26. Taxes
Tax calculation is notoriously unforgiving; one rounding error can
distort your entire ledger and expose your business to penalties.
Odoo 18 streamlines this delicate task by gathering every
configuration point in a single place: Configuration → Taxes.
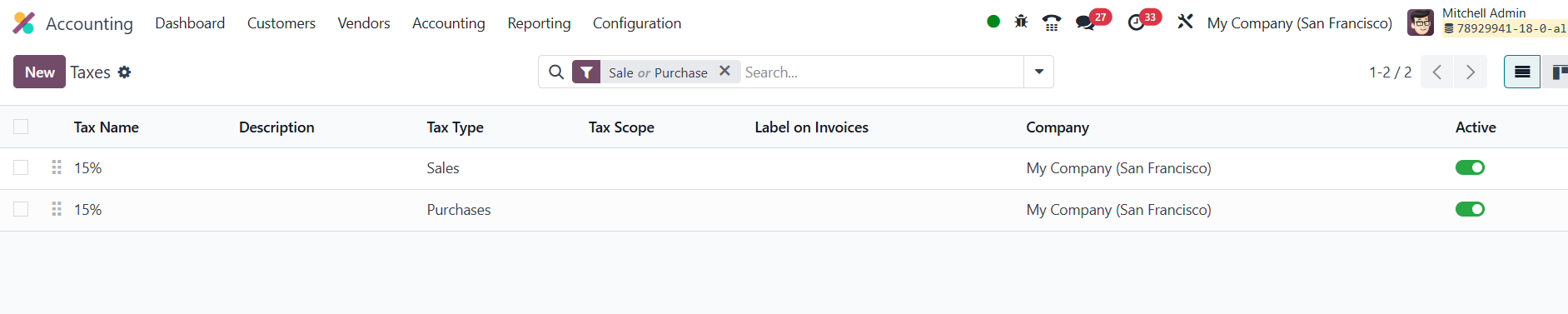
The resulting dashboard lists all existing rules and lets you slice
them any way you like, filtering by Sales or Purchases, narrowing
the view to goods or services, and toggling between active and
archived rates. The list shows the Tax Name, Description, Tax Type,
Tax Scope, Label on Invoices, and Company. When you click New, a
concise form appears, and the choices you make there determine
exactly how Odoo will behave on every subsequent invoice or bill.
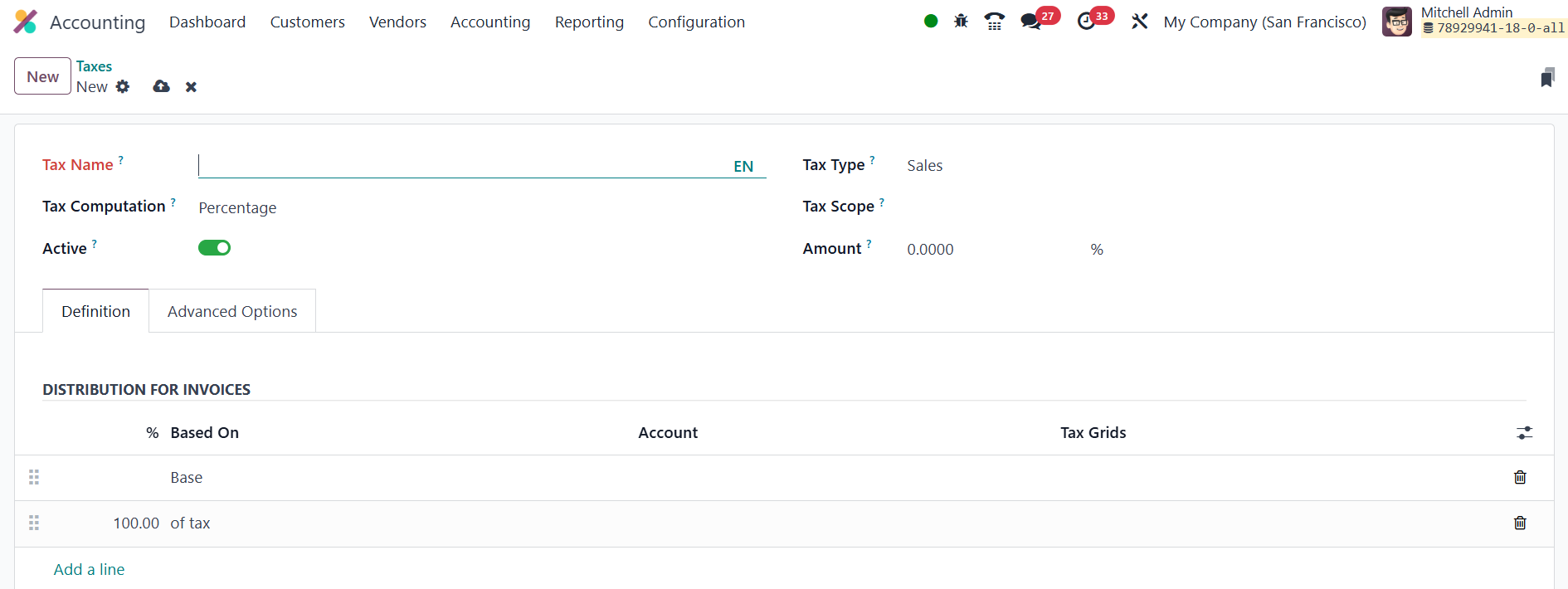
Begin by giving the rule a descriptive tax name, then decide whether
it belongs to the sales or purchase side of your books. If the levy
only applies to a subset of products, restrict it with the Tax Scope
field; if you merely want to sideline an outdated rate without
losing its history, untick Active. The most consequential setting is
Tax Computation.
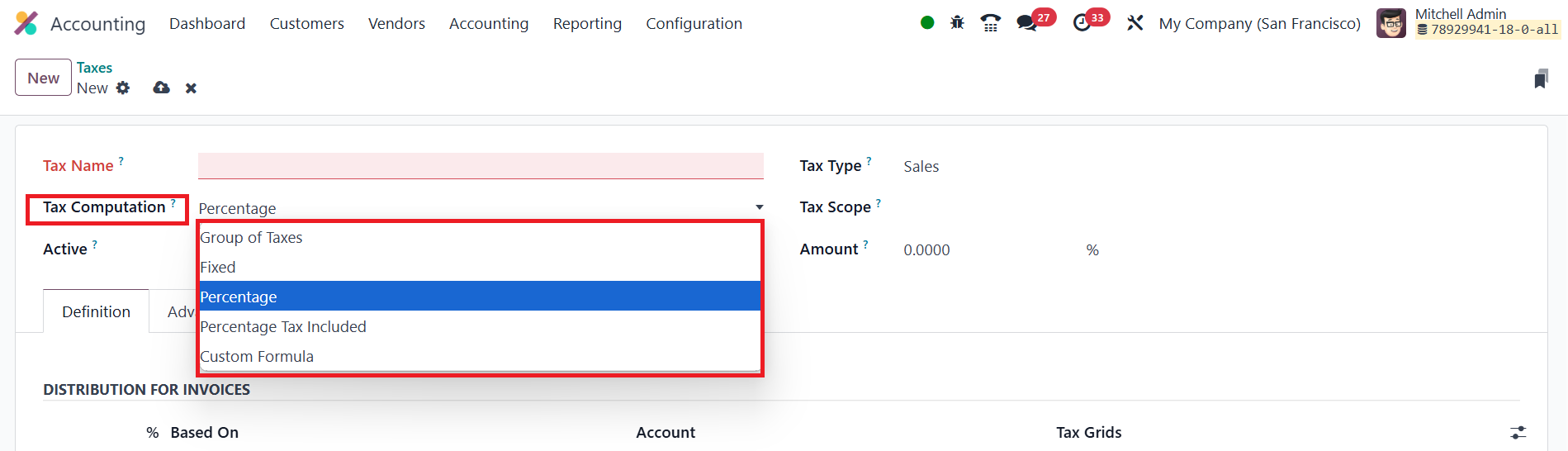
You can instruct Odoo to calculate a fixed amount, a percentage of
the net price, a percentage of a tax‑inclusive price, a custom
Python formula, or even a group that bundles several sub‑taxes.
- Group of Taxes: This method allows the creation of a composite
tax made up of multiple sub-taxes. You can include as many
individual taxes as needed and define the order in which they
should be applied.
- Fixed: This method applies a flat tax amount in the company’s
default currency, regardless of the transaction value. It is
ideal for charges like service fees or environmental levies that
remain constant.
- Percentage of Price: In this method, the tax is calculated as a
percentage of the sales price. The sales price serves as the
taxable base, and the resulting tax is directly proportional to
it.
- Percentage of Price Tax Included: Here, the total price
(including tax) serves as the base. The tax is back-calculated
as a percentage of the total, commonly used in tax-inclusive
pricing models.
- Python Code: This advanced method allows dynamic tax computation
using custom Python code. Two code snippets are used: one to
determine the tax amount and another (Applicable Code) to
specify whether the tax should apply. These are executed in an
environment that includes relevant variables such as unit price,
product, and partner details.
Choose the group option and an extra Definition tab appears, where
you add each sub‑tax line, effectively letting Odoo stack federal,
state, and municipal shares into one seamless rate.
Every computation method shares the same Definition tab.
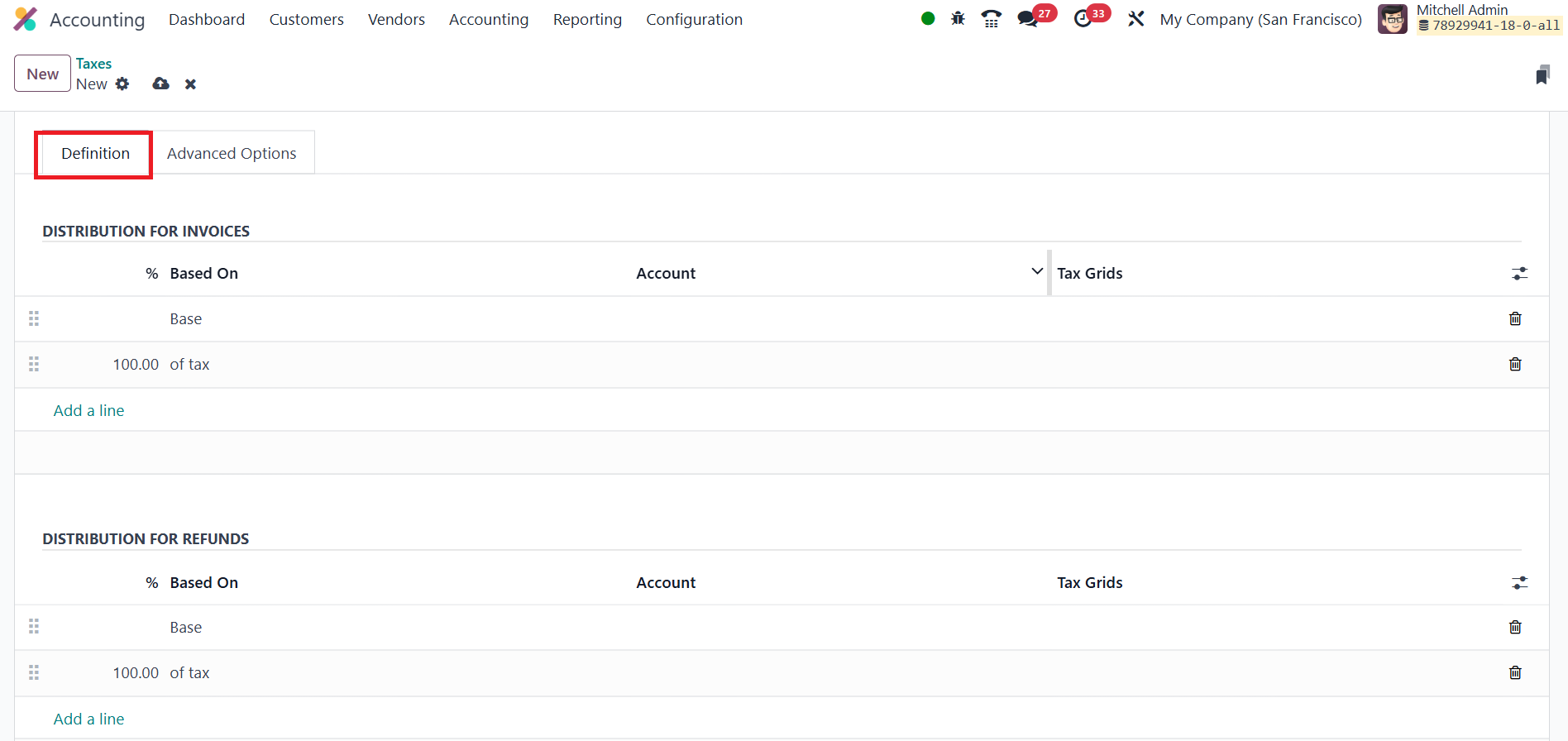
Here you tell the system which monetary base to use, which
general‑ledger account should receive the posting, and which boxes
on your tax return (the “tax grids”) should receive the numbers,
separately for invoices and refunds.
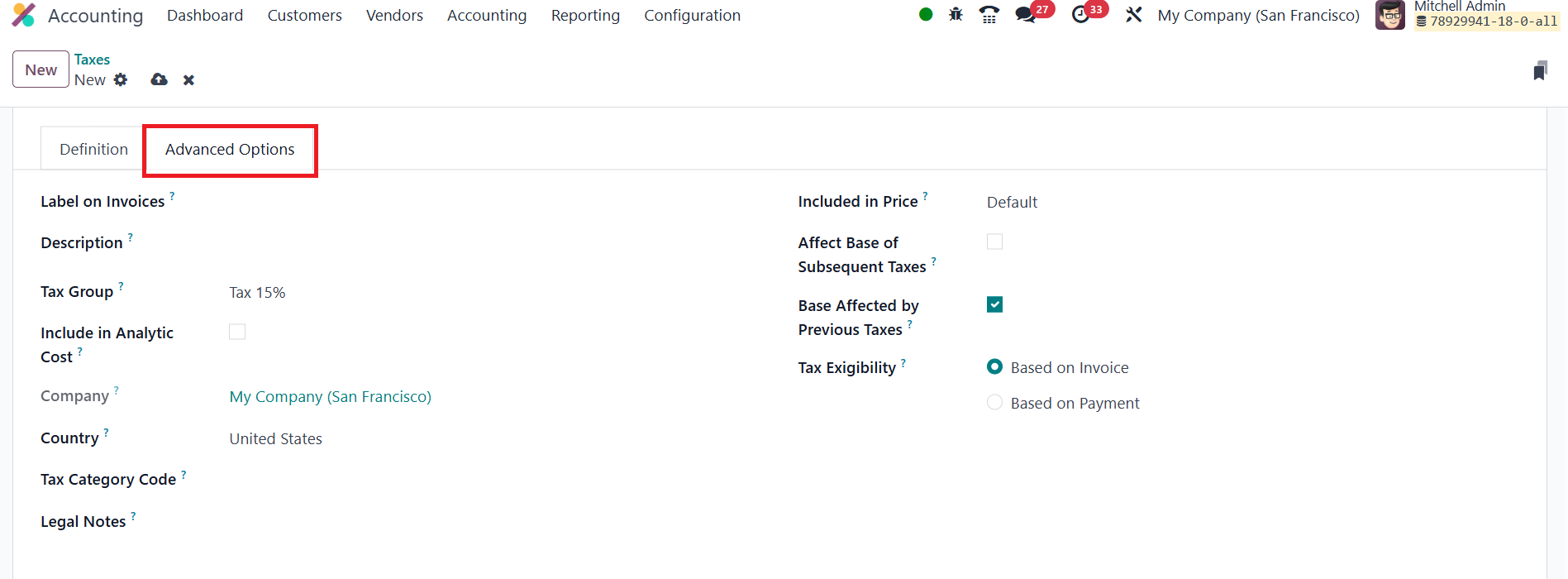
In the Advanced Options tab, you can define the label that prints on
customer documents, assign the rule to a higher‑level tax group for
reporting, and indicate whether the tax amount should flow to the
line’s analytic account. Additional switches handle more complex
cascades: flag Included in Price if your price list already contains
the levy, let the amount inflate the base for subsequent taxes, or
allow it to be altered by a preceding tax with a lower sequence
number. Finally, set Tax Exigibility to recognise the liability
either when you issue the invoice or only when the customer pays,
critical for jurisdictions that run on cash‑basis VAT.
Once the company and country fields are confirmed and you hit save,
Odoo takes over. From that point forward, every invoice, refund, and
vendor bill will pull the correct rate automatically, post it to the
right account, and populate the right grid, turning tax compliance
from a high‑risk manual chore into a background process you barely
notice.
26.1 Cash Basis
In Odoo 18, you can manage tax calculations on a cash basis, which is
particularly useful for businesses that report taxes when payments
are received or made, rather than when the invoice is issued. To
enable this feature, you need to activate the Cash Basis option in
the Accounting module's settings.
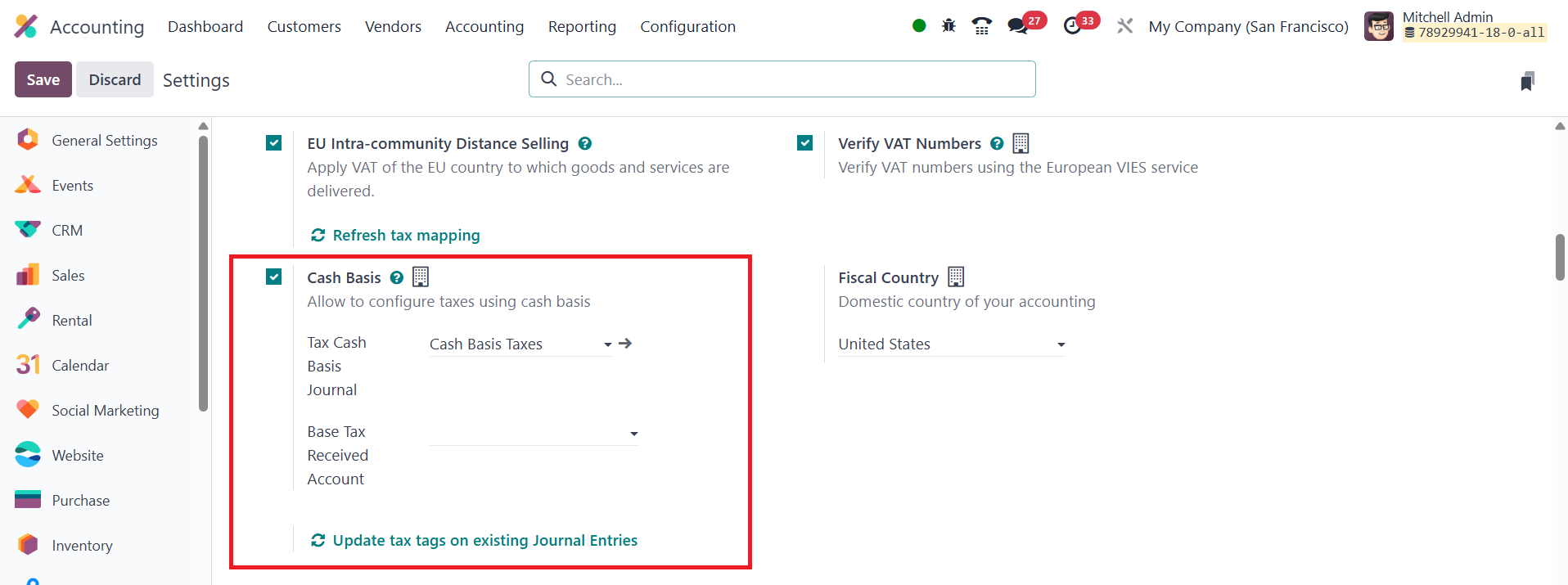
To use the Cash Basis method, you'll need to configure specific
accounts for the taxes. This involves setting up a Base Tax Received
Account and selecting a Tax Cash Basis Journal where the tax amounts
will be posted during reconciliation.
26.2 Tax Groups
In Odoo 18, taxes can be tailored to suit the specific operations of
your business, whether it's related to goods, services, suppliers,
or different accounts. From the Configuration menu within the
Accounting module, you can easily access the list of Tax Groups that
Odoo supports.
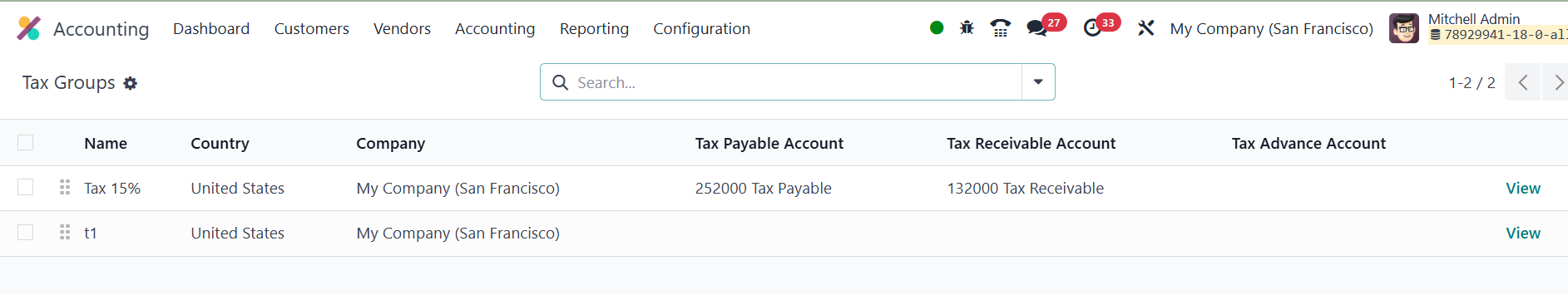
This list provides a clear overview of each tax group, making it
simple to organize and apply taxes based on your business needs.
Each tax group in the list contains essential details that are
important for tax management. These include the Name, which
identifies the tax group, and the Country, indicating where the tax
applies. The Tax Payable Account is the account where taxes owed to
the tax authorities are recorded, while the Tax Received Account
tracks the taxes collected from customers. Additionally, the Tax
Advance Account is used for businesses that make advance tax
payments, helping to manage any upfront tax liabilities.
26.3 Tax Units
In Odoo 18, the Tax Unit feature within the Configuration menu of the
Accounting module allows businesses to group their tax reports for
easier management and declaration. This feature is especially useful
for companies that need to file taxes for multiple entities or
locations. When you set up a new Tax Unit, a configuration window
will appear, enabling you to define the specifics for tax reporting.
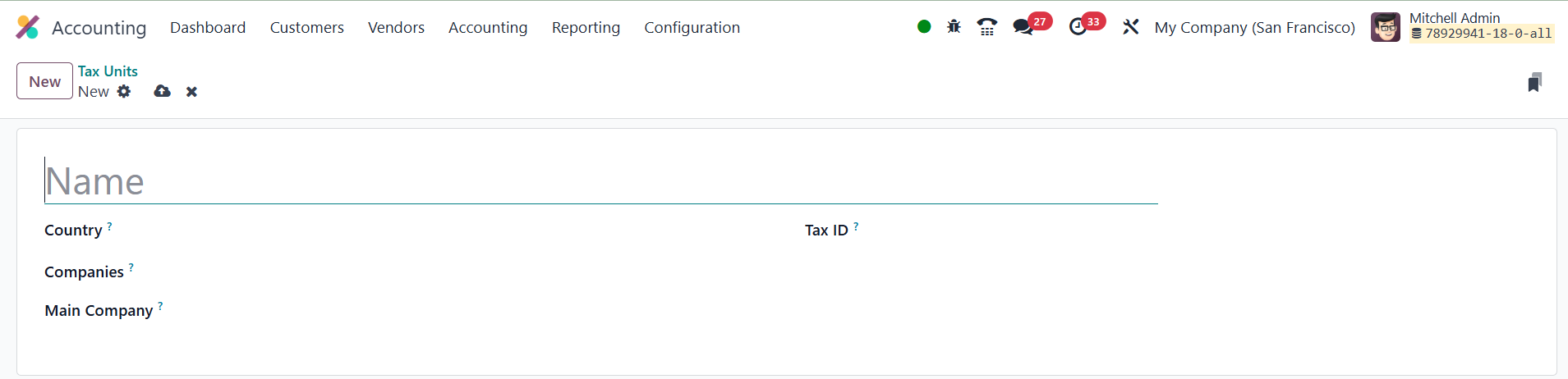
First, you’ll need to provide a Title for the tax unit, which serves
as an identifier for the report. Then, you can specify the Country
where this tax unit applies, helping to ensure that tax reports are
grouped correctly based on geographical location. Additionally, the
configuration allows you to enter the Companies involved, along with
the Main Company, which is the entity responsible for filing and
paying the taxes. This ensures that the correct company is
accountable for the tax obligations.
You can also configure a Tax ID for each tax unit, which is the
identifier used when submitting the tax report for that particular
unit. This helps in streamlining the tax filing process, especially
when dealing with multiple companies or tax jurisdictions. By using
the Tax Unit feature, businesses can organize and simplify their tax
reporting, ensuring compliance and accuracy when submitting
declarations.
26.4 Default Taxes
In Odoo 18, the Default Taxes feature helps automate the application
of taxes when no specific taxes are indicated for financial
transactions. By default, Odoo will apply the preset taxes for sales
and purchases, which simplifies the process when new items are added
to the system. You can later modify these taxes in the product form
if needed. If no other taxes are defined, the default taxes will be
used, ensuring consistency across transactions.
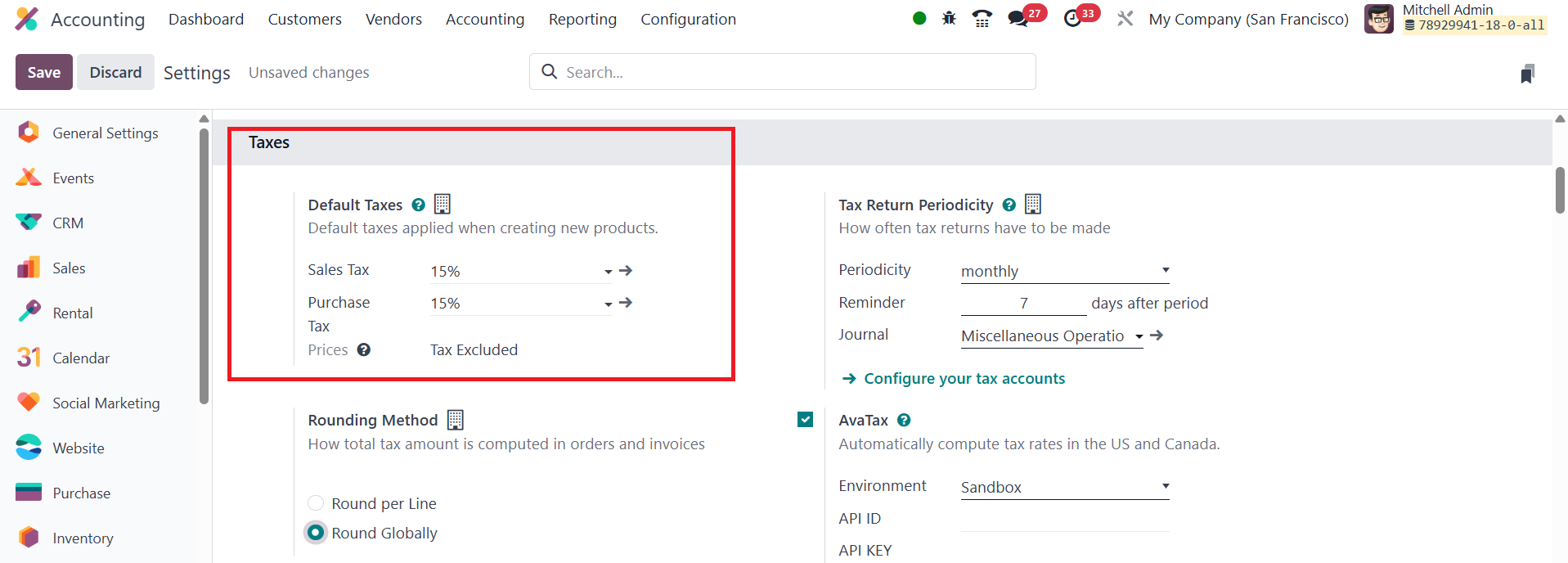
To modify the default taxes for both sales and purchases, you can
navigate to the Accounting module's Settings menu. From there, you
can adjust the default tax settings by following the internal link
in the Default Taxes section. You can also specify how frequently
tax returns need to be filed by setting the Tax Return Periodicity.
This allows you to manage the frequency of tax submissions and set
reminders for filing deadlines. You can record tax returns in the
appropriate journal and configure periodic reminders to ensure
timely submissions.
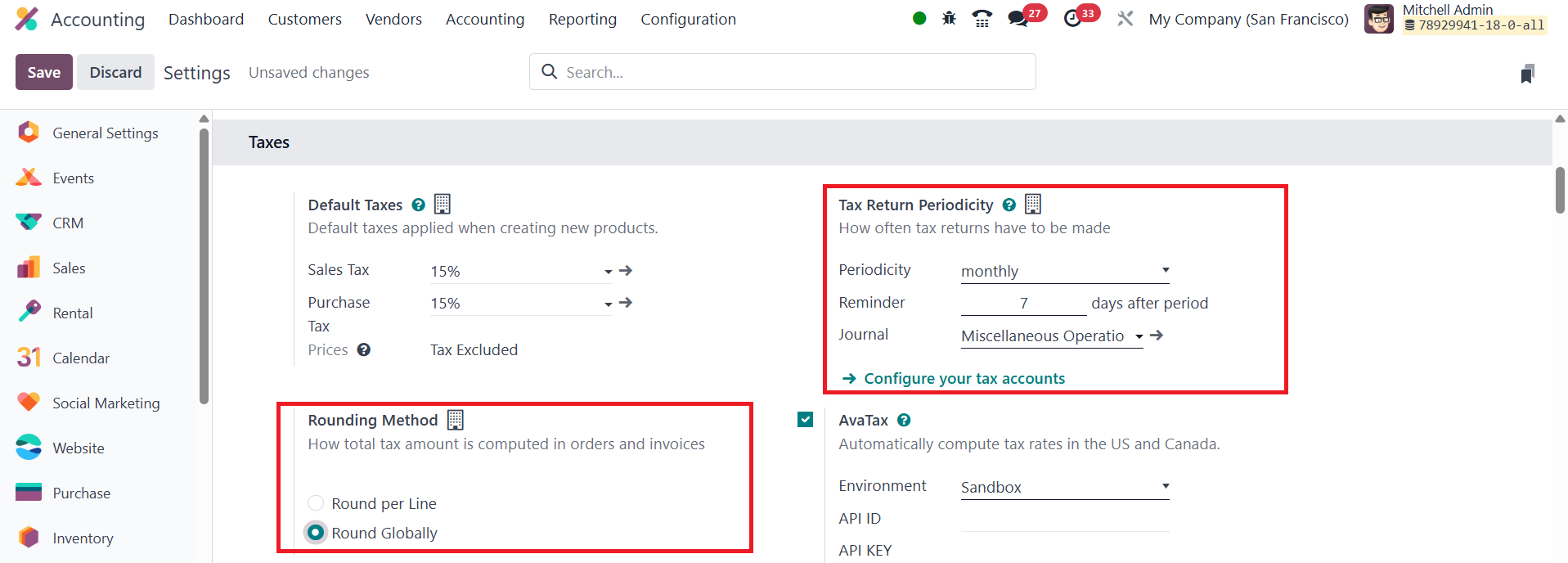
In terms of calculating the total tax amount on orders and invoices,
the Rounding Method section in Odoo allows you to choose between two
options: Round per Line or Round Globally. If your pricing includes
tax, it is generally recommended to round each line individually to
ensure accuracy in tax calculations. The total tax amount will then
be computed by adding the subtotals of each line.
26.5 AvaTax
AvaTax automatically calculates tax rates for orders and invoices.
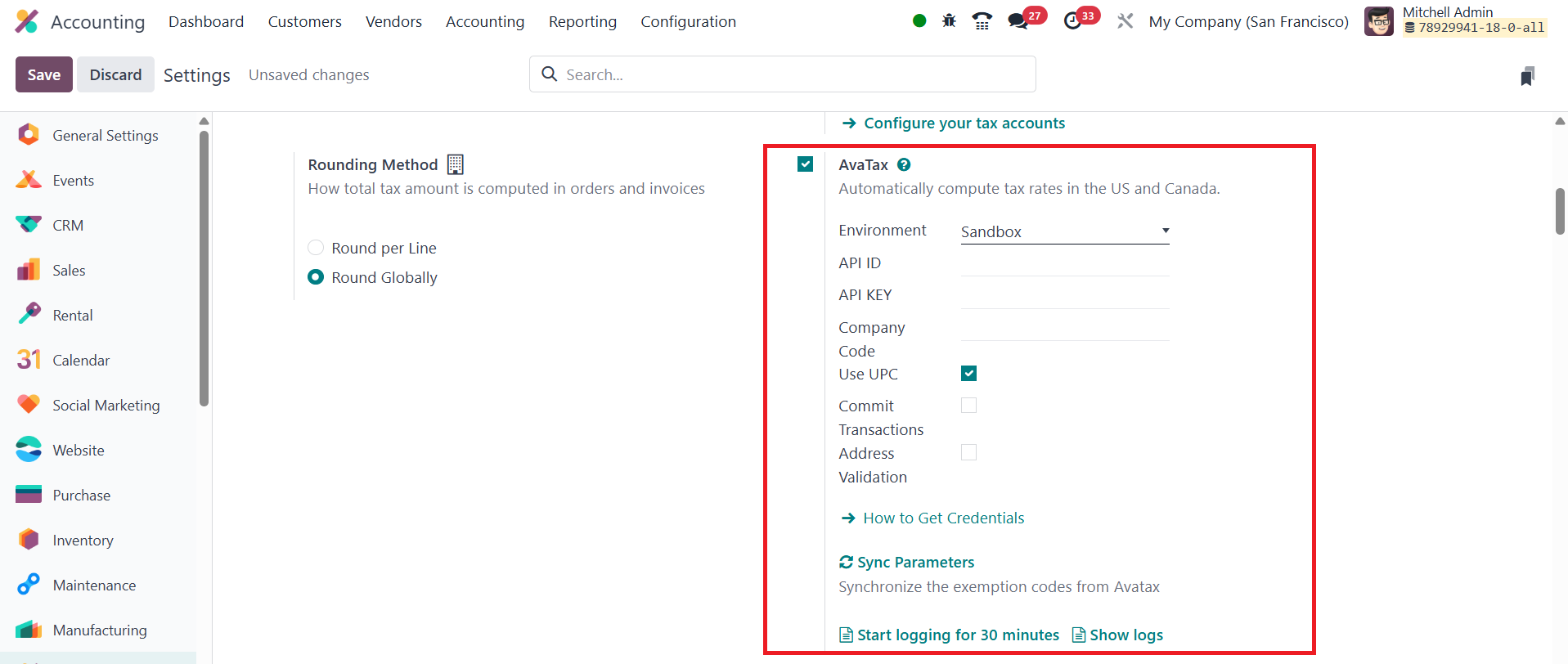
By configuring the AvaTax settings, such as Environment, API ID, API
Key, and Company Code, you ensure that taxes are computed accurately
and in real time. You can also enable additional options like
Address Validation, Commit Transactions, and Use UPC if needed.
These settings improve the accuracy of tax calculations, ensuring
compliance with tax regulations. AvaTax can be configured with item
and product categories, allowing for seamless integration across
your business operations.
26.6 EU Intra-community Distance
Selling
In Odoo 18, the EU Intra-community Distance Selling feature allows
businesses to apply VAT based on the delivery address when selling
products and services to clients in other EU nations. This is an
important feature for companies that operate within the European
Union, ensuring compliance with VAT rules for cross-border
transactions.
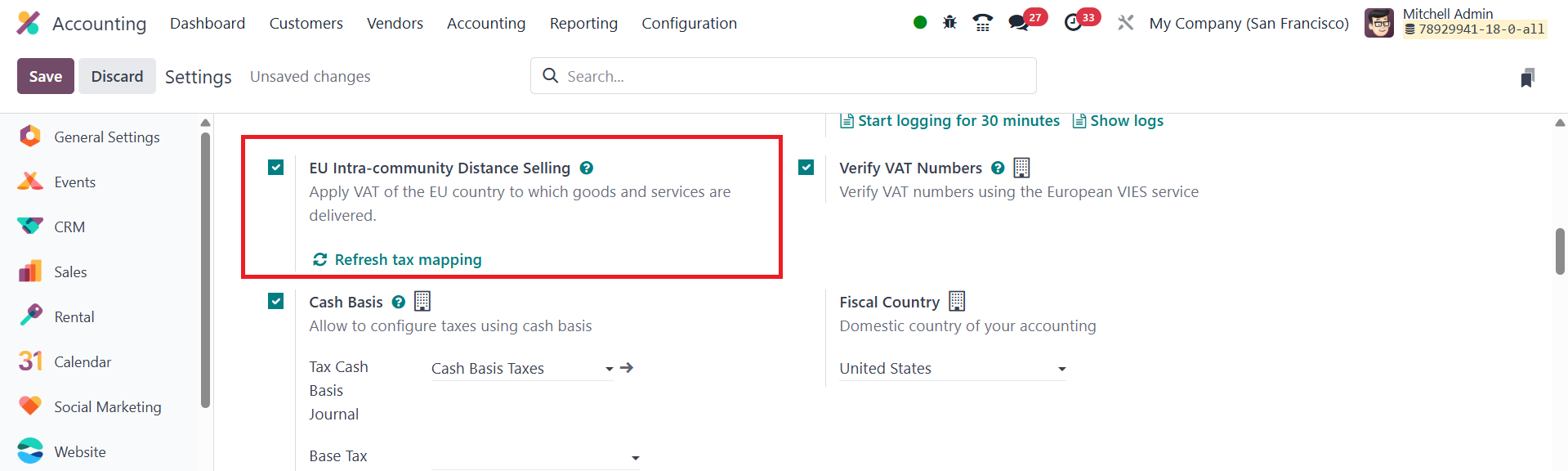
To enable this functionality, you need to turn on the EU
Intra-community Distance Selling option from the Settings menu in
the Accounting module. Once activated, Odoo will automatically
calculate the applicable VAT rates based on the delivery address of
the customer. This ensures that VAT is applied correctly according
to the country where the goods or services are being delivered,
rather than the country where the seller is located