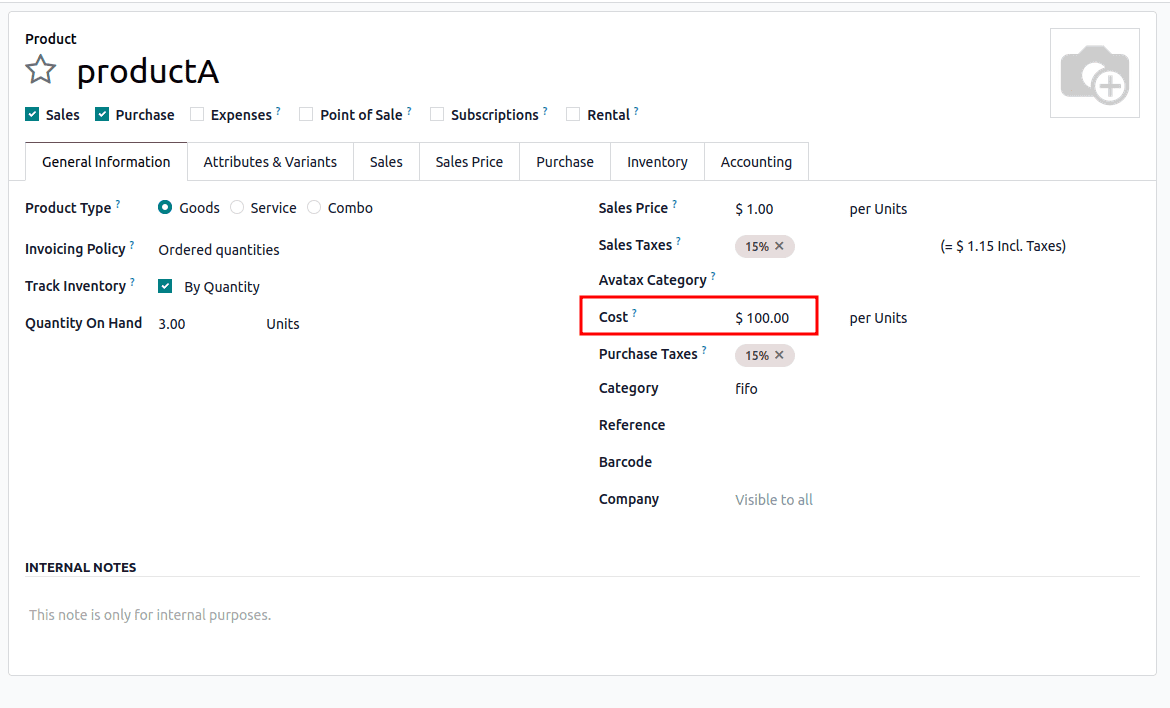
FIFO (First In, First Out)
- The oldest stock is sold first.
- Cost is based on the earliest purchase price.
- When stock runs out, the next purchase price applies.
Example:
- Buy 3 products at $100 > Cost = $100
- Later buy 5 products at $200 > New stock cost = $162.5
- Calculation : (3*100 + 5*200)/8 = 162.5
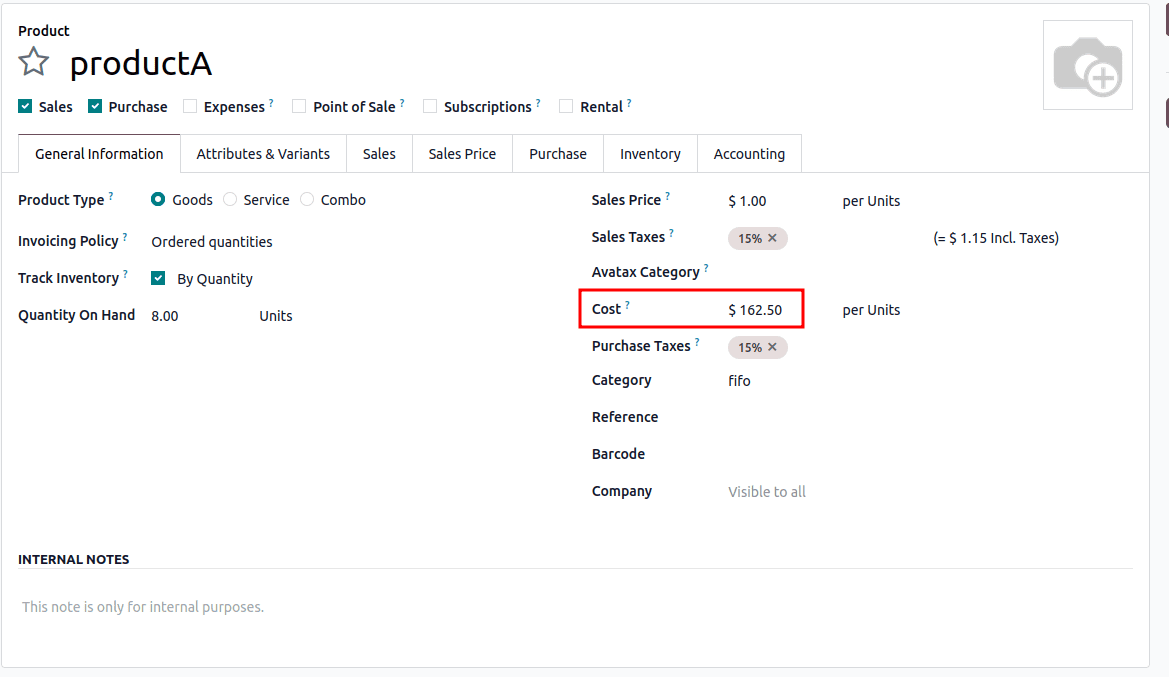
- Selling 1 product will use the $100 cost first > $171.43
- Calculation : (2*100 + 5*200)/7 = 171.429
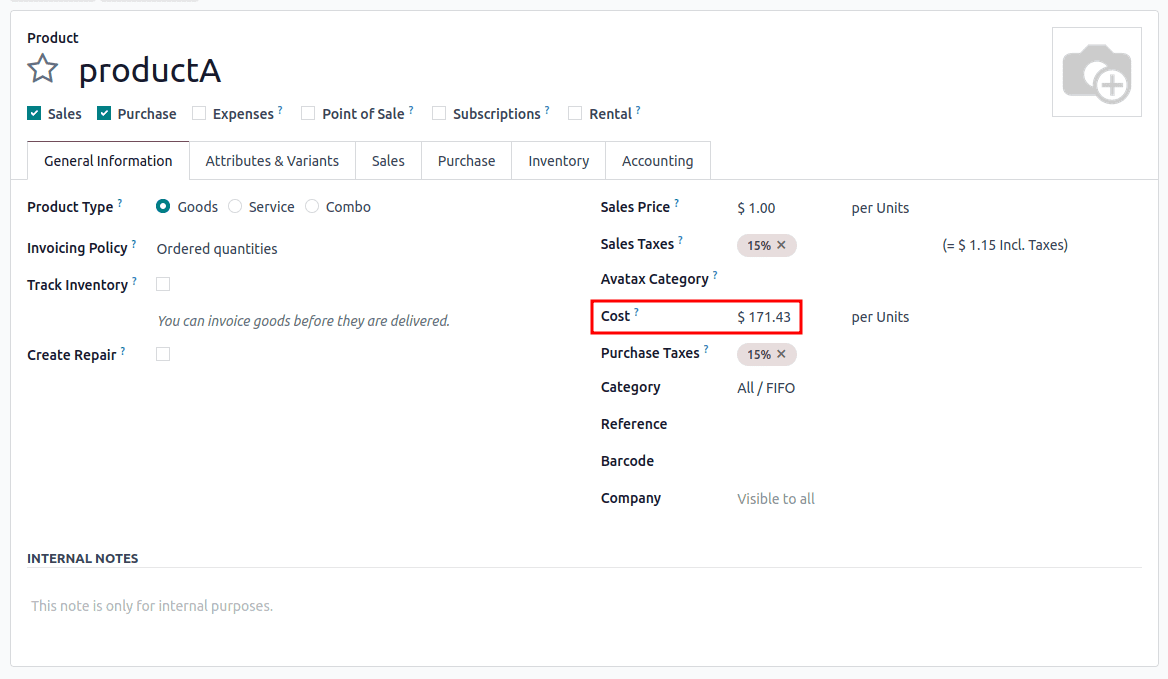
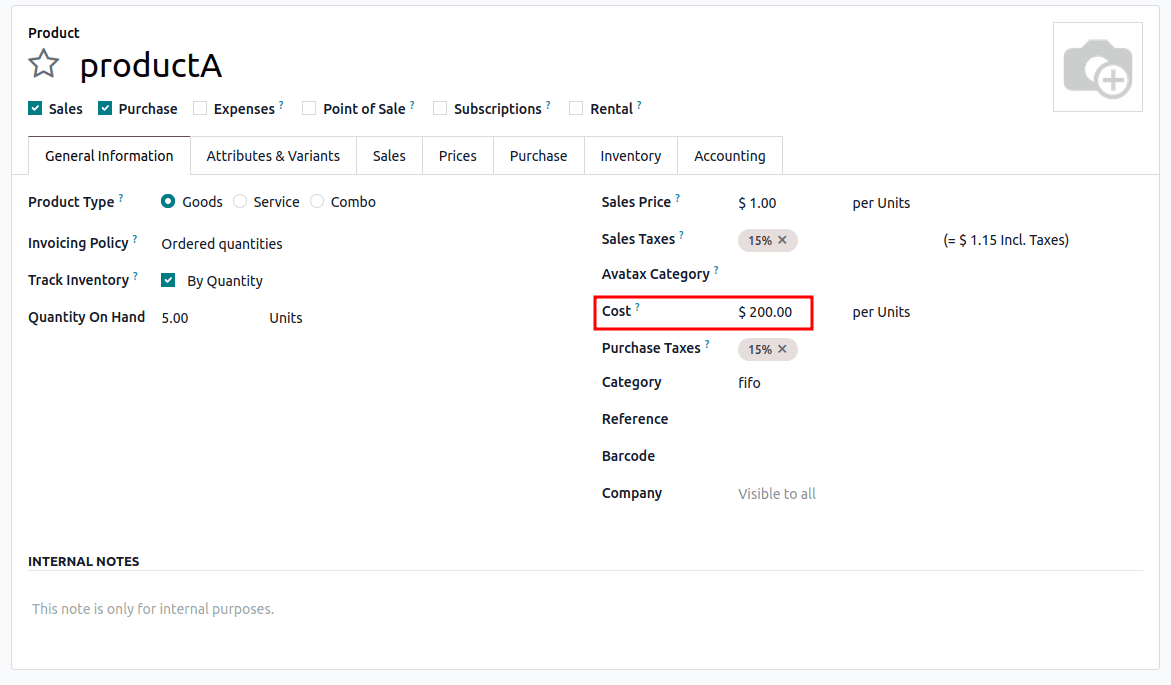
- Selling 2 products will use the $100 cost first > $171.43
- Calculation : ( 5*200)/5 = 200
In Odoo 18, product categories make it easier to keep inventory clear and organized by grouping items in a structured way. They help manage stock movements, apply the right costing method, and link sales or purchases to the correct accounts. With a well-set category structure, businesses can track products more easily, reduce errors, and gain better insights into both inventory and finances, leading to smoother day-to-day operations and smarter decisions.
To read more about How to Use Product Categories in Odoo 17 Inventory, refer to our blog How to Use Product Categories in Odoo 17 Inventory